Class 12 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 9 Continuity – Exercise 9.1 | Set 2
Last Updated :
26 May, 2021
Question 16. Discuss the continuity of the function
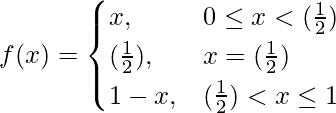 at the point x = 1/2.
at the point x = 1/2.
Solution:
Given that,
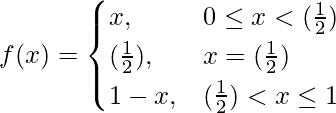
So, here we check the continuity of the given f(x) at x = 1/2,
Let us consider LHL,
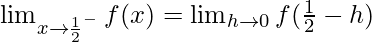
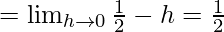
Now, let us consider RHL,
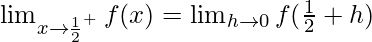
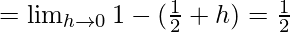
f(1/2) = 1/2
Thus, LHL= RHL = f(1/2) = 1/2
Hence, the f(x) is continuous at x = 1/2.
Question 17. Discuss the continuity of  at the point x = 0.
at the point x = 0.
Solution:
Given that,

So, here we check the continuity of the given f(x) at x = 10,
Let us consider LHL,
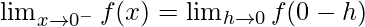
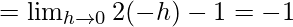
Now, let us consider RHL,
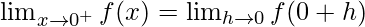
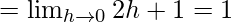
Thus, LHL ≠ RHL
Hence, the f(x) is discontinuous at x = 0.
Question 18. For what value of k is the function  continuous at x = 1 ?
continuous at x = 1 ?
Solution:
Given that,

Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 1
So,
LHL = RHL = f(1) ……(i)
Let us consider LHL,
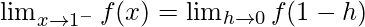
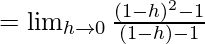
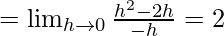
f(1) = k
From eq(i), we get
LHL = F(1)
Therefore, k = 2
Question 19. Determine the value of the constant k so that the function
 continuous at x = 1.
continuous at x = 1.
Solution:
Given that,

Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 1
So, LHL = RHL = f(1) …..(i)
Let us consider LHL,
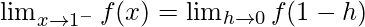

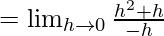
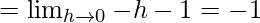
f(1) = k
From eq(i), we get
LHL = F(1)
Therefore, k = -1
Question 20. For what value of k is the function 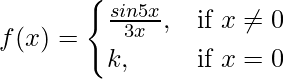 continuous at x = 0 ?
continuous at x = 0 ?
Solution:
Given that,
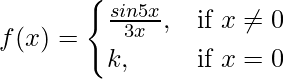
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 0
So, LHL = RHL = f(0) …..(i)
Let us consider LHL,
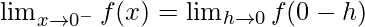
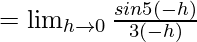
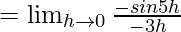

f(0) = k
Thus, from eq(i), we get
k = 5/3
Therefore, k = 5/3
Question 21. Determine the value of the constant k so that the function
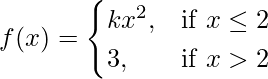 continuous at x = 2.
continuous at x = 2.
Solution:
Given that,
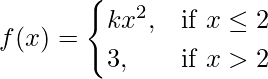
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 2
Then, f(2) = k(2)2 = 4k
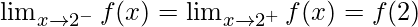
⇒ 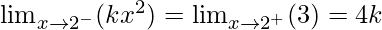
⇒ k × 22 = 3 = 4k
⇒ 4k = 3 = 4k
⇒ 4k = 3
⇒ k = 3/4
Hence, the value of k is 3/4
Question 22. Determine the value of the constant k so that the function
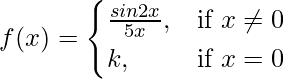 is continuous at x = 0.
is continuous at x = 0.
Solution:
Given that,
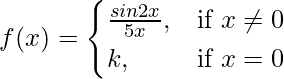
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 0
So, LHL = RHL = f(0) ….(i)
Let us consider LHL,
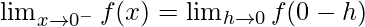
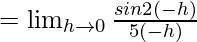

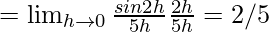
f(0) = k
From eq(i), we get
k = 2/5
Question 23. Find the values of a so that the function 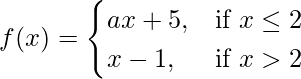 is continuous at x = 2.
is continuous at x = 2.
Solution:
Given that,
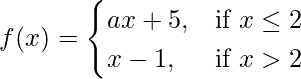
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 2
So, LHL = RHL = f(2) …….(i)
Let us consider LHL,
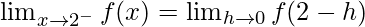
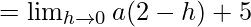
= 2a + 5
Now, let us consider RHL,
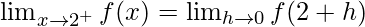

From eq(i), we get
2a + 5 = 1
⇒ a = -2
Question 24. Prove that the function
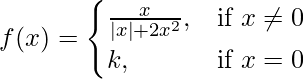 remains discontinuous at x = 0, regardless the choice of k.
remains discontinuous at x = 0, regardless the choice of k.
Solution:
Given that,
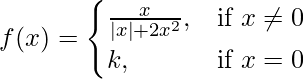
We have, at x = 0
Let us consider LHL,
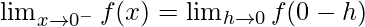
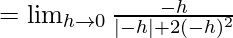
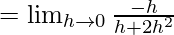
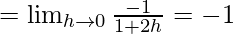
f(0) = k
Now, let us consider RHL,
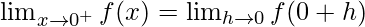
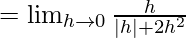
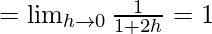
Since, LHL ≠ RHL,
Therefore, f(x) will remain discontinuous at x = 0, regardless the value of k.
Question 25. Find the value of k if f(x) is continuous at x = π/2, where
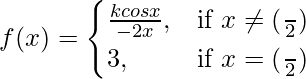
Solution:
Given that,
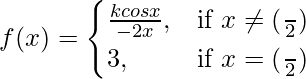
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = π/2
LHL = RHL
⇒ 
⇒ 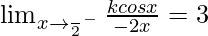
⇒ 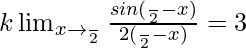
⇒ 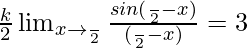
⇒ k/2 = 3
⇒ k = 6
Question 26. Determine the values of a, b, c for which the function
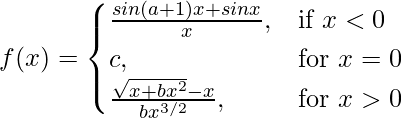
is continuous at x = 0.
Solution:
Given that,
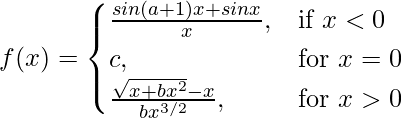
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 0
So, LHL = RHL = f(0) …..(i)
f(0) = 0
Let us consider LHL,
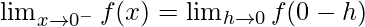
= 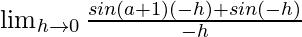
= 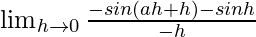
= 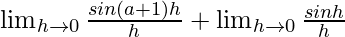
= a + 1 + 1 = a + 2
Now, let us consider RHL,
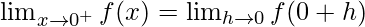
= 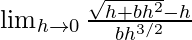
= 
= 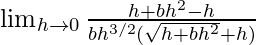
= 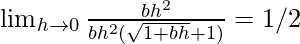
From eq(i), we get
a + 2 = 1/2 ⇒ a = -3/2
c = 1/2 and b ∈ R -{0}
Hence, a = -3/2, b ∈ R -{0}, c =1/2
Question 27. If 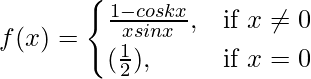 is continuous at x = 0, find k.
is continuous at x = 0, find k.
Solution:
Given that,
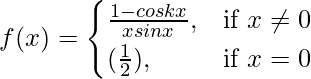
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 0
So, LHL = RHL = f(0) …….(i)
f(0) = 1/2
Let us consider LHL,
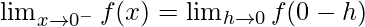
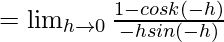
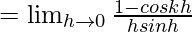
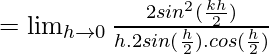
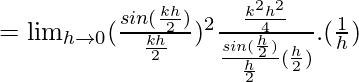
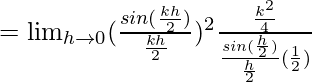
= k2/2
Using eq(i) we get,
k2/2 = 1/2 ⇒ k = ±1
Question 28. If 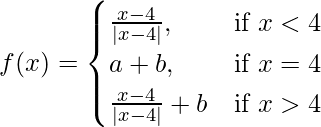 continuous at x = 4, find a, b.
continuous at x = 4, find a, b.
Solution:
Given that,
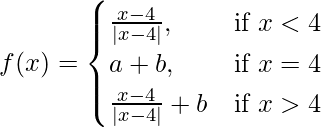
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 4
So, LHL = RHL = f(4) ……(i)
f(4) = a + b …..(ii)
Let us consider LHL,
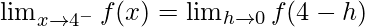
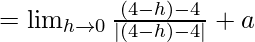
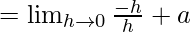
= a – 1 ……(iii)
Now, let us consider RHL,
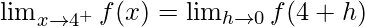
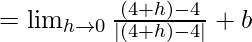
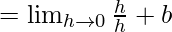
= b + 1 ……(iv)
From eq(i), we get
a – 1 = b + 1 ⇒ a – b = 2 …..(v)
From eq(ii) and eq(iii), we get
a + b = a – 1 ⇒ a – b = -1
From eq(ii) and (iv), we get
a + b = b + 1 ⇒ a = 1
Thus, a = 1 and b = -1
Question 29. For what value of k is the function
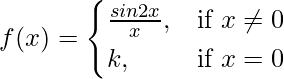 continuous at x = 0 ?
continuous at x = 0 ?
Solution:
Given that,
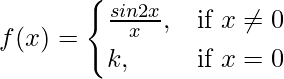
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 0
So, LHL = RHL = f(0) …..(i)
f(0) = k
Let us consider LHL,
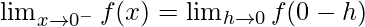

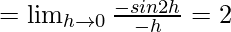
Using eq(i), we get
k = 2
Question 30. Let f(x) = 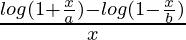 , x ≠ 0. Find the value of f at x = 0 so that f becomes continuous at x = 0.
, x ≠ 0. Find the value of f at x = 0 so that f becomes continuous at x = 0.
Solution:
Given that,
f(x) = 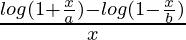
Also, f(x) is continuous at x = 0
So, LHL=RHL=f(0) ….(i)
Let us consider LHL,
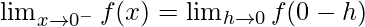
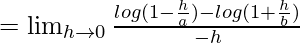
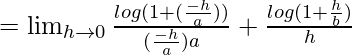
= 1/a + 1/b = (a + b)/ab
From eq(i), we get
f(0) = (a + b)/ab
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...