Creating a Pandas DataFrame
Last Updated :
22 Jun, 2021
In the real world, a Pandas DataFrame will be created by loading the datasets from existing storage, storage can be SQL Database, CSV file, and Excel file. Pandas DataFrame can be created from the lists, dictionary, and from a list of dictionary etc.

A Dataframe is a two-dimensional data structure, i.e., data is aligned in a tabular fashion in rows and columns. In dataframe datasets arrange in rows and columns, we can store any number of datasets in a dataframe. We can perform many operations on these datasets like arithmetic operation, columns/rows selection, columns/rows addition etc.
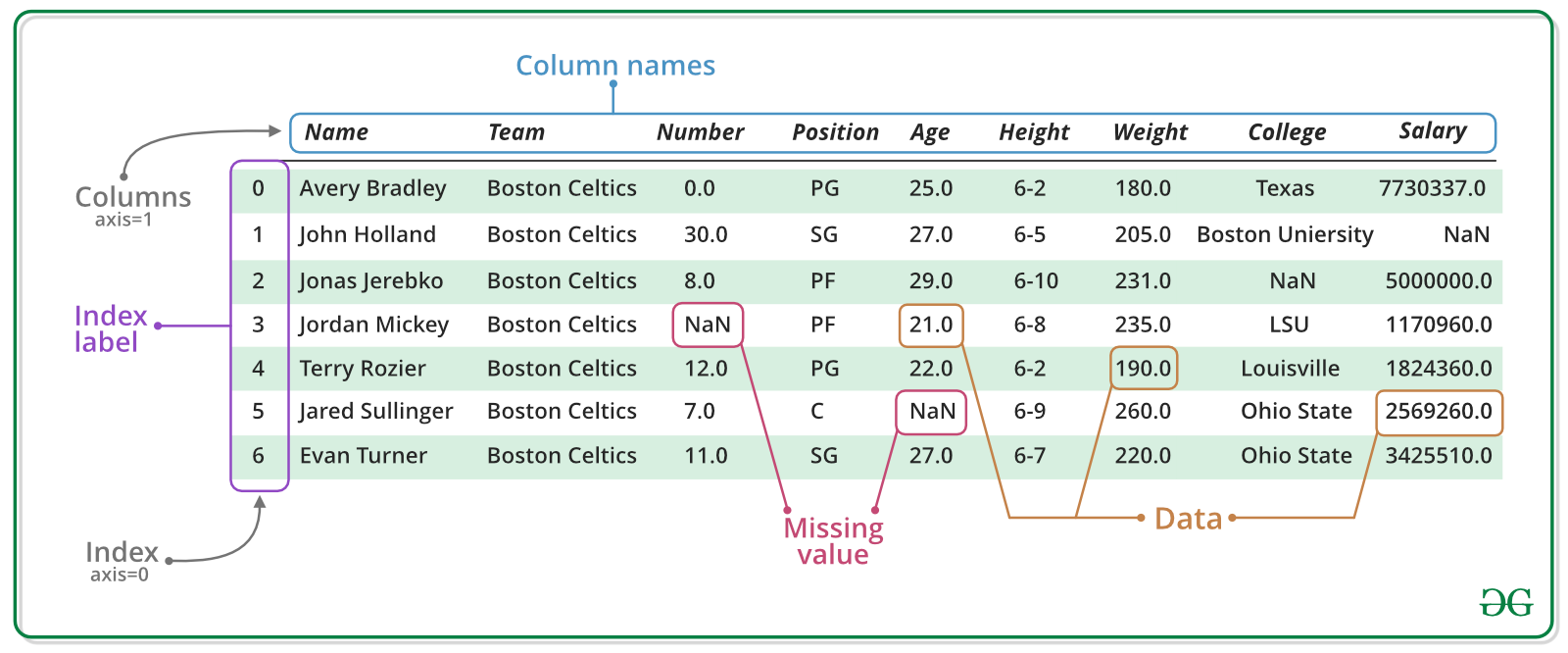
Pandas DataFrame can be created in multiple ways. Let’s discuss different ways to create a DataFrame one by one.
Creating an empty dataframe :
A basic DataFrame, which can be created is an Empty Dataframe. An Empty Dataframe is created just by calling a dataframe constructor.
Python3
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame()
print(df)
|
Output :
Empty DataFrame
Columns: []
Index: []
Creating a dataframe using List:
DataFrame can be created using a single list or a list of lists.
Python3
import pandas as pd
lst = ['Geeks', 'For', 'Geeks', 'is',
'portal', 'for', 'Geeks']
df = pd.DataFrame(lst)
print(df)
|
Output:

Creating DataFrame from dict of ndarray/lists:
To create DataFrame from dict of narray/list, all the narray must be of same length. If index is passed then the length index should be equal to the length of arrays. If no index is passed, then by default, index will be range(n) where n is the array length.
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = {'Name':['Tom', 'nick', 'krish', 'jack'], 'Age':[20, 21, 19, 18]}
df = pd.DataFrame(data)
print(df)
|
Output:
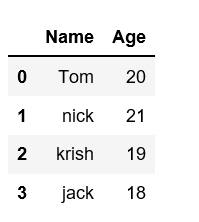
Create pandas dataframe from lists using dictionary:
Creating pandas data-frame from lists using dictionary can be achieved in different ways. We can create pandas dataframe from lists using dictionary using pandas.DataFrame. With this method in Pandas we can transform a dictionary of list to a dataframe.
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict)
print(df)
|
Output:
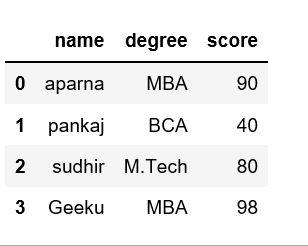
Multiple ways of creating dataframe :
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...