Python Tkinter – Toplevel Widget
Last Updated :
11 Aug, 2021
Tkinter is a GUI toolkit used in python to make user-friendly GUIs.Tkinter is the most commonly used and the most basic GUI framework available in Python. Tkinter uses an object-oriented approach to make GUIs.
Note: For more information, refer to Python GUI – tkinter
Toplevel widget
A Toplevel widget is used to create a window on top of all other windows. The Toplevel widget is used to provide some extra information to the user and also when our program deals with more than one application. These windows are directly organized and managed by the Window Manager and do not need to have any parent window associated with them every time.
Syntax:
toplevel = Toplevel(root, bg, fg, bd, height, width, font, ..)
Optional parameters
- root = root window(optional)
- bg = background colour
- fg = foreground colour
- bd = border
- height = height of the widget.
- width = width of the widget.
- font = Font type of the text.
- cursor = cursor that appears on the widget which can be an arrow, a dot etc.
Common methods
- iconify turns the windows into icon.
- deiconify turns back the icon into window.
- state returns the current state of window.
- withdraw removes the window from the screen.
- title defines title for window.
- frame returns a window identifier which is system specific.
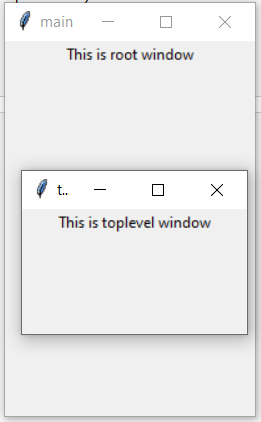
Example 1:
Python3
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.geometry("200x300")
root.title("main")
l = Label(root, text = "This is root window")
top = Toplevel()
top.geometry("180x100")
top.title("toplevel")
l2 = Label(top, text = "This is toplevel window")
l.pack()
l2.pack()
top.mainloop()
|
Output
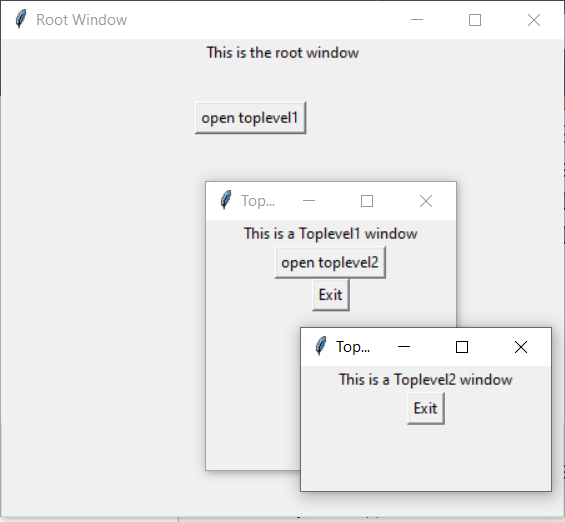
Example 2: Creating Multiple toplevels over one another
Python3
from tkinter import *
root = Tk()
root.title("Root Window")
root.geometry("450x300")
label1 = Label(root, text = "This is the root window")
def open_Toplevel2():
top2 = Toplevel()
top2.title("Toplevel2")
top2.geometry("200x100")
label = Label(top2,
text = "This is a Toplevel2 window")
button = Button(top2, text = "Exit",
command = top2.destroy)
label.pack()
button.pack()
top2.mainloop()
def open_Toplevel1():
top1 = Toplevel(root)
top1.title("Toplevel1")
top1.geometry("200x200")
label = Label(top1,
text = "This is a Toplevel1 window")
button1 = Button(top1, text = "Exit",
command = top1.destroy)
button2 = Button(top1, text = "open toplevel2",
command = open_Toplevel2)
label.pack()
button2.pack()
button1.pack()
top1.mainloop()
button = Button(root, text = "open toplevel1",
command = open_Toplevel1)
label1.pack()
button.place(x = 155, y = 50)
root.mainloop()
|
Output
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...