SEO audit is crucial for enhancing the performance and visibility of a website in search engine results. This systematic evaluation involves scrutinizing various elements, from keywords and on-page optimization to technical aspects like site structure and page speed. In this guide, we’ll outline 12 essential steps to perform a comprehensive SEO Checker, helping you identify strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities for improvement to elevate your website’s overall search engine standing.
What Is an SEO Audit?
An SEO audit is a thorough assessment of a website’s performance, structure, and content to identify opportunities for improving search engine visibility and ranking.
SEO Checker SEO Audit can be different according to the requirement, SEO Audit Procedure can be summarised into 12 major steps that are:
STEP 1. Review Indexing Issues
The First Step of the SEO Checker Process is Checking or Auditing indexing issue, identifying all the indexing issue and taking considerable steps for the same.
In Google Search Console, go to the Pages section. This report provides insights into the indexing status of your site. In Pages, following issues must be addressed:

Identify Crawl Errors – SEO Audit
- Errors Section: Look for any errors reported, such as crawl errors, URL not found (404 errors), or server errors.
- Indexing Issues: Pay attention to issues that may prevent proper indexing, such as pages marked as “Excluded” or “Crawled – currently not indexed.”
Address Crawl Errors:

Address Crawling Error – SEO Audit
- 404 Errors: If there are pages with 404 errors, fix or redirect them to relevant pages.
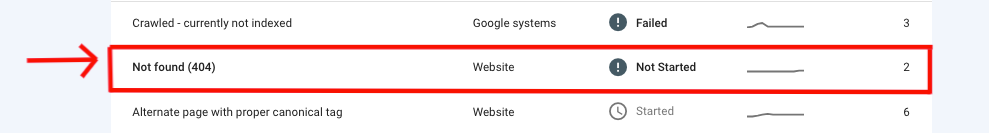
Error 404 – SEO Audit
- Server Errors: Investigate and resolve any server-related issues causing errors.
2. Ensure that All Important Pages are Indexed:
- Sitemap Submission: Submit an XML sitemap to Google Search Console. This helps search engines discover and index important pages on your site.
- Robots.txt File: Check your robots.txt file to ensure that it allows search engines to crawl and index the necessary pages. Avoid accidentally blocking important sections.
3. Identify and Resolve Issues:
- Duplicate Content: Check for duplicate content issues, as search engines may have difficulty deciding which version to index. Use canonical tags to specify the preferred version.
- Noindex Tags: Ensure that critical pages are not inadvertently marked with a “noindex” meta tag, which instructs search engines not to index them.
- Redirect Chains: Minimize the use of redirect chains as they can slow down the crawling process. Direct crawlers to the final destination page.
4. Additional Considerations:
- Pagination: If your site has paginated content, ensure that search engines can crawl and index paginated pages correctly.
- JavaScript Rendering: If your site heavily relies on JavaScript, ensure that search engines can render and index the content correctly.
STEP 2. Review Existing Content
Existing Content Improvement is the base of SEO Checker process, Auditing the quality of the exisiting content is important.
1. Readability
Assess the readability of the content. Use clear and concise language that is easy for the target audience to understand.
2. Depth of Information
Ensure that the content provides valuable and in-depth information relevant to the topic.
3. Content Structure
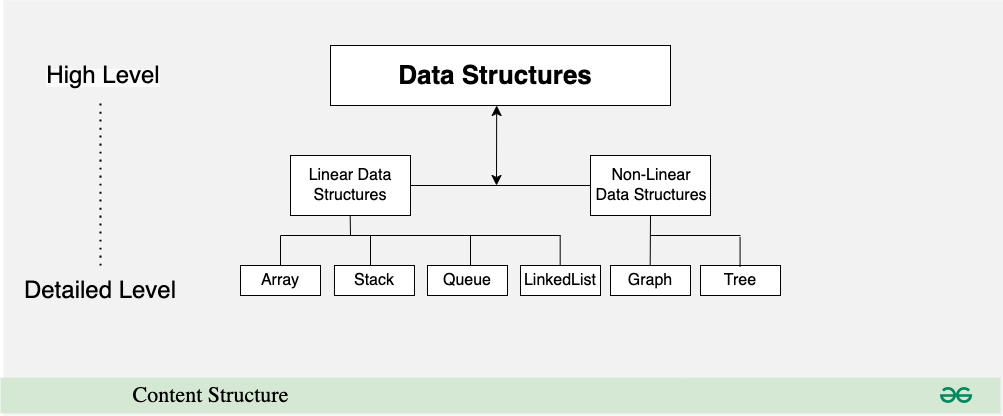
Content Structure
- Headings and Subheadings: Check if content is organized with clear headings and subheadings for easy readability and understanding.
- Bullet Points and Lists: Use bullet points and lists to break down information and make it more digestible.
4. Identify and Update Outdated or Irrelevant Content
- Publication Dates: If applicable, check for outdated content by reviewing publication dates. Update content with current information.
- Relevance: Assess the relevance of the content to current trends and industry standards
- Obsolete Pages: Identify pages that are no longer relevant and consider removing them or setting up redirects to relevant content.
5. Content Consistency:
Maintain a consistent tone and voice across your content to build a strong brand identity, and ensure that branding elements, such as logos and messaging, are consistent throughout the content.
6. Readability for All Audiences:
Make sure the content is accessible and understandable for a diverse audience.
7. Optimize Meta Tags:
- Title Tags: Ensure each page has a unique and descriptive title tag. Include relevant keywords.
- Meta Descriptions: Write compelling meta descriptions that accurately summarize the content and encourage click-throughs.
- Header Tags: Optimize header tags (H1, H2, etc.) with relevant keywords to improve content structure and SEO.
8. Schema Markup:
Implement relevant schema markup to enhance the appearance of your content in search engine results with rich snippets.
STEP 3. Image Audit
Image Audit is the third Step of SEO Checker Process, this process involves Auditing the image element of the content:
1. File Size and Format Optimization:
In the SEO audit, prioritize optimizing images by compressing them to reduce file size without compromising quality. Use appropriate formats, such as JPEG for photographs and PNG for images with transparency, to enhance website performance without sacrificing visual appeal.
2. Alt Text Review:
Conduct an audit of image alt text during the SEO assessment. Ensure each image has descriptive and relevant alt text, providing context for search engines and improving accessibility for users with visual impairments. Alt text contributes to better understanding and indexing of images by search engines.
3. Image Naming Convention:
Evaluate image file names as part of the SEO audit. Replace generic names with descriptive ones to assist search engines in comprehending the content of the images. A thoughtful naming convention contributes to improved image search visibility.
4. Responsive Image Implementation:
In the SEO audit, assess the implementation of responsive design to ensure that images adapt seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices. Responsive images enhance user experience and support better performance across a range of platforms.
5. Mobile Optimization for Images:
Optimize images specifically for mobile devices during the SEO audit. This involves refining image delivery and formatting to enhance the user experience on smartphones and tablets, contributing to overall site performance.
6. Image Sitemap Creation:
Generate an image sitemap as part of the SEO audit to offer search engines additional information about the images on your site. Submitting the image sitemap to Google Search Console enhances the visibility and indexation of your images.
7. Image Captions Evaluation:
Consider the use of image captions during the SEO audit where applicable. Captions provide supplementary context for images, aiding both users and search engines in understanding the content and context of the images.
8. Contextual Relevance Check:
Ensure, as part of the SEO audit, that images are contextually relevant to the surrounding text. This alignment helps search engines grasp the content and relevance of images, contributing to a more coherent and SEO-friendly website.
STEP 4. Monitor SEO Metrics for Traffic with Google Analytics
SEO Checker involves Monitoring the Traffic using different tools and services such as Google Analytics:
1. Audit Traffic Sources:
When conducting an SEO audit, closely monitor the flow of organic traffic to your website. Analyze trends, spikes, or declines in organic traffic to discern potential challenges or successes. This evaluation provides valuable insights into the effectiveness of your SEO strategies and helps identify areas for improvement.
2. Audit Revenue Sources:
As part of the SEO audit process, assess the sources contributing to your website’s revenue. Identify how organic traffic aligns with revenue generation and pinpoint areas for optimization. Understanding the correlation between revenue and traffic sources aids in refining marketing strategies and maximizing profitability.
3. Audit Traffic Devices:
In the SEO audit, scrutinize the devices through which your website receives traffic. Analyze whether there are variations in user behavior based on the device used (desktop, mobile, tablet). This insight is crucial for optimizing the user experience on different devices and ensuring your website caters effectively to diverse audiences.
4. Traffic Demographics:
During the SEO audit, delve into the demographics of your website’s traffic. Understand the geographical locations, age groups, and other demographic factors of your audience. This information enables you to tailor your content and SEO strategies to better resonate with your target audience.
5. Identify High-Traffic Pages:
Identify, as part of the SEO audit, the specific pages on your website that receive the highest levels of organic traffic. Prioritize the optimization of these pages to further enhance their performance. This targeted approach ensures that your most valuable content is continually refined to meet user expectations and search engine algorithms.
6. Bounce Rate Analysis:
Track the bounce rate as a key metric during the SEO audit to gauge the effectiveness of your content. A high bounce rate may indicate potential issues with content quality or relevance. Analyze pages with elevated bounce rates and implement strategies to improve engagement, encouraging visitors to explore more of your website.
STEP 5. Backlink Audit
Backlink plays an important role in SEO, So during SEO Checker Process it’s important to audit the backlinks of the website:

Backlinks
1. Internal Link Audit
- Anchor Text Optimization: Optimize anchor text by using descriptive terms that clearly convey the content of the linked page. Avoid generic phrases like “click here” and instead, choose specific, keyword-rich anchor text to enhance search engine visibility.
- Noreferral Noopener Nofollow Links Audit: Conduct an audit on links with the attributes “noreferrer,” “noopener,” and “nofollow” to ensure they are appropriately implemented. These attributes impact how search engines and browsers handle the links, and a proper audit ensures adherence to SEO best practices.
- Relevancy and Context: Guarantee the contextual relevance of internal links by linking to content that seamlessly aligns with the existing information. Link to related articles or pages that add significant value to the user’s experience and contribute to the overall thematic cohesion of the website.
- Hierarchy and Structure: Establish a coherent hierarchy in the information architecture of your website. Utilize internal links strategically to guide users through the site structure, facilitating easy navigation and enabling them to locate relevant content seamlessly. A logical hierarchy enhances user experience and search engine understanding.
- Diversify Link Types: Diversify internal linking strategies by incorporating various link types. Include contextual links within the content, navigational links in menus, and links to related posts. Additionally, create hub pages that serve as central points for specific topics, providing users with organized pathways to more in-depth content. This diversity strengthens the website’s internal linking profile, contributing to improved SEO.
2. Outbound Backlink Audit:
- Backlink Count Analysis:
- Conduct a thorough audit of the total backlinks pointing to your site, categorizing them based on their sources. Pay special attention to any abrupt increases or decreases in backlink numbers. Additionally, assess the authority and reliability of the domains linking to your site to ensure a healthy backlink profile.
- Domain Authority (DA) Assessment for Backlinks:
- Utilize tools such as Moz or Ahrefs to determine the Domain Authority of websites linking to your site. Prioritize backlinks from high-DA websites, as they typically offer more SEO value. Identify and disavow backlinks from low-quality or spammy sites to maintain a robust link profile.
- Cost vs. Revenue Examination for Backlinks:
- Evaluate the costs associated with obtaining or maintaining each backlink. Track the revenue generated from organic traffic attributed to these backlinks. Calculate the return on investment (ROI) for each backlink, factoring in the costs incurred. Identify backlinks with high costs and low revenue to assess their worthiness for retention.
STEP 6. Audit Mobile SEO
In the world full of Mobile users, it’s important to audit the mobile seo elements so Mobile SEO audit is the sixth step of SEO Checker Process:
1. Mobile Responsiveness:
- Ensure that your website is designed to be responsive, adapting seamlessly to various screen sizes and devices.
- Test the responsiveness using tools like Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
2. Mobile-Friendly Navigation:
- Simplify navigation for mobile users with intuitive menus and easy-to-tap buttons.
- Prioritize essential content to enhance the mobile user experience.
3. Touch-Friendly Elements:
- Optimize elements for touch, ensuring buttons and links are easily clickable on touchscreens.
- Adjust font sizes for readability on smaller screens.
4. Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP):
- Consider implementing AMP for content-heavy pages to provide a faster and streamlined experience for mobile users.
- AMP can improve mobile loading times and enhance user satisfaction.
5. Mobile-Optimized Images and Media:
- Optimize images for mobile devices to reduce load times without sacrificing quality.
- Use media queries to deliver appropriately sized images based on the user’s device.
STEP 7. Keyword Audit for SEO
Now All the Technical Elements have been audited, now moving onto the next step of SEO Audit, i.e Keyword Audit:
1. Keyword Placement:
- Integrate relevant keywords naturally into your content, including titles, headings, and body text.
- Avoid keyword stuffing; maintain a natural and user-friendly flow.
2. Target Keywords in Headings and Subheadings:
- Optimize header tags (H1, H2, etc.) with target keywords to structure content for both users and search engines.
- Clearly communicate the hierarchy of information.
3. Keyword Placement in Meta Tags:
- Craft compelling and keyword-rich title tags and meta descriptions to improve click-through rates from search results.
- Ensure each page has a unique and descriptive meta title.
4. Performing Keywords Analysis:
Conduct an SEO audit to identify the keywords that contribute significantly to organic traffic. Prioritize optimization efforts by aligning content around these high-performing keywords, aiming to enhance visibility and achieve better results in search engine rankings.
5. Search Query Analysis:
In the context of an SEO audit, thoroughly review and analyze search queries related to your website. Gain insights into user behavior, preferences, and intent by examining the specific terms users employ. This analysis aids in refining content strategies and optimizing for queries that align with the target audience’s search patterns.
STEP 8. Page Load Speed Audit using Lighthouse
Auditing the Page Load Speed is another aspect of SEO Checker Process, as Page Load imposes a great impact on the bounce rate:

SEO Audit : Lightroom Insights
1. Performance:
- Page Speed: Evaluate the loading speed of your web pages. Use tools like Google PageSpeed Insights to identify areas for improvement.
- Mobile Performance: Assess the website’s performance on mobile devices. Mobile-friendliness is a crucial factor in SEO rankings.
- Optimized Images: Ensure images are compressed and appropriately sized to minimize page load times.
- Browser Caching: Check if the website leverages browser caching to reduce load times for returning visitors.
- Content Delivery Network (CDN): Consider using a CDN to distribute content geographically, improving loading speed globally.
2. Accessibility:
- Mobile Responsiveness: Confirm that the website is responsive and provides a good user experience on various devices.
- Alt Text for Images: Ensure all images have descriptive alt text to assist users with visual impairments and improve SEO.
- Proper Heading Structure: Verify that the content uses a logical heading structure (H1, H2, H3, etc.) for improved accessibility and SEO.
- Keyboard Navigation: Check if the website can be easily navigated using a keyboard alone.
- Color Contrast: Assess the color contrast to ensure readability for users with visual impairments.
3. Best Practices:
- SSL Security: Confirm that the website uses HTTPS to ensure a secure connection.
- Responsive Design: Ensure the website adapts well to various screen sizes and devices.
- Valid HTML and CSS: Check for proper HTML and CSS markup to ensure compatibility with different browsers.
- Avoidance of Duplicate Content: Identify and address any instances of duplicate content, which can negatively impact SEO.
- 301 Redirects: Verify the use of proper redirects to avoid broken links and maintain SEO value during site changes.
4. PWA (Progressive Web App):
- Offline Functionality: Assess whether the website offers offline functionality for a seamless user experience.
- Push Notifications: If applicable, verify the implementation of push notifications for engagement.
- App-Like Experience: Ensure the website provides an app-like experience, enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
- Fast Loading on Low Connectivity: Confirm that the PWA performs well even on slow or unreliable network connections.
- Responsive Design for PWA: Ensure the progressive web app design is responsive and user-friendly.
Impact of Page Load Speed on Bounce Rate

Bounce Rate on Basis of Page Load Speed
Last step of SEO Checker is Social Media SEO Optimization, as it impacts the visibility of the content:
1. Content Sharing
- Strategic Content Distribution:
- Share a variety of content types, including blog posts, articles, infographics, videos, and images.
- Tailor content for each social media platform to maximize engagement.
- Consistent Posting Schedule:
- Establish a consistent posting schedule to maintain a regular presence on social media.
- Use scheduling tools to plan and automate posts, ensuring a steady flow of content.
- Visual Appeal:
- Use eye-catching visuals, such as images and videos, to accompany your social media posts.
- Visual content tends to attract more attention and engagement.
2. Audience Engagement
- Respond to Comments and Messages:
- Actively respond to comments, mentions, and direct messages.
- Encourage conversations and engage with your audience to build a sense of community.
- Ask Questions and Encourage Feedback:
- Pose questions in your posts to prompt audience interaction.
- Encourage followers to share their opinions, experiences, or feedback.
- User-Generated Content:
- Encourage users to create and share content related to your brand.
- Showcase user-generated content to build authenticity and strengthen community bonds.
- Live Sessions and Webinars:
- Host live sessions or webinars on social media platforms.
- Engage with your audience in real-time, answer questions, and provide valuable insights.
3. Brand Authority Building
- Share Industry Insights:
- Share relevant industry news, trends, and insights to position your brand as an authority in your niche.
- Provide commentary and analysis to showcase your expertise.
- Educational Content:
- Create and share educational content that addresses common questions or challenges within your industry.
- Position your brand as a valuable resource for information.
- Behind-the-Scenes Content:
- Share behind-the-scenes glimpses of your team, office, or production process.
- Humanize your brand and connect with your audience on a personal level.
- Participate in Conversations:
- Join relevant conversations in your industry or community.
- Share insights, participate in Twitter chats, and contribute to discussions to showcase your expertise.
Conclusion
In conclusion, conducting a thorough SEO audit (SEO Checker) is an essential practice for optimizing website performance and enhancing online visibility. By evaluating factors such as on-page elements, backlinks, and technical aspects, businesses can identify areas for improvement, ensuring that their online presence aligns with search engine best practices. Regular SEO audits serve as a strategic tool for maintaining and improving search rankings, ultimately contributing to a more effective and competitive digital presence.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...