Split Pandas Dataframe by Rows
Last Updated :
30 Nov, 2023
In this article, we will explore the process of Split Pandas Dataframe by Rows. The Pandas DataFrame serves as the focal point, and throughout this discussion, we will experiment with various methods to Split Pandas Dataframe by Rows.
Split Pandas DataFrame by Rows
In this article, we will elucidate several commonly employed methods for Split Pandas Dataframe by Rows. These methods are widely utilized for the purpose of dividing a Pandas DataFrame, and we will discuss the which are following:
- Using Row Index
- In Groups From Unique Column Values
- Using Predetermined-Sized Chunks
- By Shuffling Rows
Consider a dataset: To illustrate, let’s consider a dataset featuring information about diamonds.
Python3
import seaborn as sns
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
df = sns.load_dataset('diamonds')
df.head()
|
Output
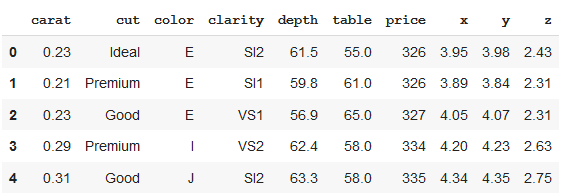
Splitting Pandas Dataframe by row index
In the below code, the dataframe is divided into two parts, first 1000 rows, and remaining rows. We can see the shape of the newly formed dataframes as the output of the given code.
Python3
df_1 = df.iloc[:1000,:]
df_2 = df.iloc[1000:,:]
print("Shape of new dataframes - {} , {}".format(df_1.shape, df_2.shape))
|
Output

Splitting Pandas Dataframe by groups formed from unique column values
Here, we will first grouped the data by column value “color”. The newly formed dataframe consists of grouped data with color = “E”.
Python3
grouped = df.groupby(df.color)
df_new = grouped.get_group("E")
df_new
|
Output
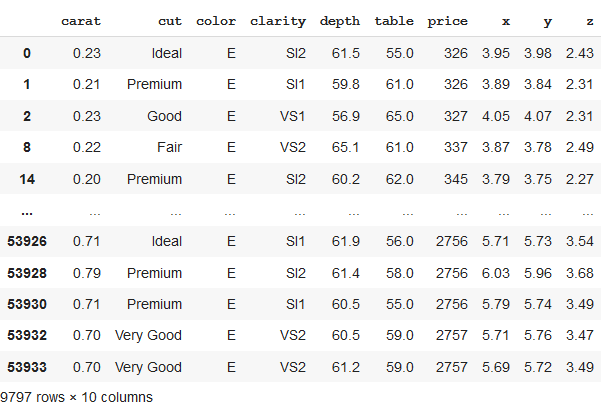
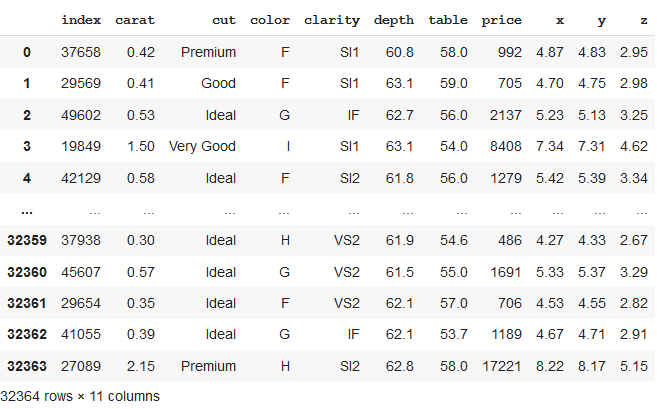
Splitting Pandas Dataframe in predetermined sized chunks
In the above code, we can see that we have formed a new dataset of a size of 0.6 i.e. 60% of total rows (or length of the dataset), which now consists of 32364 rows. These rows are selected randomly.
Python3
df_split = df.sample(frac=0.6,random_state=200)
df_split.reset_index()
|
Output
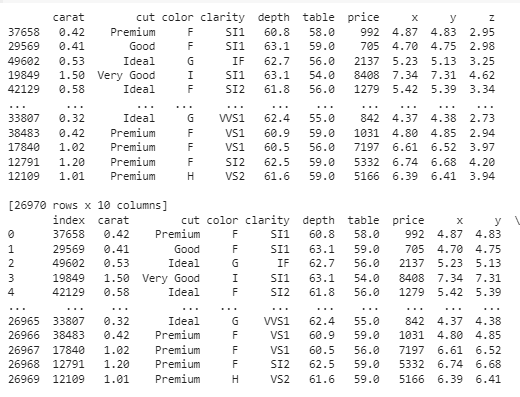
Split Pandas Dataframe by Shuffling Rows in Pandas DataFrame
In the below code , code randomly selects 50% of rows from DataFrame df into a new DataFrame df1. It then prints df1 and its index-reset version using reset_index().
Python3
df1 = df.sample(frac = 0.5, random_state = 200)
print(df1)
print(df1.reset_index())
|
Output
Conclusion
In summary, splitting Pandas DataFrames by rows offers a flexible way to organize and analyze data, allowing exploration of subsets through methods like random sampling or predetermined chunk sizes. This capability is valuable for tasks such as training machine learning models, exploratory data analysis, and efficient data processing, enhancing data manipulation in the field of data science.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...