Question 11. Find the points on the curve y = 3x2 − 9x + 8 at which the tangents are equally inclined with the axes.
Solution:
Given curve is y = 3x2 − 9x + 8. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> dy/dx = 6x − 9 . . . . (1)
We are given that the tangent is equally inclined with the axes. So θ = π/4 or –π/4.
Hence, slope of the tangent is ±1.
=> 6x − 9 = 1 or 6x − 9 = –1
=> 6x = 10 or 6x = 8
=> x = 5/3 or x = 4/3
When x = 5/3,
y = 3 (5/3)2 − 9 (5/3) + 8 = 4/3
When x = 4/3,
y = 3 (4/3)2 − 9 (5/3) + 8 = 4/3
Therefore, the required points are (5/3, 4/3) and (4/3, 4/3).
Question 12. At what points on the curve y = 2x2 − x + 1 is the tangent parallel to the line y = 3x + 4?
Solution:
Given curve is y = 2x2 − x + 1. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> dy/dx = 4x − 1 . . . . (1)
We are given that the tangent is parallel to the line y = 3x + 4. Now the slope of the line is 3, so slope of tangent must also be 3. So, we have,
=> 4x − 1 = 3
=> x = 1
Putting x = 1 in the curve y = 2x2 − x + 1, we get
y = 2(1) − 1 + 1 = 2
Therefore, the required point is (1, 2).
Question 13. Find the point on the curve y = 3x2 + 4 at which the tangent is perpendicular to the line whose slope is −1/6.
Solution:
Given curve is y = 3x2 + 4. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> dy/dx = 6x
It is given that the tangent is perpendicular to the line whose slope is −1/6. So the product of both the slopes must be −1.
Therefore the slope of tangent, dy/dx = 6.
=> 6x = 6
=> x = 1
Putting x = 1 in the curve y = 3x2 + 4, we get,
=> y = 3(1)2 + 4 = 3 + 4 = 7
Therefore, (1, 7) is the required point.
Question 14. Find the points on the curve x2 + y2 = 13, the tangent at each one of which is parallel to the line 2x + 3y = 7.
Solution:
Given curve is x2 + y2 = 13. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> 2x + 2y dy/dx = 0
=> dy/dx = −x/y . . . . (1)
It is given that the tangent is parallel to the line 2x + 3y = 7.
=> 3y = −2x + 7
=> y = −(2/3)x + 7/3
Therefore slope of the line is −2/3 and slope of the tangent is also −2/3 as slope of parallel lines are equal.
=> dy/dx = −2/3 . . . . (2)
From (1) and (2), we get,
=> −x/y = −2/3
=> x = 2y/3 . . . . (3)
Putting x = 2y/3 in the curve x2 + y2 = 13, we get,
=> 4y2/9 + y2 = 13
=> 13y2/9 = 13
=> y2 = 9
=> y = ±3
Putting y = ±3, in (3), we get,
When y = 3, x = 2 and when y = −3, x = −2.
Therefore, the required points are (2, 3) and (−2, −3).
Question 15. Find the points on the curve 2a2y = x3 − 3ax2 where the tangent is parallel to x-axis.
Solution:
Given curve is 2a2y = x3 − 3ax2. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> 2a2 dy/dx = 3x2 − 3a (2x)
=> dy/dx = 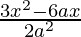
It is given that the tangent is parallel to x-axis, so the slope of the tangent becomes 0.
=>  = 0
= 0
=> 3x (x − 2a) = 0
=> x = 0 or x = 2a
When x = 0, the value of y from the curve is,
=> y = 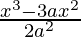
=> y = 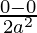
=> y = 0
And when x = 2a, the value of y is,
=> y = 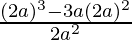
=> y = 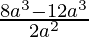
=> y = −2a
Therefore, the required points are (0, 0) and (2a, −2a).
Question 16. At what points on the curve y = x2 − 4x + 5 is the tangent perpendicular to the line 2y + x = 7?
Solution:
Given curve is y = x2 − 4x + 5. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> dy/dx = 2x − 4 . . . . (1)
It is given that the tangent is perpendicular to the line 2y + x = 7.
=> 2y = −x + 7
=> y = −(1/2)x + 7/2
Therefore slope of the line is −1/2 and product of this slope with that of tangent is −1 as both lines are perpendicular to each other.
So, slope of tangent is 2.
=> dy/dx = 2 . . . . (2)
From (1) and (2), we get,
=> 2x − 4 = 2
=> x = 3
Putting this in the curve y = x2 − 4x + 5, we get
=> y = x2 − 4x + 5
= (3)2 − 4(3) + 5
= 2
Therefore, the required point is (3, 2).
Question 17. Find points on the curve x2/4 + y2/25 = 1 at which the tangents are
(i) parallel to the x-axis
Solution:
Given curve is x2/4 + y2/25 = 1. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> 2x/4 + 2y/25 (dy/dx) = 0
=> dy/dx = −25x/4y
As it is given that the tangent is parallel to the x-axis, its slope must be 0.
=> −25x/4y = 0
=> x = 0
Putting this in the curve x2/4 + y2/25 = 1, we get
=> y2= 25
=> y = ±5
Therefore, the required points are (0, 5) and 0, −5).
(ii) parallel to the y-axis
Solution:
Slope of the tangent = dy/dx = −25x/4y
Therefore, slope of the normal = 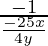 = 4y/25x
= 4y/25x
As it is given that the tangent is parallel to the y-axis, the slope of the normal must be 0.
=> 4y/25x = 0
=> y = 0
Putting this in the curve x2/4 + y2/25 = 1, we get
=> x2= 4
=> x = ±2
Therefore, the required points are (2, 0) and (−2, 0).
Question 18. Find the points on the curve x2 + y2 − 2x − 3 = 0 at which the tangents are parallel to
(i) x-axis
Solution:
Given curve is x2 + y2 − 2x − 3 = 0. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> 2x + 2y (dy/dx) − 2 = 0
=> dy/dx = (1−x)/y
As it is given that the tangent is parallel to the x-axis, its slope must be 0.
=> (1−x)/y = 0
=> x = 1
Putting this in the curve x2 + y2 − 2x − 3 = 0, we get
=> 1 + y2 − 2 − 3 = 0
=> y2 = 4
=> y = ±2
Therefore, the required points are (1, 2) and (1, −2).
(ii) y-axis
Solution:
Slope of the tangent = dy/dx = (1−x)/y
Therefore, slope of the normal =  = y/(x−1)
= y/(x−1)
As it is given that the tangent is parallel to the y-axis, the slope of the normal must be 0.
=> y/(x−1) = 0
=> y = 0
Putting this in the curve x2 + y2 − 2x − 3 = 0, we get
=> x2 − 2x − 3 = 0
=> x = −1, 3
Therefore, the required points are (−1, 0) and (3, 0).
Question 19. Find points on the curve x2/9 + y2/16 = 1 at which the tangents are
(i) parallel to the x-axis
Solution:
Given curve is x2/9 + y2/16 = 1. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> 2x/9 + 2y/16 (dy/dx) = 0
=> dy/dx = −16x/9y
As it is given that the tangent is parallel to the x-axis, its slope must be 0.
=> −16x/9y = 0
=> x = 0
Putting this in the curve x2/9 + y2/16 = 1, we get
=> y2= 16
=> y = ±4
Therefore, the required points are (0, 4) and 0, −4).
(ii) parallel to the y-axis
Solution:
Slope of the tangent = dy/dx = −16x/9y
Therefore, slope of the normal = 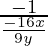 = 9y/16x
= 9y/16x
As it is given that the tangent is parallel to the y-axis, the slope of the normal must be 0.
=> 9y/16x = 0
=> y = 0
Putting this in the curve x2/9 + y2/16 = 1, we get
=> x2= 9
=> x = ±3
Therefore, the required points are (3, 0) and (−3, 0).
Question 20. Show that the tangents to the curve y = 7x3 + 11 at the points where x = 2 and x = −2 are parallel.
Solution:
Given curve is y = 7x3 + 11. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> dy/dx = 21x2
Now slope at x = 2 is
=> dy/dx = 21(2)2 = 84
And slope at x = −2 is,
=> dy/dx = 21(−2)2 = 84
As the slopes at x = 2 and x = −2 are equal, these tangents are parallel.
Hence proved.
Question 21. Find the points on the curve y = x3 where the slope of the tangent is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.
Solution:
Given curve is y = x3. We know that the slope of the tangent of a curve is given by dy/dx.
=> dy/dx = 3x2
It is given that the slope of the tangent is equal to the x-coordinate of the point.
=> 3x2 = x
=> x(3x − 1) = 0
=> x = 0 or x = 1/3
When x = 0, y = 03 = 0
And when x = 1/3, y = (1/3)3 = 1/27
Therefore, the required points are (0, 0) and (1/3, 1/27).
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...