Class 12 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 11 Differentiation – Exercise 11.5 | Set 2
Last Updated :
26 May, 2021
Question 21. Find dy/dx when 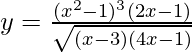 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> 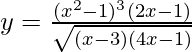
=> 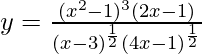
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> 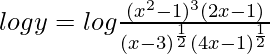
=> 
=> 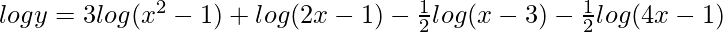
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{y}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[3log(x^2-1)+log(2x-1)-\frac{1}{2}log(x-3)-\frac{1}{2}log(4x-1)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8ac8cc93c3f499ea7f6209cd6c8f2289_l3.png)
=> 
=> 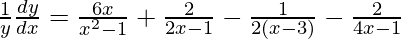
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=y\left[\frac{6x}{x^2-1}+\frac{2}{2x-1}-\frac{1}{2(x-3)}-\frac{2}{4x-1}\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-25c8be35dff2d2bb6dc7de57aebe2c2c_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{(x^2-1)^3(2x-1)}{\sqrt{(x-3)(4x-1)}}\left[\frac{6x}{x^2-1}+\frac{2}{2x-1}-\frac{1}{2(x-3)}-\frac{2}{4x-1}\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2009aaa4bafcb70ef29ffd7f09289dc6_l3.png)
Question 22. Find dy/dx when 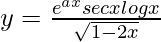 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> 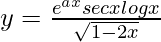
=> 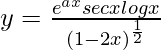
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> 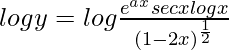
=> 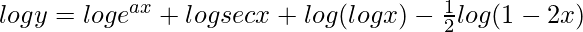
=> 
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{y}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[ax+logsecx+log(logx)-\frac{1}{2}log(1-2x)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-553c2aad89b55baad8de781868c654a0_l3.png)
=> 
=> 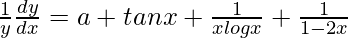
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=y\left[a+tanx+\frac{1}{xlogx}+\frac{1}{1-2x}\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d997e3e9dd0db385d3176689d47aea7b_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{e^{ax}secxlogx}{\sqrt{1-2x}}\left[a+tanx+\frac{1}{xlogx}+\frac{1}{1-2x}\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-37c70675d7111328b17ad5bf037002c8_l3.png)
Question 23. Find dy/dx when y = e3x sin 4x 2x.
Solution:
We have
=> y = e3x sin 4x 2x.
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log y = log (e3x sin 4x 2x)
=> log y = log e3x + log (sin 4x) + log 2x
=> log y = 3x log e + log (sin 4x) + x log 2
=> log y = 3x + log (sin 4x) + x log 2
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{y}\frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[3x + log (sin 4x) + x log 2]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ffabf75f88be2cc33077957f2ad4df55_l3.png)
=> 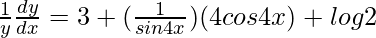
=> 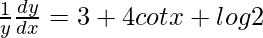
=> 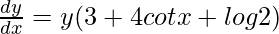
=> 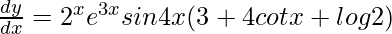
Question 24. Find dy/dx when y = sin x sin 2x sin 3x sin 4x.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = sin x sin 2x sin 3x sin 4x
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log y = log (sin x sin 2x sin 3x sin 4x)
=> log y = log sin x + log sin 2x + log sin 3x + log sin 4x
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 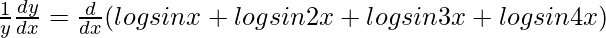
=> 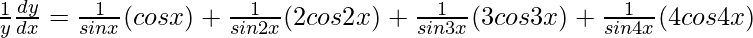
=> 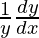 = cotx + 2cot2x + 3cot3x + 4cot4x
= cotx + 2cot2x + 3cot3x + 4cot4x
=> 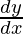 = y(cotx + 2cot2x + 3cot3x + 4cot4x)
= y(cotx + 2cot2x + 3cot3x + 4cot4x)
=> 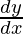 = (sinxsin2x sin3xsin4x)(cotx + 2cot2x + 3cot3x + 4cot4x)
= (sinxsin2x sin3xsin4x)(cotx + 2cot2x + 3cot3x + 4cot4x)
Question 25. Find dy/dx when y = xsin x + (sin x)x.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = xsin x + (sin x)x.
Let u = xsin x and v = (sin x)x. Therefore, y = u + v.
Now, u = xsin x
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log u = log xsin x
=> log u = sin x log x
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 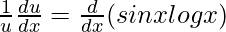
=> 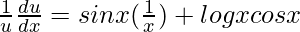
=> 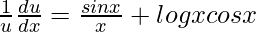
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{du}{dx}=u\left[\frac{sinx}{x}+logxcosx\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d804edd34ac17a3f3d02313ea74a9b19_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{du}{dx}=x^{sinx}\left[\frac{sinx}{x}+logxcosx\right]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7ae6e93471bcf7650026ea6afc04b0fa_l3.png)
Also, v = (sin x)x
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log v = log (sin x)x
=> log v = x log sin x
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 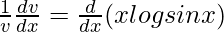
=> 
=> 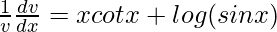
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dv}{dx}=v[xcotx+log(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-60918e4e1a4a45a28d520d713a9b3674_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dv}{dx}=(sinx)^x[xcotx+log(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e91113c3edd23ecdc7143bfdaf350190_l3.png)
Now we have, y = u + v.
=> 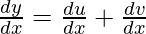
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=x^{sinx}\left[\frac{sinx}{x}+logxcosx\right]+(sinx)^x[xcotx+log(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d696f905e4b3898bc71bdb0dcbbd917d_l3.png)
Question 26. Find dy/dx when y = (sin x)cos x + (cos x)sin x.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = (sin x)cos x + (cos x)sin x
=> 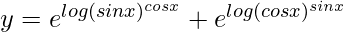
=> 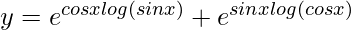
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{cosxlog(sin x)})[cosx(\frac{1}{sinx})cosx+log(sinx)(-sinx)] + (e^{sinxlog(cos x)})[sinx(\frac{1}{cosx})(-sinx)+log(cosx)(cosx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-381af831a4aebeb66d66c1bb943808c2_l3.png)
=> 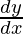 = (sinx)cosx[cosxcotx – sinxlog(sinx)] + (cosx)sinx[-tanxsinx + cosxlog(cosx)]
= (sinx)cosx[cosxcotx – sinxlog(sinx)] + (cosx)sinx[-tanxsinx + cosxlog(cosx)]
=> 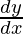 = (sinx)cosx[cosxcotx – sinxlog(sinx)] + (cosx)sinx[cosxlog(cosx) – tanxsinx]
= (sinx)cosx[cosxcotx – sinxlog(sinx)] + (cosx)sinx[cosxlog(cosx) – tanxsinx]
Question 27. Find dy/dx when y = (tan x)cot x + (cot x)tan x.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = (tan x)cot x + (cot x)tan x
=> 
=> 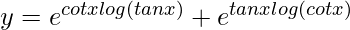
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 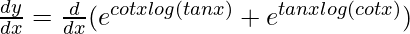
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{cotxlog(tanx)})[cotx(\frac{1}{tanx})(sec^2x)+log(tanx)(-cosec^2x)] + (e^{tanxlog(cot x)})[tanx(\frac{1}{cotx})(-cosec^2x)+log(cotx)(sec^2x)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-700347737176ab2e9b9f7c2431ebd2fe_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(tanx)^{cotx}[cot^2x(sec^2x)-log(tanx)(cosec^2x)] + (cotx)^{tanx}[tan^2x(-cosec^2x)+log(cotx)(sec^2x)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4169c6a5a4d3f70c0663646b393bd270_l3.png)
=> 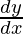 = (tanx)cotx[cosec2x – log(tanx)(cosec2x)] + (cotx)tanx[-sec2x + log(cotx)(sec2x)]
= (tanx)cotx[cosec2x – log(tanx)(cosec2x)] + (cotx)tanx[-sec2x + log(cotx)(sec2x)]
=> 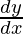 = (tanx)cotx[cosec2x – cosec2xlog(tanx)] + (cotx)tanx[sec2xlog(cotx) – sec2x]
= (tanx)cotx[cosec2x – cosec2xlog(tanx)] + (cotx)tanx[sec2xlog(cotx) – sec2x]
Question 28. Find dy/dx when y = (sin x)x + sin−1 √x.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = (sin x)x + sin−1 √x
=> 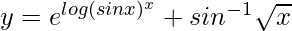
=> 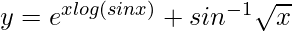
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[e^{xlog(sinx)} + sin^{-1}\sqrt{x}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-78802374b26d96dab8a1a0e312cfe54c_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{xlog(sinx)})[x(\frac{1}{sinx})cosx+log(sinx)]+(\frac{1}{\sqrt{1-x}})(\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x}})](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2ce49aab47aff6cfcb8a58006113784b_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{xlog(sinx)})[xcotx+log(sinx)]+\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x-x^2}}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5f352d15f952d2b35266aa0f8ffa1bcd_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(sinx)^x[xcotx+log(sinx)]+\frac{1}{2\sqrt{x-x^2}}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-4d3c0ebde07b7381493295c1e747c418_l3.png)
Question 29. Find dy/dx when
(i) y = xcos x + (sin x)tan x
Solution:
We have,
=> y = xcos x + (sin x)tan x
=> 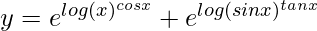
=> 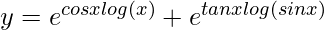
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[e^{cosxlog(x)} + e^{tanxlog(sinx)}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a0bf858a96fa2d43acd79ec4346b64ef_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{cosxlogx})[cosx(\frac{1}{x})+logx(-sinx)] + (e^{tanxlog(sinx)})[tanx(\frac{1}{sinx})(cosx)+log(sinx)sec^2x]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1922a26dfd2bac900945c5e03ae6c9ac_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=x^{cosx}[\frac{cosx}{x}-logxsinx] +(sinx)^{tanx}[tanx(cotx)+log(sinx)sec^2x]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-39d4531145fc1927eccfdb5156111f25_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=x^{cosx}[\frac{cosx}{x}-logxsinx] +(sinx)^{tanx}[1+sec^2xlog(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-20e9fbfeece01bdcfeab39562fb42004_l3.png)
(ii) y = xx + (sin x)x
Solution:
We have,
=> y = xx + (sin x)x
=> 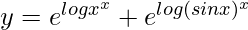
=> 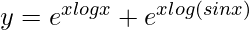
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[e^{xlogx} + e^{xlog(sinx)}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-6e06469c1d931e1541561bada6988b37_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{xlogx})[x(\frac{1}{x})+logx] + (e^{xlog(sinx)})[x(\frac{1}{sinx})(cosx)+log(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-18c5160f226655716598aac7e0b0ee45_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{xlogx})[1+logx] + (e^{xlog(sinx)})[xcotx+log(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d6b024e3b3cc53d50de1e201e94636a0_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=x^x(1+logx) + (sinx)^x[xcotx+log(sinx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-26a6f82f09d26377abbbd9b1dd839b5b_l3.png)
Question 30. Find dy/dx when y = (tan x)log x + cos2 (π/4).
Solution:
We have,
=> y = (tan x)log x + cos2 (π/4)
=> 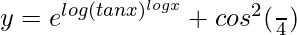
=> 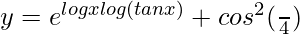
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[e^{logxlog(tanx)} +cos^2(\frac{π}{4})]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-d82cc0236a3de4541a08684f03770665_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{logxlog(tanx)})[logx(\frac{1}{tanx})(sec^2x)+log(tanx)(\frac{1}{x})] +0](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7fa51d8e3ee8018cb14d24895ac7c66e_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{logxlog(tanx)})[\frac{logxsec^2x}{tanx}+\frac{log(tanx)}{x}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0bd156fa39c7259bae8d71f97122c289_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(tanx)^{logx}[\frac{logxsec^2x}{tanx}+\frac{log(tanx)}{x}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-01319860a9e5010df29a4d2ac1d6ca16_l3.png)
Question 31. Find dy/dx when 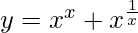 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> 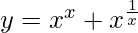
=> 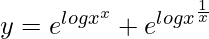
=> 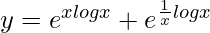
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[e^{xlogx} + e^{\frac{1}{x}logx}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1c38df05107307daa548a3b73225ab1f_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{xlogx})[x(\frac{1}{x})+logx] + (e^{\frac{1}{x}logx})[(\frac{1}{x})(\frac{1}{x})+logx(\frac{-1}{x^2})]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-04fc7270c58e0924b5f3a001a1c4cc5a_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(e^{xlogx})(1+logx) + (e^{\frac{1}{x}logx})[\frac{1}{x^2}-\frac{logx}{x^2}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-2c1c052d1d8a58416bf9bcfef772faf6_l3.png)
=> 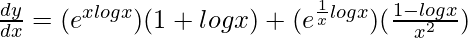
=> 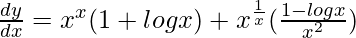
Question 32. Find dy/dx when y = (log x)x+ xlogx.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = (log x)x+ xlogx
Let u = (log x)x and v = xlogx. Therefore, y = u + v.
Now, u = (log x)x
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log u = log (log x)x
=> log u = x log (log x)
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{u}\frac{du}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[x log (log x)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ef0a375589bd3e31b83cbf4c4755a3ea_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{u}\frac{du}{dx}=[x(\frac{1}{logx})(\frac{1}{x})+log(logx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-1b3def0c9ce80a7024f9cea7ba9f9d08_l3.png)
=> 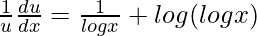
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{du}{dx}=u[\frac{1}{logx}+log(logx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ff87e2265b2e9fbdd9f66e10c9b4097c_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{du}{dx}=(logx)^x[\frac{1}{logx}+log(logx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-5e9a0f9c62697bd389add0bedffa7c85_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{du}{dx}=(logx)^x[\frac{1+logxlog(logx)}{logx}]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e4819cc6ace23e0e8eb62caafbc3cdc5_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{du}{dx}=(logx)^{x-1}[1+logxlog(logx)]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-a2379891bbe492c5030d27556043ce25_l3.png)
Also, v = xlogx
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log v = log xlogx
=> log v = log x (log x)
=> log v = (log x)2
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{v}\frac{dv}{dx}=\frac{d}{dx}[(log x)^2]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-ecab6eab0a776d0c15efe9f8167bbfd6_l3.png)
=> 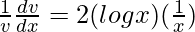
=> 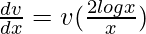
=> 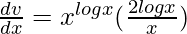
=> 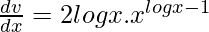
Now, y = u + v
=> 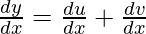
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}=(logx)^{x-1}[1+logxlog(logx)]+2logx.x^{logx-1}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0dab3b999316ecfd01b3c019f070bcc4_l3.png)
Question 33. If x13y7 = (x+y)20, prove that 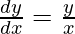 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> x13y7 = (x+y)20
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log x13y7 = log (x+y)20
=> log x13 + log y7 = log (x+y)20
=> 13 log x + 7 log y = 20 log (x+y)
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 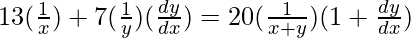
=> 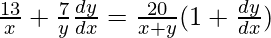
=> 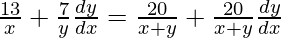
=> 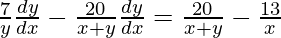
=> 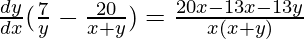
=> 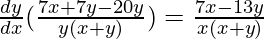
=> 
=> 
Hence proved.
Question 34. If x16y9 = (x2 + y)17, prove that 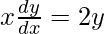 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> x16y9 = (x2 + y)17
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log x16y9 = log (x2 + y)17
=> log x16 + log y9 = log (x2 +y)17
=> 16 log x + 9 log y = 17 log (x2 + y)
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 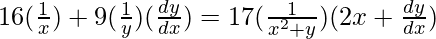
=> 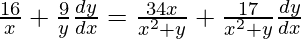
=> 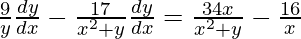
=> 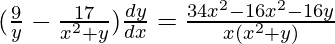
=> 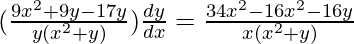
=> 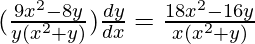
=> 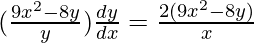
=> 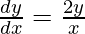
=> 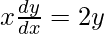
Hence proved.
Question 35. If y = sin xx, prove that 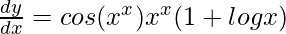 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> y = sin xx
Let u = xx. Now y = sin u.
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log u = log xx
=> log u = x log x
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 
=> 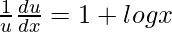
=> 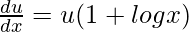
=> 
Now, y = sin u
=> 
=> 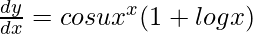
=> 
Hence proved.
Question 36. If xx + yx = 1, prove that 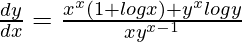 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> xx + yx = 1
=> 
=> 
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (e^{xlogx})[x(\frac{1}{x})+logx] + (e^{xlogy})[x(\frac{1}{y})(\frac{dy}{dx})+logy] = 0](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-9ff0bf360a24b3799867eb8c072edbf0_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (e^{xlogx})(1+logx) + (e^{xlogy})[(\frac{x}{y})(\frac{dy}{dx})+logy] = 0](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-594220d004fff963cc7e0f6e4c26de66_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com x^x(1+logx) + y^x[(\frac{x}{y})(\frac{dy}{dx})+logy] = 0](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e73a77285a41d940427f1c8430b4d1b1_l3.png)
=> 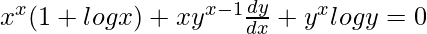
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com xy^{x-1}\frac{dy}{dx} = -[x^x(1+logx)+y^xlogy ]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e32532b016ac0d40b2db630216d6c708_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx} = \frac{-[x^x(1+logx)+y^xlogy]}{xy^{x-1}}](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-0bc675ab194fcac825bdabb65819721e_l3.png)
Hence proved.
Question 37. If xy × yx = 1, prove that 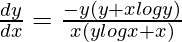 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> xy × yx = 1
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log (xy × yx) = log 1
=> log xy + log yx = log 1
=> y log x + x log y = log 1
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 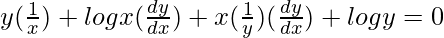
=> 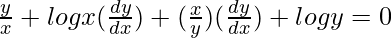
=> 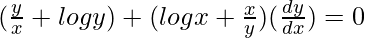
=> 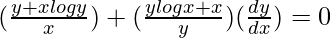
=> 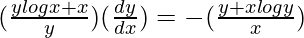
=> 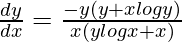
Hence proved.
Question 38. If xy + yx = (x+y)x+y, find dy/dx.
Solution:
We have,
=> xy + yx = (x+y)x+y
=> 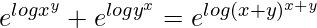
=> 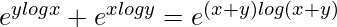
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com (e^{ylogx})[y(\frac{1}{x})+logx(\frac{dy}{dx})] + (e^{xlogy})[x(\frac{1}{y})(\frac{dy}{dx})+logy]=(e^{(x+y)log(x+y)})[(x+y)(\frac{1}{x+y})(1+\frac{dy}{dx})+log(x+y)(1+\frac{dy}{dx})]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-bc3faa98d841e3e35271fb6ea78c02d7_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com e^{ylogx}[\frac{y}{x}+logx(\frac{dy}{dx})] + (e^{xlogy})[(\frac{x}{y})(\frac{dy}{dx})+logy]=(e^{(x+y)log(x+y)})[1+\frac{dy}{dx}+log(x+y)(1+\frac{dy}{dx})]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-c055c357eceda950cfaa2dc219d98c95_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com x^y[\frac{y}{x}+logx(\frac{dy}{dx})] + y^x[(\frac{x}{y})(\frac{dy}{dx})+logy]=(x+y)^{x+y}[1+\frac{dy}{dx}+log(x+y)(1+\frac{dy}{dx})]](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-8f2f4fc7bfbcebf75af2f3a732e7b94b_l3.png)
=> ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{dy}{dx}[x^ylogx+xy^{x-1}-(x+y)^{x+y}(1+log(x+y))]=(x+y)^{x+y}(1+log(x+y))-yx^{y-1}-y^xlogy](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-903e4408e5dd206249232b7014c062eb_l3.png)
=> 
Question 39. If xm yn = 1, prove that  .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> xm yn = 1
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log (xm yn)= log 1
=> log xm + log yn = log 1
=> m log x + n log y = log 1
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 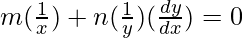
=> 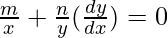
=> 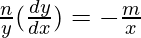
=> 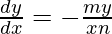
Hence proved.
Question 40. If yx = ey−x, prove that 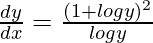 .
.
Solution:
We have,
=> yx = ey−x
On taking log of both the sides, we get,
=> log yx = log ey−x
=> x log y = (y − x) log e
=> x log y = y − x
On differentiating both sides with respect to x, we get,
=> 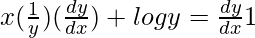
=> 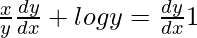
=> 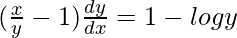
=> 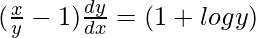
=> 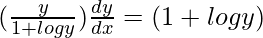
=> 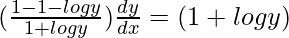
=> 
=> 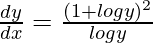
Hence proved.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...