Question 1. Find the equation of the ellipse whose focus is (1,–2) and directrix is 3x – 2y + 5 = 0, and eccentricity is 1/2.
Solution:
Given that,
Focus is (1, -2)
directrix is 3x – 2y + 5 = 0,
eccentricity(e) is 1/2.
As we know, SP = ePM
⇒ SP = PM/2
⇒ (SP)2 = 1/4(PM)2
⇒ 4(SP)2 = (PM)2
⇒ 4[(x – 1)2 + (y + 2)2] = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\frac{3x-2y+5}{\sqrt{3^2+2^2}}]^2](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-29dba88395afb43aab86eb60da0329ac_l3.png)
⇒ 4[x2 + 1 – 2x + y2 + 4 + 4y] = 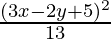
⇒ 52[x2 + 1 – 2x + y2 + 4 + 4y] = (3x – 2y + 5)2
⇒ 52[x2 + 1 – 2x + y2 + 4 + 4y] = 9x2 + 4y2 + 25 – 12xy – 20y + 30x
Thus 43x2 + 43y2 + 12xy – 134x + 228y + 235 = 0 is the required equation.
Question 2. Find the equation of the ellipse if:
(i) Focus is (0, 1), directrix is x + y = 0 and e = 1/2.
Solution:
Given that,
focus is (0, 1),
directrix is x + y = 0
eccentricity(e) is 1/2
As we know, SP = ePM
⇒ SP = PM/2
⇒ (SP)2 = 1/4(PM)2
⇒ 4(SP)2 = (PM)2
⇒ 4[(x – 0)2 + (y – 1)2] = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\frac{x+y}{\sqrt{1^2+1^2}}]^2](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-7f27f2e363eb333d3ed7cf133be6a891_l3.png)
⇒ 8[x2 + y2 – 2y + 1] = x2 + y2 + 2xy
Thus 7x2 + 7y2 – 2xy – 16y + 8 = 0 is the required equation.
(ii) Focus is (–1,1), directrix is x – y + 3 = 0 and e = 1/2.
Solution:
Given that,
focus is (-1, 1),
directrix is x – y + 3 = 0
eccentricity(e) is 1/2
As we know, SP = ePM
⇒ SP = PM/2
⇒ (SP)2 = 1/4(PM)2
⇒ 4(SP)2 = (PM)2
⇒ 4[(x + 1)2 + (y – 1)2] = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\frac{x-y+3}{\sqrt{1^2+1^2}}]^2](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-e0e0959b64c23b8bd25c14ba326e27d6_l3.png)
⇒ 4[(x + 1)2 + (y – 1)2] = (x – y + 3)2/2
⇒ 8[(x + 1)2 + (y – 1)2] = (x – y + 3)2
⇒ 8[(x + 1)2 + (y – 1)2] = x2 + y2 + 9 – 6y – 2xy + 6x
⇒ 8[(x2 + 1 + 2x) + (y2 + 1 – 2y)] = x2 + y2 + 9 – 6y – 2xy + 6x
⇒ 8[x2 + y2 + 2 + 2x – 2y] = x2 + y2 + 9 – 6y – 2xy + 6x
Thus 7x2 + 7y2 + 2xy + 10x – 10y + 7 = 0 is the required equation.
(iii) Focus is (–2,3), directrix is 2x + 3y + 4 = 0 and e = 4/5.
Solution:
Given that,
focus is (-2, 3),
directrix is 2x + 3y + 4 = 0
eccentricity(e) is 4/5
As we know, SP = ePM
⇒ SP = 4/5(PM)
⇒ (SP)2 = 16/25(PM)2
⇒ 25(SP)2 = 16(PM)2
⇒ 25[(x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2] = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com 16[\frac{2x+3y+4}{\sqrt{2^2+3^2}}]^2](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-93d383e0636df58fecc1403da5d33d7d_l3.png)
⇒ 25[(x + 2)2 + (y – 3)2] = 16(2x + 3y + 4)2/13
Thus 325[x2 + y2 + 4x – 6y + 13] = 16(2x + 3y + 4)2 is the required equation.
(iv) Focus is (1, 2), directrix is 3x + 4y – 5 = 0 and e = 1/2.
Solution:
Given that,
focus is (1, 2),
directrix is 3x + 4y – 5 = 0
eccentricity(e) is 1/2
We know, SP = ePM
⇒ SP = PM/2
⇒ (SP)2 = 1/4(PM)2
⇒ 4(SP)2 = (PM)2
⇒ 4[(x – 1)2 + (y – 2)2] = ![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com [\frac{3x+4y-5}{\sqrt{3^2+4^2}}]^2](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-151d3979d9c7ce33ff869e619526c19f_l3.png)
⇒ 4[(x – 1)2 + (y – 2)2] = (3x + 4y – 5)2/25
⇒ 100[(x – 1)2 + (y – 2)2] = 9x2 + 16y2 + 25 + 24xy – 40y – 30x
⇒ 100[(x2 + 1 – 2x) + (y2 + 4 – 4y)] = 9x2 + 16y2 + 25 + 24xy – 40y – 30x
Thus 91x2 + 84y2 – 24xy – 170x – 360y + 475 = 0 is the required equation.
Question 3. Find the eccentricity, coordinates of foci, length of the latus- rectum of the ellipse:
(i) 4x2 + 9y2 = 1
Solution:
Given that 4x2 + 9y2 = 1
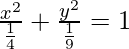
So,
⇒ Eccentricity = 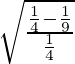
= √5/3
Length of latus rectum = 
= 4/9
Foci are(√5/6; 0) and (-√5/6; 0)
(ii) 5x2 + 4y2 = 1
Solution:
Given that 5x2 + 4y2 = 1

So,
⇒ Eccentricity = 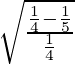
= 1/√5
Length of latus rectum = 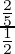
= 4/5
Foci are (0; 1/2√5) and (0; -1/2√5)
(iii) 4x2 + 3y2 = 1
Solution:
Given that 4x2 + 3y2 = 1
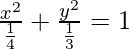
So,
⇒ Eccentricity = 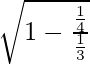
= 1/2
Length of latus rectum = 2a2/b
= 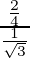
= √3/2
Foci are (0; 1/2√3) and (0; -1/2√3).
(iv) 25x2 + 16y2 = 1600
Solution:
Given that 25x2 + 16y2 = 1600
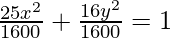
⇒ 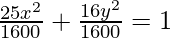
So,
⇒ Eccentricity = 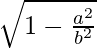
= 3/5
⇒ Coordinates of foci are (0, 6) and (0, –6).
⇒ Length of latus rectum = 2a2/b
= 2 x (64/10)
= 64/5
(v) 9x2 + 25y2 = 225
Solution:
Given that 9x2 + 25y2 = 225
=> \frac{9x^2}{225}+\frac{25y^2}{225}=1
=> 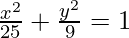
Clearly, a = 5 and b = 3.
So,
⇒ Eccentricity = 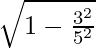
= 4/5
⇒ Coordinates of foci are (4, 0) and (–4, 0).
⇒ Length of latus rectum = 2b2/a
= 2 x (9/5)
= 18/5
Question 4. Find the equation of the ellipse passing through the point (–3, 1) and has eccentricity  .
.
Solution:
Let the equation of the plane be:
 …(i)
…(i)
It is given that the ellipse pass through the point (–3, 1), so,
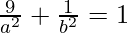 …(ii)
…(ii)
⇒ 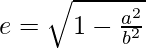
⇒ 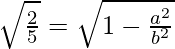
⇒ b2/a2 = 3/5
⇒ b2 = 3a2/5
⇒ b2 = 3a2/5 ……(iii)
Now put the value of b2 in equation (ii), we get
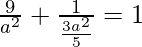
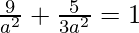
![Rendered by QuickLaTeX.com \frac{1}{a^2}[9 + \frac{5}{3}]=1](https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/wp-content/ql-cache/quicklatex.com-cf5b064c302dcb6d2daf703e4f03ff64_l3.png)
9 + 5/3 = a2
a2 = 32/3
Now put the value of a2 in eq(iii), we get,
b2 = 3/5 x 32/3 = 32/5
Now put the a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
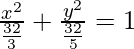
Thus 3x2 + 5y2 = 32 is the required equation of the plane.
Question 5. Find the equation of the ellipse if:
(i) e = 1/2 and foci (±2, 0).
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 …(i)
…(i)
Now, ae = 2
or, a2 = 16
Now, b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ b2 = 16(1 – (1/2)2)
⇒ b2 = 12
Now put the a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,

Thus 3x2 + 4y2 = 48 is the equation of the ellipse.
(ii) e = 2/3 and length of latus- rectum = 5
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 …(i)
…(i)
Now,
⇒ 2b2/a = 5
⇒ b2 = 5a/2 ….(ii)
Since, b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ 5a/2 = a2(1 – (2/3)2)
⇒ a = 9/2
⇒ a2 = 81/4
Now put the value of a in eq(ii), we get
b2 = 5/2 x 9/2
b2 = 45/4
Now put the a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,

Thus 20x2 + 36y2 = 405 is the required equation.
(iii) e = 1/2 and semi-major axis = 4
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Semi – major axis = a = 4
⇒ a2 = 16
We know, a2 = b2(1 – e2)
⇒ 16 = b2(1 – (12/22))
⇒ b2 = 12
Now put the a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
⇒ 
Thus 3x2 + 4y2 = 48 is the required equation.
(iv) e = 1/2 and major axis = 12
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given, 2a = 12
⇒ a = 6
We know, 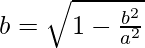
⇒ 
⇒ b2 = 27
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
⇒ 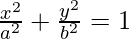
⇒ 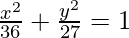
Thus 3x2 + 4y2 = 108 is the equation of the ellipse.
(v) It passes through (1, 4) and (–6, 1).
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
It is given that ellipse passes through (1, 4) and (–6, 1), we get
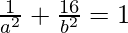
Let p = 1/a2 and r = 1/b2
⇒ p + 16r = 1 ……(ii)
Since the ellipse also passes through the point (–6, 1), we have
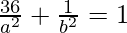
⇒ 36p + r = 1 ……(iii)
On solving eq(ii) and (iii), we have:
p = 3/115; r = 7/115
On substituting the values in eq(i), we get;
⇒ 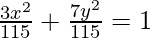
Thus 3x2 + 7y2 = 115 is the required equation.
(vi) Its vertices are (±5, 0) and foci(±4, 0)
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given that a = 5 and ae = 4
Thus, e = 4/5 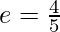
Now, b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ b2 = 25(1 – 16/25)
⇒ b2 = 9
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
Thus 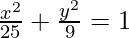 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(vii) Vertices are (0, ±13) and foci(0, ±5)
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given: b = 13 and be = 5
Hence, e = 5/13
Now, a2 = b2(1 – e2)
⇒ a2 = 169(1 – 25/169)
⇒ a2 = 144
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
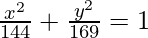
Thus 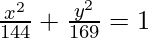 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(viii) Its vertices are (±6, 0) and foci(±4, 0)
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given: a = 6 and ae = 4
Thus, e = 2/3
Now, b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ b2 = 36(1 – 16/36)
⇒ b2 = 20
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
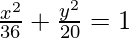
Thus 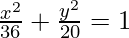 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(ix) Ends of the major axis (±3, 0) and ends of the minor axis (0, ±2).
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be 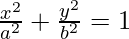 …..(i)
…..(i)
Ends of major axis = (±3, 0)
Ends of minor axis = (0, ±2)
Since the ends of the major and minor axes are (±a, 0) and (0, ±b) respectively.
Hence, a = 3 and b = 2
So, a2 = 9, b2 = 4
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
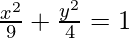
Thus, 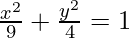 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(x) Ends of the major axis (0, ±√5) and ends of the minor axis (±1, 0).
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be 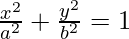 ….(i)
….(i)
Ends of major axis = (0, ±√5)
Ends of minor axis = (±1, 0)
Since the ends of the major and minor axes are (±a, 0) and (0, ±b) respectively.
Hence, a = 1 and b = √5
So, a2 = 1, b2 = 5
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
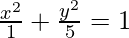
Thus, 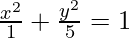 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(xi) Length of the major axis is 26 and foci (±5, 0).
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given that the length of major axis = 26 and foci (±5, 0).
We have, 2a = 26
⇒ a = 13
⇒ a2 = 169
Also, ae = 5
⇒ e = 5/13
We know, 
⇒ 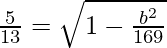
⇒ b2 = 144
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
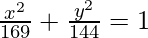
Thus 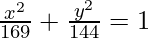 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(xii) Length of minor axis is 16 and foci(0, ±6)
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given that, length of minor axis is 16
2a = 16
a = 8
a2 = 64
Now the coordinates of foci are (0, ±be)
So, be = 6
(be)2 = 36
We know, a2 = b2(1 – e2)
a2 = b2 – b2e2
64 = b2 – 36
b2 = 100
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
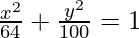
Thus,  is the required equation.
is the required equation.
(xiii) Foci are (±3, 0) and a = 4
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be:
 ….(i)
….(i)
Given that, ae = 3 and a = 4
Thus, e = 3/4 and a2 = 16
We know, 
⇒ 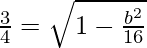
⇒ b2 = 7
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
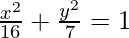
Thus  is the required equation of the ellipse.
is the required equation of the ellipse.
Question 6. Find the equation of the ellipse whose foci are (±4, 0), e = 1/3.
Solution:
Let the equation of the ellipse be  ….(i)
….(i)
Then the coordinates of the foci are (±a, 0).
We have, ae = 4 and e = 1/3
Thus, a = 12
and a2 = 144
We know that, b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ b2 = 144(1 – (1/3)2)
⇒ b2 = 144(8/9)
⇒ b2 = 128
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
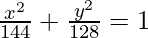
Thus, 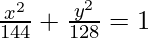 is the required equation.
is the required equation.
Question 7. Find the equation of the ellipse in the standard form whose minor axis is equal to the distance between the foci and whose latus rectum is 10.
Solution:
Given that, the coordinates of foci are (±ae, 0).
2b = 2ae
⇒ b = ae
⇒ b2 = a2e2 ….(i)
Also given that the latus rectum is 10
So, 2b2/a = 10
b2= 5a ….(ii)
As we know that b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ b2 = a2(1 – e2)
⇒ b2 = a2 – a2e2
⇒ b2 = a2 – b2
⇒ 2b2 = a2
⇒ b2 = a2/2 ….(iii)
Now put the value of b2 in eq(ii), we get
a2/2 = 5a
a = 10
So, a2 = 100
Now put the value a2 of in eq(iii), we get
b2 = 100/2
b2 = 50
On substituting the values of a2 and b2 in eq(i), we get,
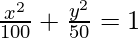
Hence, x2 + 2y2 = 100 is the required equation.
Question 8. Find the equation of the ellipse whose centre is (-2, 3) and whose semi- axis are 3 and 2 when the major axis is (i) parallel to the x-axis (ii) parallel to the y-axis.
Solution:
(i) When the major axis is parallel to the x-axis
Let us assume  be the equation.
be the equation.
So, on substituting the values x1 = -2, y1 = 3, a = 3, and b = 2 in the equation, we have:

Thus, 4x2 + 9y2 + 16x – 54y + 61 = 0 is the required equation.
(ii) When the major axis is parallel to the y-axis
Let us assume  be the equation.
be the equation.
So, on substituting the values x1 = -2, y1 = 3, a = 2, and b = 3 in the equation, we have:
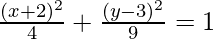
Thus, 9x2 + 4y2 + 36x – 24y + 36 = 0 is the required equation.
Question 9. Find the eccentricity of an ellipse whose:
(i) Latus rectum is half of its minor axis
Solution:
Given that, 2b2/a = 2b/2
⇒ 2b2 = ab
⇒ 2b = a
Since, 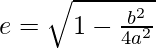
⇒ 
⇒ e = √3/2
Hence, the eccentricity of an ellipse is √3/2
(ii) Latus rectum is half of its major axis
Solution:
Given that, 2b2/a = 2a/2
⇒ 2b2 = a2
Since, 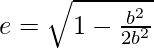
⇒ 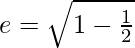
⇒ e = 1/√2
Question 10. Find the centre, the lengths of the axes, eccentricity, foci of the following ellipse:
(i) x2 + 2y2 – 2x + 12y + 10 = 0
Solution:
Given that x2 + 2y2 – 2x + 12y + 10 = 0
(x2 – 2x) + 2(y2 + 6y) = -10
⇒ (x2 – 2x + 1) + 2(y2 + 6y + 9) = -10 + 18 + 1
⇒ 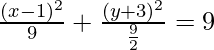
So, x1 = 1, y1 = -3
and a = 3 and b = 3/√2
Centre = (1, -3)
Major axis = 2a = 2(3) = 6
Minor axis = 2b = 3\sqrt2
e=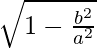
= 1/√2
Foci = (1 ± 3/√2; -3)
(ii) x2 + 4y2 – 4x + 24y + 31 = 0
Solution:
Given that x2 + 4y2 – 4x + 24y + 31 = 0
(x2 – 4x) + 4(y2 + 6y) = -31
⇒ (x2 – 4x + 4) + 4(y2 + 6y + 9) = 9
⇒ 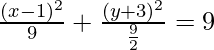
So, x1 = 1, y1 = -3
and a = 3 and b = 3/2
Centre = (2, -3)
Major axis = 2a = 2(3) = 6
Minor axis = 2b = 3
e= 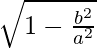
= √3/2
Foci = (2 ± 3/√2; -3)
(iii) 4x2 + y2 – 8x + 2y +1 = 0
Solution:
Given that 4x2 + y2 – 8x + 2y +1 = 0
4(x2 – 2x) + (y2 + 2y) = -1
4(x2 – 2x + 1) + (y2 + 2y + 1) = -1 + 4 + 1
4(x2 – 1) + (y2 + 1) = 4
⇒ 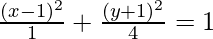
So, x1 = 1, y1 = -1
and a = 1 and b = 2
Centre = (1,-1)
Minor axis = 2a = 2(1) = 2
Minor axis = 2b = 4
e = 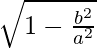
e = √3/2
Foci = (1, -1 ± √3)
(iv) 3x2 + 4y2 – 12x – 8y + 4 = 0
Solution:
Given that 3x2 + 4y2 – 12x – 8y + 4 = 0
3(x2 – 4x) + 4(y2 – 2y) = -4
3(x2 – 4x + 4) + 4(y2 – 2y + 1) = -4 + 12 + 4
⇒ 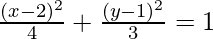
So, x1 = 2, y1 = -1
and a = 2 and b = √3
Centre = (2, 1)
Major axis = 2a = 2(2) = 4
Minor axis = 2b = 2(√3) = 2√3
e = 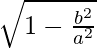
e = 1/2
Foci = (2 ± 1, 1)
(v) 4x2 + 16y2 – 24x – 32y – 12 = 0
Solution:
Given that 4x2 + 16y2 – 24x – 32y – 12 = 0
4(x2 – 6x) + 16(y2 – 2y) = 12
4(x2 – 6x + 9) + 16(y2 – 2y + 1) = 12 + 36 + 16
4(x – 3) + 16(y – 1) = 64
⇒ 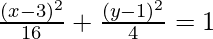
So, x1 = 3, y1 = 1
and a = 4 and b = 2
Centre = (3, 1)
Major axis = 2a = 2(4) = 8
Minor axis = 2b = 2(2) = 4
e = 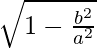
e = √3/2
Foci = (3 ±2√3; 1)
(vi) x2 + 4y2 – 2x = 0
Solution:
Given that x2 + 4y2 – 2x = 0
(x2 – 2x) + 4y2 = 0
(x2 – 2x + 1) + 4y2 = 0
(x – 1)2 + 4y2 = 0
⇒ 
So, x1 = 1, y1 = 0
and a = 1 and b = 1/4
Centre = (1, 0)
Major axis = 2a = 2(1) = 2
Minor axis = 2b = 2(1/2) = 1
e = 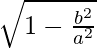
e = √3/2
Foci = (1 ±√3/2, 0)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...