Difference between RAM and ROM
Last Updated :
20 Sep, 2023
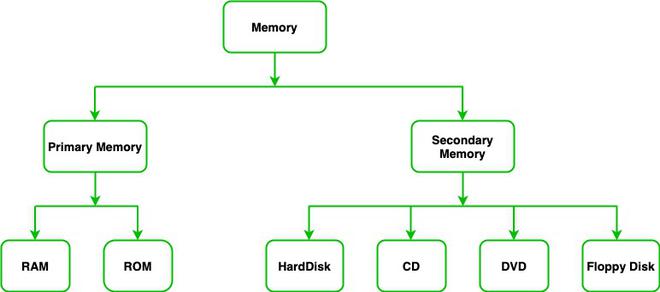
Memory is an important part of the Computer which is responsible for the storage of data and information on a temporary or permanent basis. Memory can be classified into two broad categories:
- Primary Memory
- Secondary Memory
Primary Memory
Primary Memory is a type of Computer Memory which is directly accessed by the Preprocessor. It is basically used to store data on which computer is currently working. It has lesser storage than Secondary Memory. It is basically of two types:
- Random Access Memory (RAM)
- Read Only Memory (ROM)
Secondary Memory
Secondary Memory is a type of Computer Memory which is used to permanently store the data and Information. It has a larger data storage capacity than Primary Memory. Secondary Memory is not directly accessible from CPU. It is basically of four types:
- HardDisk
- Compact Disc (CD)
- Digital Versatile Disk (DVD)
- Floppy Disk
Types of Memory
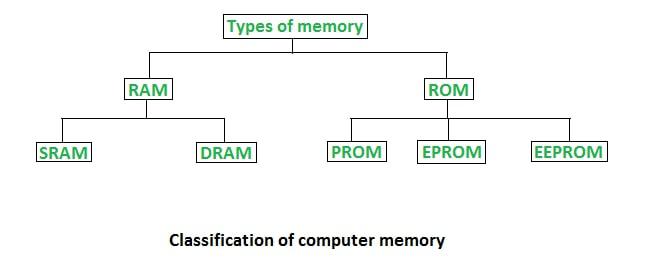
Primary Memory is classified into two types: RAM and ROM. In this Article, we are going to discuss the Differences between RAM and ROM.
Random Access Memory
Random Access Memory (RAM) is used to store the programs and data being used by the CPU in real time. The data on the random access memory can be read, written, and erased any number of times. RAM is a hardware element where the data currently used is stored. It is a volatile memory. It is also called as Main Memory or Primary Memory. This is users memory. The software(program) as well as data files are stored on the hard dish when the software or those files are opened. They get expanded into RAM. It id a users space where the temporary data are automatically stored fill the user saves it into the secondary storage devices.
Types of RAM
- Static RAM: Static RAM or SRAM stores a bit of data using the state of a six-transistor memory cell.
- Dynamic RAM: Dynamic RAM or DRAM stores a bit of data using a pair of transistors and capacitors which constitute a DRAM memory cell.
Types of Primary Memory
Read Only Memory
Read Only Memory (ROM) is a type of memory where the data has been prerecorded. Data stored in ROM is retained even after the computer is turned off ie, non-volatile. It is generally used in Embedded Parts, where the programming requires almost no changes. It is also called as Secondary Memory. It is a permanent CNO4 erasable memory gets initiated when the power is supplied to the computer ROM is a memory chip fixed on the motherboard at the time of manufacturing. It stores a program called BIOS(Basic Input Output Setup). This program checks the status of all the devices attached to the computer.
Types of ROM
- Programmable ROM: It is a type of ROM where the data is written after the memory chip has been created. It is non-volatile.
- Erasable Programmable ROM: It is a type of ROM where the data on this non-volatile memory chip can be erased by exposing it to high-intensity UV light.
- Electrically Erasable Programmable ROM: It is a type of ROM where the data on this non-volatile memory chip can be electrically erased using field electron emission.
- Mask ROM: It is a type of ROM in which the data is written during the manufacturing of the memory chip.
Difference between RAM and ROM
| Data-Retention |
RAM is a volatile memory that could store the
data as long as the power is supplied.
|
ROM is a non-volatile memory that the could retain the
data even when the power is turned off.
|
| Read/Write |
Read and write operations are supported. |
Only read operations are supported. |
| Use |
Used to store the data that has to be currently processed by CPU temporarily. |
It is typically used to store firmware or microcode, which is used
to initialize and control hardware components of the computer.
|
| Speed |
It is a high-speed memory. |
It is much slower than the RAM. |
| CPU Interaction |
CPU can easily access data stored in RAM. |
CPU cannot easily access data stored in ROM. |
| Size and Capacity |
Large size with higher capacity, concerning ROM. |
Small size with less capacity, concerning RAM. |
| Used as/in |
CPU Cache, Primary memory. |
Firmware, Micro-controllers. |
| Accessibility |
The data stored is easily accessible. |
The data stored is not as easily accessible as in the concerning RAM. |
| Cost |
RAM is more costlier than ROM. |
ROM is cheaper than RAM. |
| Chip Size |
A RAM chip can store only a few gigabytes (GB) of data. |
A ROM chip can store multiple megabytes (MB) of data. |
| Function |
Used for the temporary storage of data currently being processed by the CPU. |
Used to store firmware, BIOS, and other data that needs to be retained. |
FAQs
1. What are the types of Random Access Memory (RAM)?
There are two types of RAM:
- Static RAM (SRAM)
- Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
2. What are the types of Read Only Memory (ROM)?
There are four types of RAM:
- Masked ROM (MROM)
- Programmable ROM (PROM)
- Erasable Programmable ROM (EPROM)
- Electrically erasable programmable ROM (EEPROM)
Advantages of RAM
- Speed: RAM is much faster than other types of memory, such as hard disk drives, making it ideal for storing and accessing data that needs to be accessed quickly.
- Volatility: RAM is volatile memory, which means that it loses its contents when power is turned off. This property allows RAM to be easily reprogrammed and reused.
- Flexibility: RAM can be easily upgraded and expanded, allowing for more memory to be added as needed.
Disadvantages of RAM
- Limited capacity: RAM has a limited capacity, which can limit the amount of data that can be stored and accessed at any given time.
- Volatility: The volatile nature of RAM means that data must be saved to a more permanent form of storage, such as a hard drive or SSD, to prevent data loss.
- Cost: RAM can be relatively expensive, particularly for high-capacity modules, which can make it difficult to scale memory as needed.
Advantages of ROM
- Non-volatile: ROM is non-volatile memory, which means that it retains its contents even when power is turned off. This property makes ROM ideal for storing permanent data, such as firmware and system software.
- Stability: ROM is stable and reliable, which makes it a good choice for critical systems and applications.
- Security: ROM cannot be easily modified, which makes it less susceptible to malicious attacks, such as viruses and malware.
Disadvantages of ROM
- Limited flexibility: ROM cannot be easily reprogrammed or updated, which makes it difficult to modify or customize the contents of ROM.
- Limited capacity: ROM has a limited capacity, which can limit the amount of data that can be stored and accessed at any given time.
- Cost: ROM can be relatively expensive to produce, particularly for custom or specialized applications, which can make it less cost-effective than other types of memory.
Conclusion
In conclusion, RAM (Random Access Memory) and ROM (Read Only Memory) are two types of computer memory that are important and have different features. RAM is high-speed, volatile memory used to store and process temporary data. ROM, on the other hand, is non-volatile memory used to store lasting data like firmware. RAM is more flexible, but it costs more, while ROM is more stable and secure, but it doesn’t have as much freedom. Understanding the differences between these two types of memory is important for running a computer and managing files well.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...