Pascal’s Triangle
Last Updated :
20 Oct, 2023
Pascal’s triangle is a triangular array of binomial coefficients. Write a function that takes an integer value N as input and prints the first N lines of Pascal’s triangle.
Example:
The below image shows the Pascal’s Triangle for N=6
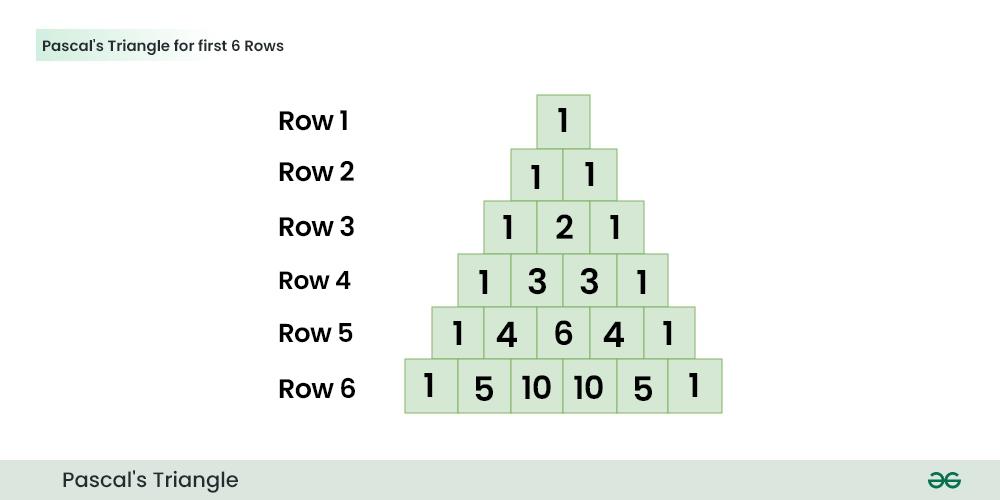
The number of entries in every line is equal to line number. For example, the first line has “1“, the second line has “1 1“, the third line has “1 2 1“,.. and so on. Every entry in a line is value of a Binomial Coefficient. The value of ith entry in line number line is C(line, i). The value can be calculated using following formula.
- C(line, i) = line! / ( (line-i)! * i! )
Algorithm:
- Run a loop for each row of pascal’s triangle i.e. 1 to N.
- For each row, run an internal loop for each element of that row.
- Calculate the binomial coefficient for the element using the formula mentioned in the approach.
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int binomialCoeff(int n, int k);
void printPascal(int n)
{
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++) {
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
cout << " " << binomialCoeff(line, i);
cout << "\n";
}
}
int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int res = 1;
if (k > n - k)
k = n - k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i) {
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n = 7;
printPascal(n);
return 0;
}
|
C
#include <stdio.h>
int binomialCoeff(int n, int k);
void printPascal(int n)
{
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
printf("%d ",
binomialCoeff(line, i));
printf("\n");
}
}
int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int res = 1;
if (k > n - k)
k = n - k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n = 7;
printPascal(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static void printPascal(int n)
{
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
System.out.print(binomialCoeff
(line, i)+" ");
System.out.println();
}
}
static int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int res = 1;
if (k > n - k)
k = n - k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int n = 7;
printPascal(n);
}
}
|
Python3
def printPascal(n) :
for line in range(0, n) :
for i in range(0, line + 1) :
print(binomialCoeff(line, i),
" ", end = "")
print()
def binomialCoeff(n, k) :
res = 1
if (k > n - k) :
k = n - k
for i in range(0 , k) :
res = res * (n - i)
res = res // (i + 1)
return res
n = 7
printPascal(n)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static void printPascal(int n)
{
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
Console.Write(binomialCoeff
(line, i)+" ");
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
static int binomialCoeff(int n, int k)
{
int res = 1;
if (k > n - k)
k = n - k;
for (int i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
public static void Main()
{
int n = 7;
printPascal(n);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function printPascal(n)
{
for (let line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (let i = 0; i <= line; i++)
document.write(binomialCoeff
(line, i)+" ");
document.write("<br />");
}
}
function binomialCoeff(n, k)
{
let res = 1;
if (k > n - k)
k = n - k;
for (let i = 0; i < k; ++i)
{
res *= (n - i);
res /= (i + 1);
}
return res;
}
let n = 7;
printPascal(n);
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function binomialCoeff($n, $k)
{
$res = 1;
if ($k > $n - $k)
$k = $n - $k;
for ($i = 0; $i < $k; ++$i)
{
$res *= ($n - $i);
$res /= ($i + 1);
}
return $res;
}
function printPascal($n)
{
for ($line = 0; $line < $n; $line++)
{
for ($i = 0; $i <= $line; $i++)
echo "".binomialCoeff($line, $i)." ";
echo "\n";
}
}
$n=7;
printPascal($n);
?>
|
Output
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
1 5 10 10 5 1
1 6 15 20 15 6 1
Time complexity: O(N^3), where N is the number of rows you want to print
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
If we take a closer at the triangle, we observe that every entry is sum of the two values above it. So using dynamic programming we can create a 2D array that stores previously generated values. In order to generate a value in a line, we can use the previously stored values from array.

Cases:
- If line == 0 or line == i
- Else:
- arr[line][i] = arr[line-1][i-1] + arr[line-1][i]
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printPascal(int n)
{
int arr[n][n];
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
{
if (line == i || i == 0)
arr[line][i] = 1;
else
arr[line][i] = arr[line - 1][i - 1] +
arr[line - 1][i];
cout << arr[line][i] << " ";
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
return 0;
}
|
C
void printPascal(int n)
{
int arr[n][n];
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
{
if (line == i || i == 0)
arr[line][i] = 1;
else
arr[line][i] = arr[line-1][i-1] + arr[line-1][i];
printf("%d ", arr[line][i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void main (String[] args) {
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
}
public static void printPascal(int n)
{
int[][] arr = new int[n][n];
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
{
if (line == i || i == 0)
arr[line][i] = 1;
else
arr[line][i] = arr[line-1][i-1] + arr[line-1][i];
System.out.print(arr[line][i]);
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
|
Python3
def printPascal(n:int):
arr = [[0 for x in range(n)]
for y in range(n)]
for line in range (0, n):
for i in range (0, line + 1):
if(i is 0 or i is line):
arr[line][i] = 1
print(arr[line][i], end = " ")
else:
arr[line][i] = (arr[line - 1][i - 1] +
arr[line - 1][i])
print(arr[line][i], end = " ")
print("\n", end = "")
n = 5
printPascal(n)
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
public static void printPascal(int n)
{
int[,] arr = new int[n, n];
for (int line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (int i = 0; i <= line; i++)
{
if (line == i || i == 0)
arr[line, i] = 1;
else
arr[line, i] = arr[line - 1, i - 1] +
arr[line - 1, i];
Console.Write(arr[line, i]);
}
Console.WriteLine("");
}
}
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
var n = 5;
printPascal(n);
function printPascal(n)
{
arr = a = Array(n).fill(0).map(x => Array(n).fill(0));
for (line = 0; line < n; line++)
{
for (i = 0; i <= line; i++)
{
if (line == i || i == 0)
arr[line][i] = 1;
else
arr[line][i] = arr[line-1][i-1] + arr[line-1][i];
document.write(arr[line][i]);
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function printPascal($n)
{
$arr = array(array());
for ($line = 0; $line < $n; $line++)
{
for ($i = 0; $i <= $line; $i++)
{
if ($line == $i || $i == 0)
$arr[$line][$i] = 1;
else
$arr[$line][$i] = $arr[$line - 1][$i - 1] +
$arr[$line - 1][$i];
echo $arr[$line][$i] . " ";
}
echo "\n";
}
}
$n = 5;
printPascal($n);
?>
|
Output
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
Time Complexity: O(N^2)
Auxiliary Space: O(N^2)
Note: This method can be optimized to use O(n) extra space as we need values only from previous row. So we can create an auxiliary array of size n and overwrite values. Following is another method uses only O(1) extra space.
Pascal’s Triangle using Binomial Coefficient (Space Optimised):
This method is based on approach using Binomial Coefficient. We know that ith entry in a line number line is Binomial Coefficient C(line, i) and all lines start with value 1. The idea is to calculate C(line, i) using C(line, i-1). It can be calculated in O(1) time.
- C(line, i) = line! / ( (line-i)! * i! )
- C(line, i-1) = line! / ( (line – i + 1)! * (i-1)! )
- We can derive following expression from above two expressions.
- C(line, i) = C(line, i-1) * (line – i + 1) / i
- So C(line, i) can be calculated from C(line, i-1) in O(1) time
below is the implementation of the approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void printPascal(int n)
{
for (int line = 1; line <= n; line++) {
int C = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= line; i++) {
cout << C << " ";
C = C * (line - i) / i;
}
cout << "\n";
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
return 0;
}
|
C
void printPascal(int n)
{
for (int line = 1; line <= n; line++)
{
int C = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= line; i++)
{
printf("%d ", C);
C = C * (line - i) / i;
}
printf("\n");
}
}
int main()
{
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
public static void printPascal(int n)
{
for(int line = 1; line <= n; line++)
{
int C=1;
for(int i = 1; i <= line; i++)
{
System.out.print(C+" ");
C = C * (line - i) / i;
}
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main (String[] args) {
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
}
}
|
Python3
def printPascal(n):
for line in range(1, n + 1):
C = 1;
for i in range(1, line + 1):
print(C, end = " ");
C = int(C * (line - i) / i);
print("");
n = 5;
printPascal(n);
|
C#
using System;
class GFG
{
public static void printPascal(int n)
{
for(int line = 1;
line <= n; line++)
{
int C = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= line; i++)
{
Console.Write(C + " ");
C = C * (line - i) / i;
}
Console.Write("\n") ;
}
}
public static void Main ()
{
int n = 5;
printPascal(n);
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function printPascal(n)
{
for(line = 1; line <= n; line++)
{
var C=1;
for(i = 1; i <= line; i++)
{
document.write(C+" ");
C = C * (line - i) / i;
}
document.write("<br>");
}
}
var n = 5;
printPascal(n);
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function printPascal($n)
{
for($line = 1; $line <= $n; $line++)
{
$C = 1;
for($i = 1; $i <= $line; $i++)
{
print($C . " ");
$C = $C * ($line - $i) / $i;
}
print("\n");
}
}
$n = 5;
printPascal($n);
?>
|
Output
1
1 1
1 2 1
1 3 3 1
1 4 6 4 1
Time Complexity: O(n2)
Auxiliary Space: O(1)
Variations of the problem that may be asked in interviews:
- Find the whole pascal triangle as shown above.
- Find just the one element of a pascal’s triangle given row number and column number in O(n) time.
- Find a particular row of pascal’s triangle given a row number in O(n) time.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...