How to Create an App in Django ?
Last Updated :
22 Dec, 2022
Prerequisite – How to Create a Basic Project using MVT in Django?
Django is famous for its unique and fully managed app structure. For every functionality, an app can be created like a completely independent module. This article will take you through how to create a basic app and add functionalities using that app.
For example, if you are creating a Blog, Separate modules should be created for Comments, Posts, Login/Logout, etc. In Django, these modules are known as apps. There is a different app for each task.
Benefits of using Django apps –
- Django apps are reusable i.e. a Django app can be used with multiple projects.
- We have loosely coupled i.e. almost independent components
- Multiple developers can work on different components
- Debugging and code organization is easy. Django has an excellent debugger tool.
- It has in-built features like admin pages etc, which reduces the effort of building the same from scratch
Pre-installed apps –
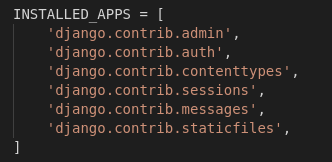
Django provides some pre-installed apps for users. To see pre-installed apps, navigate to projectName –> projectName –> settings.py
In your settings.py file, you will find INSTALLED_APPS. Apps listed in INSTALLED_APPS are provided by Django for the developer’s comfort.
Also, Visit :Django ORM – Inserting, Updating & Deleting Data
Creating an App in Django :
Let us start building an app.
Method-1
- To create a basic app in your Django project you need to go to the directory containing manage.py and from there enter the command :
python manage.py startapp projectApp
Method-2
- To create a basic app in your Django project you need to go to the directory containing manage.py and from there enter the command :
django-admin startapp projectApp
- Now you can see your directory structure as under :

To consider the app in your project you need to specify your project name in INSTALLED_APPS list as follows in settings.py:
Python3
INSTALLED_APPS = [
'django.contrib.admin',
'django.contrib.auth',
'django.contrib.contenttypes',
'django.contrib.sessions',
'django.contrib.messages',
'django.contrib.staticfiles',
'projectApp'
]
|
So, we have finally created an app but to render the app using URLs we need to include the app in our main project so that URLs redirected to that app can be rendered. Let us explore it.
Move to projectName -> projectName -> urls.py and add below code in the header
from django.urls import include
Now in the list of URL patterns, you need to specify the app name for including your app URLs. Here is the code for it –
Python3
from django.contrib import admin
from django.urls import path, include
urlpatterns = [
path('admin/', admin.site.urls),
path('', include("projectApp.urls")),
]
|
- Now You can use the default MVT model to create URLs, models, views, etc. in your app and they will be automatically included in your main project.
The main feature of Django Apps is independence, every app functions as an independent unit in supporting the main project.
Now the urls.py in the project file will not access the app’s url.
To run your Django Web application properly the following actions must be taken:-
1. Create a file in the apps directory called urls.py
2. Include the following code:
Python3
from django.urls import path
from . import views
urlpatterns=[
path('',views.index)
]
|
The above code will call or invoke the function which is defined in the views.py file so that it can be seen properly in the Web browser. Here it is assumed that views.py contains the following code :-
Python3
from django.http import HttpResponse
def index(request):
return HttpResponse("Hello Geeks")
|
After adding the above code, go to the settings.py file which is in the project directory, and change the value of ROOT_URLCONF from ‘project.urls’ to ‘app.urls’
From this:-

To this:

3. And then you can run the server(127.0.0.1:8000) and you will get the desired output
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...