Find the value of m and c such that a straight line y = mx + c, best represents the equation of a given set of points (x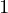 , y
, y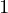 ), (x
), (x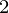 , y
, y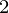 ), (x
), (x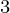 , y
, y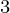 ), ……., (x
), ……., (x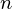 , y
, y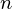 ), given n >=2.
), given n >=2.
Examples:
Input : n = 5
x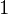 = 1, x
= 1, x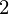 = 2, x
= 2, x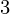 = 3, x
= 3, x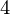 = 4, x
= 4, x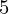 = 5y
= 5y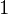 = 14, y
= 14, y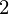 = 27, y
= 27, y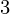 = 40, y
= 40, y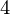 = 55, y
= 55, y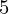 = 68 Output : m = 13.6c = 0 If we take any pair of number ( x
= 68 Output : m = 13.6c = 0 If we take any pair of number ( x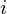 , y
, y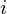 ) from the given data, these value of m and cshould make it best fit into the equation for a straight line, y = mx + c. Take x
) from the given data, these value of m and cshould make it best fit into the equation for a straight line, y = mx + c. Take x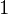 = 1 and y
= 1 and y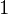 = 14, then using valuesof m and c from the output, and putting it in the following equation,y = mx + c,L.H.S.: y = 14, R.H.S: mx + c = 13.6 x 1 + 0 = 13.6So, they are approximately equal.Now, take x
= 14, then using valuesof m and c from the output, and putting it in the following equation,y = mx + c,L.H.S.: y = 14, R.H.S: mx + c = 13.6 x 1 + 0 = 13.6So, they are approximately equal.Now, take x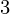 = 3 and y
= 3 and y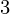 = 40,L.H.S.: y = 40, R.H.S: mx + c = 13.6 x 3 + 0 = 40.8So, they are also approximately equal, and so onfor all other values.Input : n = 6x
= 40,L.H.S.: y = 40, R.H.S: mx + c = 13.6 x 3 + 0 = 40.8So, they are also approximately equal, and so onfor all other values.Input : n = 6x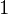 = 1, x
= 1, x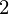 = 2, x
= 2, x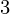 = 3, x
= 3, x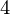 = 4, x
= 4, x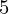 = 5, x
= 5, x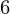 = 6y
= 6y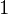 = 1200, y
= 1200, y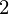 = 900, y
= 900, y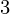 = 600, y
= 600, y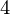 = 200, y
= 200, y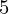 = 110, y
= 110, y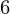 = 50Output : m = -243.42c = 1361.97
= 50Output : m = -243.42c = 1361.97
Approach
To best fit a set of points in an equation for a straight line, we need to find the value of two variables, m and c. Now, since there are 2 unknown variables and depending upon the value of n, two cases are possible –
Case 1 – When n = 2 : There will be two equations and two unknown variables to find, so, there will be a unique solution .
Case 2 – When n > 2 : In this case, there may or may not exist values of m and c, which satisfy all the n equations, but we can find the best possible values of m and c which can fit a straight line in the given points .
So, if we have n different pairs of x and y, then, we can form n no. of equations from them for a straight line, as follows
f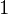 = mx
= mx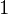 + c,f
+ c,f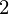 = mx
= mx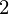 + c,f
+ c,f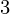 = mx
= mx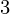 + c,......................................,......................................,f
+ c,......................................,......................................,f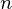 = mx
= mx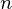 + c,where, f
+ c,where, f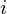 , is the value obtained by putting x
, is the value obtained by putting x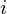 in equation mx + c.
in equation mx + c.
Then, since ideally f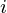 should be same as y
should be same as y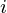 , but still we can find the f
, but still we can find the f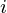 closest to y
closest to y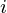 in all the cases, if we take a new quantity, U = ?(y
in all the cases, if we take a new quantity, U = ?(y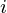 – f
– f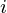 )
)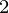 , and make this quantity minimum for all value of i from 1 to n.
, and make this quantity minimum for all value of i from 1 to n.
Note:(y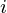 – f
– f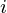 )
)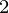 is used in place of (y
is used in place of (y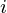 – f
– f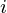 ), as we want to consider both the cases when f
), as we want to consider both the cases when f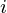 or when y
or when y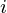 is greater, and we want their difference to be minimum, so if we would not square the term, then situations in which f
is greater, and we want their difference to be minimum, so if we would not square the term, then situations in which f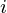
is greater and situation in which y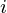 is greater will cancel each other to an extent, and this is not what we want. So, we need to square the term.
is greater will cancel each other to an extent, and this is not what we want. So, we need to square the term.
Now, for U to be minimum, it must satisfy the following two equations –
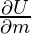 = 0 and
= 0 and  = 0.
= 0.
On solving the above two equations, we get two equations, as follows :
?y = nc + m?x, and
?xy = c?x + m?x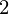 , which can be rearranged as - m = (n * ?xy - ?x?y) / (n * ?x
, which can be rearranged as - m = (n * ?xy - ?x?y) / (n * ?x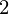 - (?x)
- (?x)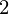 ), andc = (?y - m?x) / n,
), andc = (?y - m?x) / n,
So, this is how values of m and c for both the cases are obtained, and we can represent a given set of points, by the best possible straight line.
The following code implements the above given algorithm –
C++
#include <cmath>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
void bestApproximate(int x[], int y[], int n)
{
float m, c, sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0, sum_xy = 0, sum_x2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum_x += x[i];
sum_y += y[i];
sum_xy += x[i] * y[i];
sum_x2 += pow(x[i], 2);
}
m = (n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y) / (n * sum_x2 - pow(sum_x, 2));
c = (sum_y - m * sum_x) / n;
cout << "m =" << m;
cout << "\nc =" << c;
}
int main()
{
int x[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int y[] = { 14, 27, 40, 55, 68 };
int n = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
bestApproximate(x, y, n);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
void bestApproximate(int x[], int y[], int n)
{
int i, j;
float m, c, sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0, sum_xy = 0, sum_x2 = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum_x += x[i];
sum_y += y[i];
sum_xy += x[i] * y[i];
sum_x2 += (x[i] * x[i]);
}
m = (n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y) / (n * sum_x2 - (sum_x * sum_x));
c = (sum_y - m * sum_x) / n;
printf("m =% f", m);
printf("\nc =% f", c);
}
int main()
{
int x[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int y[] = { 14, 27, 40, 55, 68 };
int n = sizeof(x) / sizeof(x[0]);
bestApproximate(x, y, n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
import static java.lang.Math.pow;
public class A {
static void bestApproximate(int x[], int y[])
{
int n = x.length;
double m, c, sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0,
sum_xy = 0, sum_x2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum_x += x[i];
sum_y += y[i];
sum_xy += x[i] * y[i];
sum_x2 += pow(x[i], 2);
}
m = (n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y) / (n * sum_x2 - pow(sum_x, 2));
c = (sum_y - m * sum_x) / n;
System.out.println("m = " + m);
System.out.println("c = " + c);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int x[] = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int y[] = { 14, 27, 40, 55, 68 };
bestApproximate(x, y);
}
}
|
Python3
def bestApproximate(x, y, n):
sum_x = 0
sum_y = 0
sum_xy = 0
sum_x2 = 0
for i in range (0, n):
sum_x += x[i]
sum_y += y[i]
sum_xy += x[i] * y[i]
sum_x2 += pow(x[i], 2)
m = (float)((n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y)
/ (n * sum_x2 - pow(sum_x, 2)));
c = (float)(sum_y - m * sum_x) / n;
print("m = ", m);
print("c = ", c);
x = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ]
y = [ 14, 27, 40, 55, 68]
n = len(x)
bestApproximate(x, y, n)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void bestApproximate(int[] x, int[] y)
{
int n = x.Length;
double m, c, sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0,
sum_xy = 0, sum_x2 = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
sum_x += x[i];
sum_y += y[i];
sum_xy += x[i] * y[i];
sum_x2 += Math.Pow(x[i], 2);
}
m = (n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y) / (n * sum_x2 - Math.Pow(sum_x, 2));
c = (sum_y - m * sum_x) / n;
Console.WriteLine("m = " + m);
Console.WriteLine("c = " + c);
}
public static void Main()
{
int[] x = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
int[] y = { 14, 27, 40, 55, 68 };
bestApproximate(x, y);
}
}
|
PHP
<?php
function bestApproximate($x, $y, $n)
{
$i; $j;
$m; $c;
$sum_x = 0;
$sum_y = 0;
$sum_xy = 0;
$sum_x2 = 0;
for ($i = 0; $i < $n; $i++)
{
$sum_x += $x[$i];
$sum_y += $y[$i];
$sum_xy += $x[$i] * $y[$i];
$sum_x2 += ($x[$i] * $x[$i]);
}
$m = ($n * $sum_xy - $sum_x * $sum_y) /
($n * $sum_x2 - ($sum_x * $sum_x));
$c = ($sum_y - $m * $sum_x) / $n;
echo "m =", $m;
echo "\nc =", $c;
}
$x =array(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
$y =array (14, 27, 40, 55, 68);
$n = sizeof($x);
bestApproximate($x, $y, $n);
?>
|
Javascript
<script>
function bestApproximate(x, y, n)
{
let m, c, sum_x = 0, sum_y = 0,
sum_xy = 0, sum_x2 = 0;
for(let i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
sum_x += x[i];
sum_y += y[i];
sum_xy += x[i] * y[i];
sum_x2 += Math.pow(x[i], 2);
}
m = (n * sum_xy - sum_x * sum_y) /
(n * sum_x2 - Math.pow(sum_x, 2));
c = (sum_y - m * sum_x) / n;
document.write("m =" + m);
document.write("<br>c =" + c);
}
let x = [ 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 ];
let y = [ 14, 27, 40, 55, 68 ];
let n = x.length;
bestApproximate(x, y, n);
</script>
|
Output:
m=13.6
c=0.0
Analysis of above code-
Auxiliary Space : O(1)
Time Complexity : O(n). We have one loop which iterates n times, and each time it performs constant no. of computations.
Reference-
1-Higher Engineering Mathematics by B.S. Grewal.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...