Memory Hierarchy Design and its Characteristics
Last Updated :
19 Jun, 2023
In the Computer System Design, Memory Hierarchy is an enhancement to organize the memory such that it can minimize the access time. The Memory Hierarchy was developed based on a program behavior known as locality of references. The figure below clearly demonstrates the different levels of the memory hierarchy.
Why Memory Hierarchy is Required in the System?
Memory Hierarchy is one of the most required things in Computer Memory as it helps in optimizing the memory available in the computer. There are multiple levels present in the memory, each one having a different size, different cost, etc. Some types of memory like cache, and main memory are faster as compared to other types of memory but they are having a little less size and are also costly whereas some memory has a little higher storage value, but they are a little slower. Accessing of data is not similar in all types of memory, some have faster access whereas some have slower access.
Types of Memory Hierarchy
This Memory Hierarchy Design is divided into 2 main types:
- External Memory or Secondary Memory: Comprising of Magnetic Disk, Optical Disk, and Magnetic Tape i.e. peripheral storage devices which are accessible by the processor via an I/O Module.
- Internal Memory or Primary Memory: Comprising of Main Memory, Cache Memory & CPU registers. This is directly accessible by the processor.
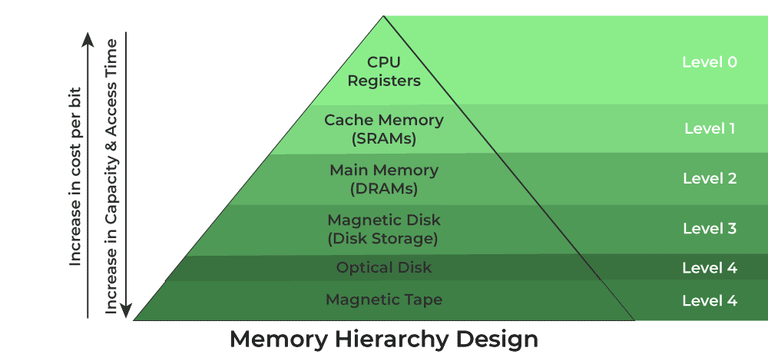
Memory Hierarchy Design
Memory Hierarchy Design
1. Registers
Registers are small, high-speed memory units located in the CPU. They are used to store the most frequently used data and instructions. Registers have the fastest access time and the smallest storage capacity, typically ranging from 16 to 64 bits.
2. Cache Memory
Cache memory is a small, fast memory unit located close to the CPU. It stores frequently used data and instructions that have been recently accessed from the main memory. Cache memory is designed to minimize the time it takes to access data by providing the CPU with quick access to frequently used data.
3. Main Memory
Main memory, also known as RAM (Random Access Memory), is the primary memory of a computer system. It has a larger storage capacity than cache memory, but it is slower. Main memory is used to store data and instructions that are currently in use by the CPU.
Types of Main Memory
- Static RAM: Static RAM stores the binary information in flip flops and information remains valid until power is supplied. It has a faster access time and is used in implementing cache memory.
- Dynamic RAM: It stores the binary information as a charge on the capacitor. It requires refreshing circuitry to maintain the charge on the capacitors after a few milliseconds. It contains more memory cells per unit area as compared to SRAM.
4. Secondary Storage
Secondary storage, such as hard disk drives (HDD) and solid-state drives (SSD), is a non-volatile memory unit that has a larger storage capacity than main memory. It is used to store data and instructions that are not currently in use by the CPU. Secondary storage has the slowest access time and is typically the least expensive type of memory in the memory hierarchy.
5. Magnetic Disk
Magnetic Disks are simply circular plates that are fabricated with either a metal or a plastic or a magnetized material. The Magnetic disks work at a high speed inside the computer and these are frequently used.
6. Magnetic Tape
Magnetic Tape is simply a magnetic recording device that is covered with a plastic film. It is generally used for the backup of data. In the case of a magnetic tape, the access time for a computer is a little slower and therefore, it requires some amount of time for accessing the strip.
Characteristics of Memory Hierarchy
- Capacity: It is the global volume of information the memory can store. As we move from top to bottom in the Hierarchy, the capacity increases.
- Access Time: It is the time interval between the read/write request and the availability of the data. As we move from top to bottom in the Hierarchy, the access time increases.
- Performance: Earlier when the computer system was designed without a Memory Hierarchy design, the speed gap increased between the CPU registers and Main Memory due to a large difference in access time. This results in lower performance of the system and thus, enhancement was required. This enhancement was made in the form of Memory Hierarchy Design because of which the performance of the system increases. One of the most significant ways to increase system performance is minimizing how far down the memory hierarchy one has to go to manipulate data.
- Cost Per Bit: As we move from bottom to top in the Hierarchy, the cost per bit increases i.e. Internal Memory is costlier than External Memory.
Advantages of Memory Hierarchy
- It helps in removing some destruction, and managing the memory in a better way.
- It helps in spreading the data all over the computer system.
- It saves the consumer’s price and time.
System-Supported Memory Standards
According to the memory Hierarchy, the system-supported memory standards are defined below:
| Level |
1 |
2 |
3 |
4 |
| Name |
Register |
Cache |
Main Memory |
Secondary Memory |
| Size |
<1 KB |
less than 16 MB |
<16GB |
>100 GB |
| Implementation |
Multi-ports |
On-chip/SRAM |
DRAM (capacitor memory) |
Magnetic |
| Access Time |
0.25ns to 0.5ns |
0.5 to 25ns |
80ns to 250ns |
50 lakh ns |
| Bandwidth |
20000 to 1 lakh MB |
5000 to 15000 |
1000 to 5000 |
20 to 150 |
| Managed by |
Compiler |
Hardware |
Operating System |
Operating System |
| Backing Mechanism |
From cache |
from Main Memory |
from Secondary Memory |
from ie |
FAQs
1. What do you mean by Memory Hierarchy?
Answer:
Memory Hierarchy can be simply illustrated as the organization of the memory for saving the access time. Because of the nicely written codes or program, memory hierarchy works well. It takes less time in accessing at the current level.
2. Explain the types of Memory Hierarchy.
Answer:
Here are the some types of the Memory Hierarchy:
- External Memory or Secondary Memory
- Internal Memory or Primary Memory
3. In DBMS, How memory Hierarchy is listed?
Answer:
In Database Management System, Memory Hierarchy can be illustrated as follows:
- CPU Registers
- Cache Memory
- Main Memory or Primary Memory
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...