Class 11 RD Sharma Solutions – Chapter 23 The Straight Lines- Exercise 23.10 | Set 2
Last Updated :
17 Feb, 2022
Question 11. Find the orthocenter of the triangle the equations of whose sides are x + y = 1, 2x + 3y = 6, and 4x – y + 4 = 0.
Solution:
Let us considered ABC is a triangle, in which A, B, and C are the vertices of the triangle
So according to the question the equations of the sides of the triangle are:
AB = x + y = 1 …..(1)
BC = 2x + 3y = 6 …..(2)
AC = 4x – y + 4 …..(3)
On solving eq (1) and (2), we get point B(-3, 4)
On solving eq (1) and (3), we get point A(-3/5, 8/5)
Now the altitude from A to BC is
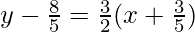
10y – 16 = 151x + 9
15x – 10y + 25 = 0
3x – 2y + 5 = 0 …..(4)
Similarly, the altitude form B to AC given by
y – 4 = -1/4(x + 3)
4y – 16 = -x -3
4y – 16 = -x – 3
x + 4 – 13 = 0 …..(5)
On solving eq(4) and (5) we get
orthocenter of the triangle i.e., O(3/7, 22/7)
Question 12. The sides AB, BC, and CA of a triangle ABC are 5x – 3y + 2 = 0, x – 3y – 2 = 0, and x + y – 6 = 0 respectively. Find the equation of the altitude through the vertex A.
Solution:
According to the question
ABC is a triangle in which the equations of the sides are:
AB = 5x – 3y + 2 = 0
BC = x – 3y – 2 = 0
CA = x + y – 6 = 0
On solving the above equations of AB, BC and CA we get
the coordinates of the vertices of the triangle ABC
B = (-1, -1)
A = (2, 4)
C = (5, 1)
Now the slope of BC = 1/3 then slope of AE = -3
Slope of AC = -1 then the slope of BD = 1
Slope of AB = 5/3 then the slope of CF = -3/5
Let us assume AD, BE, CF are altitudes of ∆ABC
So, the equation are
BD = y + 1 = 1(x + 1) ⇒ x – y = 0
AE = y – 4 = -3(x – 2) ⇒ 3x + y = 10
CF = y – 1 = 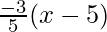 ⇒ 3x + 5y = 20
⇒ 3x + 5y = 20
Hence, the equation of the altitude through the vertex A is 3x + y = 10
Question 13. Find the coordinates of the orthocenter of the triangle whose vertices are (-1, 3), (2, -1), and (0, 0).
Solution:
Let us considered ABC is a triangle whose vertices are A(-1, 3), B(2, -1), and D(0, 0).
Here, AD ⊥ BC, CF ⊥ AB, and BE ⊥ AC
Let us assume O be the orthocenter of triangle
So, O(h, k)
Now, AO⊥BC
(slope of AO) * (slope of BC) = -1
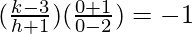
k – 3 = 2(h + 1)
k – 2h = 5 …..(1)
And BO ⊥ AC
(slope of BO) * (slope of AC) = -1
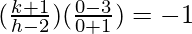
3(k + 1) = h – 2
3k – h = -5 …..(2)
Now from eq(1) and (2), we get the orthocenter O of triangle is (-4,-3)
Question 14. Find the coordinates of the incentre and centroid of the triangle whose sides have the equations 3x – 4y = 0, 12y + 5x = 0 and y – 15 = 0.
Solution:
Let us considered ABC be the triangle whose sides BC, CA, and AB have the equations
BC = y – 15 = 0
AC = 3x – 4y = 0
AB = 5x + 12y = 0
On solving the above equations we get
A(0, 0), B(-36, 15), C(20, 15)
Now the centroid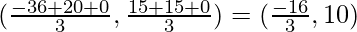
For incentre, we have
a = BC = 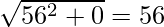
b = CA = 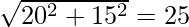
c = AB = 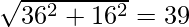
Now the coordinates of incentre are
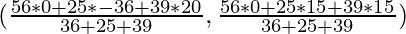
= (-1, 8)
Question 15. Prove that the lines√3x + y = 0, √3y + x = 0, √3x + y = 1 and √3y + x = 1 form a rhombus.
Solution:
Let us considered ABCD be a quadrilateral with sides AB, BC, CD, BA as
√3x + y = 0, √3y + x = 0, √3x + y = 1 and √3y + x = 1
So, the slope of AB = -√3 …..(1)
The slope of BC = -1/√3 …..(2)
The slope of CD = -√3 …..(3)
The slope of DA = -1/√3 …..(4)
From eq (1), (2), (3) and (4) we conclude that the slope opposite sides of quadrilateral are equal.
So, the opposite sides are parallel.
Hence, ABCD is a parallelogram.
We also conclude that the distance between (AD and BC) and (DC and AB) is equal =1 unit
So, sides AD = AB = DC
Hence, the ABCD is a rhombus
Hence, proved
Question 16. Find the equation of line passing through the intersection of the lines 3x + y = 5 and x + 3y + 8 = 0 and parallel to the line 3x + 4y = 7.
Solution:
Given that the equations of lines are:
2x + y = 5
x + 3y + 8 = 0
On solve the above equations we get the
intersection point(23/5, -12/5)
It is given that the line is parallel to 3x + 4y = 7 and passing through above point(23/5, -12/5)
So the equation of line is
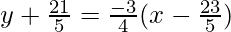
20y + 84 = -15x + 69
15x + 20y + 15 = 0
3x + 4y + 3 = 0
Question 17. Find the equation of the line passing through the point of intersection of the lines 5x – 6y – 1 = 0 and perpendicular to the line 3x – 5y + 11 = 0.
Solution:
Given that the equations of lines are:
5x – 6y – 1 = 0
2y + 5 = 0
On solve the above equations we get the
intersection point(-1, 1)
It is given that the line is perpendicular to 3x – 5y + 11 = 0 and passing through above point(-1, 1)
So, the equation of line is
(y + 1) = -5/3(x + 1)
3y + 5x + 8 = 0
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...