What are Widgets in Tkinter?
Last Updated :
19 Oct, 2022
Tkinter is Python’s standard GUI (Graphical User Interface) package. tkinter provides us with a variety of common GUI elements which we can use to build out interface – such as buttons, menus and various kind of entry fields and display areas. We call these elements Widgets.
Widgets
In general, Widget is an element of Graphical User Interface (GUI) that displays/illustrates information or gives a way for the user to interact with the OS. In Tkinter , Widgets are objects ; instances of classes that represent buttons, frames, and so on.
Each separate widget is a Python object. When creating a widget, you must pass its parent as a parameter to the widget creation function. The only exception is the “root” window, which is the top-level window that will contain everything else and it does not have a parent.
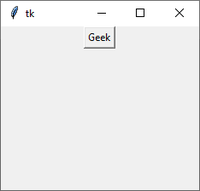
Example :
Python
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
frame = Frame(root)
frame.pack()
button = Button(frame, text ='Geek')
button.pack()
root.mainloop()
|
Output :
Widget Classes
Tkinter supports the below mentioned core widgets –
| Widgets |
Description |
| Label |
It is used to display text or image on the screen |
| Button |
It is used to add buttons to your application |
| Canvas |
It is used to draw pictures and others layouts like texts, graphics etc. |
| ComboBox |
It contains a down arrow to select from list of available options |
| CheckButton |
It displays a number of options to the user as toggle buttons from which user can select any number of options. |
| Radio Button |
It is used to implement one-of-many selection as it allows only one option to be selected |
| Entry |
It is used to input single line text entry from user |
| Frame |
It is used as container to hold and organize the widgets |
| Message |
It works same as that of label and refers to multi-line and non-editable text |
| Scale |
It is used to provide a graphical slider which allows to select any value from that scale |
| Scrollbar |
It is used to scroll down the contents. It provides a slide controller. |
| SpinBox |
It is allows user to select from given set of values |
| Text |
It allows user to edit multiline text and format the way it has to be displayed |
| Menu |
It is used to create all kinds of menu used by an application |
Geometry Management
Creating a new widget doesn’t mean that it will appear on the screen. To display it, we need to call a special method: either grid, pack(example above), or place.
| Method |
Description |
| pack() |
The Pack geometry manager packs widgets in rows or columns. |
| grid() |
The Grid geometry manager puts the widgets in a 2-dimensional table.
The master widget is split into a number of rows and columns, and each “cell” in the resulting table can hold a widget. |
| place() |
The Place geometry manager is the simplest of the three general geometry managers provided in Tkinter.
It allows you explicitly set the position and size of a window, either in absolute terms, or relative to another window. |
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...