Prove the following identities:
Question 16. cos2 (π/4 – x) – sin2 (π/4 – x) = sin 2x
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= cos2 (π/4 – x) – sin2(π/4 – x)
As we know that,
cos2 A – sin2 A = cos 2A
So,
= cos2 (π/4 – x) sin2 (π/4 – x)
= cos 2 (π/4 – x)
= cos (π/2 – 2x)
= sin 2x [As we know that, cos (π/2 – A) = sin A]
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved.
Question 17. cos 4x = 1 – 8 cos2x + 8 cos4 x
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= cos 4x
As we know that,
cos 2x = 2 cos2x – 1
So,
cos 4x = 2 cos2 2x – 1
= 2(2 cos2 2x – 1)2 – 1
= 2[(2 cos2 2x)2 + 12 – 2 × 2 cos2x] – 1
= 2(4 cos4 2x + 1 – 4 cos2x) – 1
= 8 cos4 2x + 2 – 8 cos2 x – 1
= 8 cos4 2x + 1 – 8 cos2x
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved.
Question 18. sin 4x = 4 sin x cos3 x – 4 cos x sin3 x
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= sin 4x
As we know that,
sin 2x = 2 sin x cos x
cos 2x = cos2x – sin2x
So,
sin 4x = 2 sin 2x cos 2x
= 2 (2 sin x cos x) (cos2 x – sin2 x)
= 4 sin x cos x (cos2 x – sin2 x)
= 4 sin x cos3 x – 4 sin3 x cos x
LHS = RHS
Hence proved.
Question 19. 3(sin x – cos x)4 + 6 (sin x + cos x)2 + 4 (sin6 x + cos6 x) = 13
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= 3(sin x – cos x)4 + 6 (sin x + cos x)2 + 4 (sin6 x + cos6 x)
As we know that,
(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
(a – b)2 = a2 + b2 – 2ab
a3 + b3 = (a+b)(a2 + b2 – ab)
So,
= 3{(sinx – cosx)2}2 + 6 {(sinx)2 + (cosx)2 + 2 sinx cosx} + 4 {(sin2x)3 + (cos2x)3}
= 3{(sinx)2 + (cosx)2 – 2 sinx cosx}2 + 6(sin2x + cos2x + 2 sinx cosx) + 4{(sin2x + cos2x)(sin4x + cos4x – sin2x cos2x)}
= 3(1 – 2 sinx cosx)2 + 6(1 + 2 sinx cosx) + 4{(1)(sin4x + cos4x – sini2x cos2x)}
Since,
sin2x + cos2x = 1
So,
= 3{12 + (2 sinx cosx)2 – 4 sinx cosx} + 6(1 + 2 sinx cosx) + 4{(sin2x)2 + (cos2x)2 + 2 sin2x cos2x – 3 sin2x cos2x}
= 3{1 + 4 sin2x cos2x – 4 sinx cosx} + 6(1 + 2 sinx cosx) + 4{(sin2x + cos2x)2 – 3 sin2x cos2x}
= 3 + 12 sin2x cos2x – 12 sinx cosx + 6 + 12 sinx cosx + 4{(1)2 – 3 sin2x cos2x}
= 9 + 12 sin2x cos2x + 4(1 – 3 sin2x cos2x)
= 9 + 12 sin2x cos2x + 4 – 12 sin2x cos2x
= 13
LHS = RHS
Hence proved.
Question 20. 2(sin6x + cos6x) – 3(sin4x + cos4x) + 1 = 0
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= 2(sin6 x + cos6 x) – 3(sin4 x + cos4 x) + 1
As we know that,
(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
a3 + b3 = (a + b) (a2 + b2 – ab)
So,
= 2(sin6x + cos6x) – 3(sin4x + cos4x) + 1
= 2{(sin2x)3 + (cos2x)3} – 3{(sin2x)2 + (cos2x)2} + 1
= 2((sin2x + cos2x)(sin4x + cos4x – sin2x cos2x) – 3{(sin2x)2 + (cos2x)2 + 2 sin2x cos2x – 2sin2x cos2x} + 1
= 2{(1)(sin4x + cos4x + 2 sin2x cos2x – 3 sin2x cos2x) – 3((sin2x + cos2x)2 – 2sin2x cos2x) + 1
Since
sin2x + cos2x = 1
So,
= 2{(sin2x + cos2x)2 – 3 sin2x cos2x} – 3{(1)2 – 2 sin2x cos2x} + 1
= 2{(1)2 – 3 sin2x cos2x} – 3(1 – 2 sin2x cos2x) + 1
= 2(1 – 3 sin2x cos2x) – 3 + 6 sin2x cos2x + 1
= 2 – 6 sin2x cos2x – 2 + 6 sin2x cos2x
= 0
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved.
Question 21. cos6 x – sin6 x = cos 2x (1 – 1/4 sin2 2x)
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= cos6 x – sin6 x
As we know that,
(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab
a3 – b3 = (a – b) (a2 + b2 + ab)
So,
cos6 x – sin6 x = (cos2 x)3 – (sin2 x)3
= (cos2x – sin2x) (cos4x + sin4x + cos2x sin2x)
As we know that,
cos 2x = cos2x – sin2x
So,
= cos 2x [(cos2x)2 + (sin2x)2 + 2 cos2x sin2x – cos2x sin2x]
= cos 2x [(cos2x)2 + (sin2x)2 – 1/4 × 4 cos2x sin2x]
As we know that,
sin2x + cos2x = 1
So,
= cos2x [(1)2 – 1/4 × (2 cosx sinx)2]
As we know that,
sin2x = 2 sinx cosx
So,
= cos 2x [1 – 1/4 × (sin 2x)2]
= cos 2x [1 – 1/4 × sin22x]
LHS = RHS
Hence proved.
Question 22. tan (π/4 + x) + tan (π/4 – x) = 2 sec2x
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= tan (π/4 + x) + tan (π/4 – x)
As we know that,
tan (A + B) = (tan A + tan B)/(1 – tan A tan B)
tan (A – B) = (tan A – tan B)/(1 + tan A tan B)
So,
= 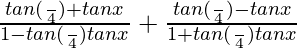
Since, tan π/4 = 1
So,
= 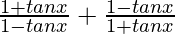
= 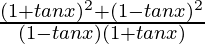
By using formulas, we get
(a – b)(a + b) = a2 – b2
(a + b)2 = a2 + b2 + 2ab & (a – b)2 = a2+ b2 – 2ab
So,
= 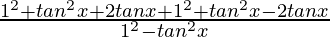
= 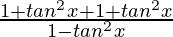
= 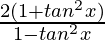
As we know that,
tan x = sin x/cos x
So,
= 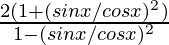
= 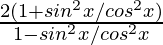
= 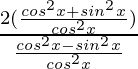
By using the formulas, we get
cos2x+ sin2x = 1 & cos 2x = cos2x – sin2x
So,
= 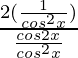
= 2/cos2x
= 2 sec2x
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved.
Question 23. cot2x – tan2x = 4cot2x cosec2x
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= cot2x – tan2x
= cos2x/sin2x – sin2x/cos2x
= [(cos2x)2 – (sin2x)2] / sin2xcos2x
= [(cos2x + sin2x)(cos2x – sin2x)] / sin2xcos2x
= (1 × cos2x) / sin2xcos2x
= 4cos2x / 4sin2xcos2x
= 4(cos2x) / (sin2x)2
= 4(cos2x) / (sin2x) × 1 / (sin2x)
= 4 cot2x cosex2x
LHS = RHS
Hence Proved
Question 24. cos4x – cos4α = 8(cosx – cosα)(cosx + cosα)(cosx – sinα)(cosx + sinα)
Solution:
Let us solve RHS,
= 8(cosx – cosα)(cosx + cosα)(cosx – sinα)(cosx + sinα)
= 8(cos2x – cos2α)(cos2x – sin2α)
= 8(cos4x – cos2x × sin2α – cos2α × cos2x + cos2α × sin2α)
= 8{cos4x – cos2x(sin2α + cos2α) + cos2α × sin2α}
= 8{cos4x – cos2x + cos2α × (1 – cos2α)}
= 8{cos4x – cos2x + cos2α – cos4α)}
= 8{cos2x(cos2x – 1) + cos2α × (1 – cos2α)}
= 8{1/2 cos2x (2cos2x – 1 – 1) – 1/2 cos2α (2cos2α – 1 -1)}
= 8{1/2 cos2x (cos2x – 1) – 1/2cos2α (cos2α – 1)}
= 8[1/4 {2cos2x (cos2x – 1) – 2cos2x (cos2α – 1)}]
= 8[1/4 {(1 + cos2x)(cos2x – 1) – (1 + cos2α)(cos2α – 1)}]
= 8[1/4 { cos22x – 1 – cos22α + 1}]
= 8[1/8 {2cos22x – 2cos22α}]
= [{(1 + cos4x) – (1 + cos4α)}]
= [1 + cos4x – 1 – cos4α]
= cos4x – cos4α
LHS = RHS
Hence proved
Question 25. sin3x + sin2x – sinx = 4 sinx cos(x/2) cos(3x/2)
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
= sin3x + sin2x – sinx
= sin3x + 2sin(2x – x)/2 cos(2x + x)/2
= sin3x + 2sin(x/2) cos(3x/2)
= 2sin(3x/2) cos(3x/2) + 2sin(3x/2) cos(x/2)
= 2cos(3x/2)[sin(3x/2) cos(x/2)]
= 2cos(3x/2)[2sin(3x/2+x/2)/2 cos(3x/2 – x/2)/2]
= 2cos(3x/2)[2sinx cos(x/2)]
= 4 sinx cos(x/2) cos(3x/2)
LHS = RHS
Hence proved.
Question 26. 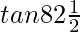 = (√3 + √2)(√2 + 1) = √2 + √3 + √4 + √6
= (√3 + √2)(√2 + 1) = √2 + √3 + √4 + √6
Solution:
Let us solve LHS,
tan(82.5)° = tan(90 – 7.5)° = cot(7.5)° = 1/ tan(7.5)°
We have,
tan(x/2) = sinx/(1 + cosx)
Now on putting x = 15°, we get
tan(15/2) = sin15°/(1 + cos15°)
= sin(45-30)°/{1 + cos(45-30)°}
= (sin45°cos30° – sin30°cos45°) / (1 + cos45° sin30°)
= 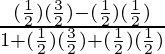
= 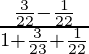
= 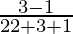
Now,
tan(82.5)° = 1/tan(7.5)°
= (2√2 + √3 + 1)/(√3 – 1)
= (2√2 + √3 + 1)/(√3 – 1) × (√3 + 1)/(√3 + 1)
= [√3 + 1(2√2 + √3 + 1)] / [(√3)2 – 12]
= (2√6 + 3 + √3 + 2√2 + √3 + 1) / (3 – 1)
= (2√6 + 2√3 + 2√2 + 4) / (2)
= √6 + √3 + √2 + 2
= √2 + √3 + √4 + √6 …..(i)
= √6 + √3 + 2 + √2
= √3(√2 + 1) + √2(√2 + 1)
= (√3 + √2)(√2 + 1) …..(ii)
From equ (i) and (ii), we get
tan(82.5)° = (√3 + √2)(√2 + 1) = √2 + √3 + √4 + √6
LHS = RHS
Hence proved
Question 27. 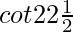 = √2 + 1
= √2 + 1
Solution:
As we know that, π/8 = 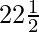 = 45°
= 45°
Let A = 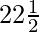
By using the identity cot2A = (cot2A – 1)/2cotA, we get
cot45° = {cot2(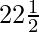 )° – 1} / 2cot(
)° – 1} / 2cot(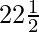 )°
)°
⇒ 1 = {cot2(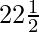 )° – 1} / 2cot(
)° – 1} / 2cot(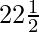 )°
)°
⇒ 2cot(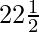 )° – cot2(
)° – cot2(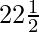 )° + 1 = 0
)° + 1 = 0
⇒ cot2(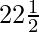 )° – 2cot(
)° – 2cot(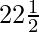 )° – 1 = 0
)° – 1 = 0
⇒ { cot2(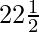 ) – 2cot(
) – 2cot(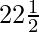 )° + 1} – 2 = 0
)° + 1} – 2 = 0
⇒ { cot(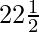 )° – 1}2 = 2
)° – 1}2 = 2
⇒ cot(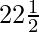 )° – 1 = √2
)° – 1 = √2
⇒ cot(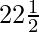 )° = √2 + 1
)° = √2 + 1
LHS = RHS
Hence proved
Question 28 (i). If cosx = (-3/5) and x lies in the 3rd quadrant, find the values of cos(x/2), sin(x/2), sin2x.
Solution:
Given that,
cosx = (-3/5)
⇒ cosx = cos2(x/2) – sin2(x/2)
⇒ -3/5 = 2cos2(x/2) – 1
⇒ 1 – 3/5 = 2cos2(x/2)
⇒ 2/5 = 2cos2(x/2)
⇒ 1/5 = cos2(x/2)
⇒ cos(x/2) = ± √(1/5)
Also, given that x lies in 3rd quadrant, so x/2 lies in 2nd quadrant.
cos(x/2) = – √(1/5)
Again,
cosx = cos2(x/2) – sin2(x/2)
⇒ -3/5 = (- √(1/5))2 – sin2(x/2)
⇒ – 3/5 = 1/5 – sin2(x/2)
⇒ -1/5 -3/5 = -sin2(x/2)
⇒ 4/5 = sin2(x/2)
⇒ sin(x/2) = ± 2/√5
It is given x lies in 3rd quadrant, so x/2 lies in 2nd quadrant.
sin(x/2) = 2/√5
Now,
sinx = √(1 – cos2x)
= √(1 – (-3/5))2
= √(1 – 9/25)
= ± 4/5
It is given x lies in 3rd quadrant, so sinx is negative.
sinx = – 4/5
sin2x = 2 sinx cosx
= 2 (-4/5) (-3/5)
= 24/25
Hence, the value of cos(x/2) = – √(1/5), sin(x/2) = 2/√5, and sin2x = 24/25.
Question 28 (ii). If cosx = (-3/5) and x lies in the 3rd quadrant, find the values of sin2x and sin(x/2).
Solution:
Given that,
cosx = (-3/5)
sinx = 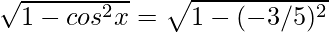
⇒ sinx = ± 4/5
Here, x lies in the second quadrant
So, sinx = 4/5
As we know that,
sin2x = 2 sinx cosx
sin2x = 2 × 4/5 × (-3/5) = (-24/25)
Now,
cosx = 1 – 2 sin2(x/2)
⇒ 2sin2(x/2) = 1 – (-3/5) = 8/5
⇒ sinx2(x/2) = 4/5
⇒ sin(x/2) = ± 2/√5
Since x lies in the second quadrant,
x/2 lies in the first quadrant
So, sin(x/2) = 2/√5
Hence, the value of sin2x = (-24/25) and sin(x/2) = 2/√5
Question 29. If sinx = √5/3 and x lies in 2nd quadrant, find the values of cos(x/2), sin(x/2) and tan(x/2).
Solution:
Given that, sinx = √5/3
As we know that sinx = P/H
So, P = √5, H = 3 and B = 2
Now, cosx = B/H = -2/3
So,
cos(x/2) = √{(1 + cosx)/2} = √{(1 – 2/3)/2} = 1/√6
sin(x/2) = √{(1 – cosx)/2} = √{(1 + 2/3)/2} = √(5/6)
tan(x/2) = sin(x/2)/cos(x/2) = {√(5/6)} / (1/√6) = √5
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...