Boolean Indexing in Pandas
Last Updated :
08 Jun, 2022
In boolean indexing, we will select subsets of data based on the actual values of the data in the DataFrame and not on their row/column labels or integer locations. In boolean indexing, we use a boolean vector to filter the data.

Boolean indexing is a type of indexing that uses actual values of the data in the DataFrame. In boolean indexing, we can filter a data in four ways:
- Accessing a DataFrame with a boolean index
- Applying a boolean mask to a dataframe
- Masking data based on column value
- Masking data based on an index value
Accessing a DataFrame with a boolean index:
In order to access a dataframe with a boolean index, we have to create a dataframe in which the index of dataframe contains a boolean value that is “True” or “False”.
Example
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [True, False, True, False])
print(df)
|
Output:
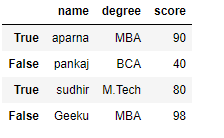
Now we have created a dataframe with the boolean index after that user can access a dataframe with the help of the boolean index. User can access a dataframe using three functions that is .loc[], .iloc[], .ix[]
Accessing a Dataframe with a boolean index using .loc[]
In order to access a dataframe with a boolean index using .loc[], we simply pass a boolean value (True or False) in a .loc[] function.
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
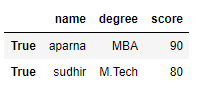
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [True, False, True, False])
print(df.loc[True])
|
Output:
Accessing a Dataframe with a boolean index using .iloc[]
In order to access a dataframe using .iloc[], we have to pass a boolean value (True or False) but iloc[] function accepts only integer as an argument so it will throw an error so we can only access a dataframe when we pass an integer in iloc[] function
Code #1:
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [True, False, True, False])
print(df.iloc[True])
|
Output:
TypeError
Code #2:
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [True, False, True, False])
print(df.iloc[1])
|
Output:

Accessing a Dataframe with a boolean index using .ix[]
In order to access a dataframe using .ix[], we have to pass boolean value (True or False) and integer value to .ix[] function because as we know that .ix[] function is a hybrid of .loc[] and .iloc[] function.
Code #1:
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
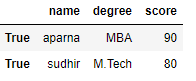
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [True, False, True, False])
print(df.ix[True])
|
Output:
Code #2:
Python
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
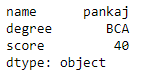
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [True, False, True, False])
print(df.ix[1])
|
Output:
Applying a boolean mask to a dataframe :
In a dataframe, we can apply a boolean mask. In order to do that we can use __getitems__ or [] accessor. We can apply a boolean mask by giving a list of True and False of the same length as contain in a dataframe. When we apply a boolean mask it will print only that dataframe in which we pass a boolean value True. To download “nba1.1” CSV file click here.
Code #1:
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["MBA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "MBA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [0, 1, 2, 3])
print(df[[True, False, True, False]])
|
Output:
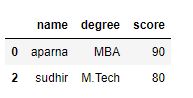
Code #2:
Python3
import pandas as pd
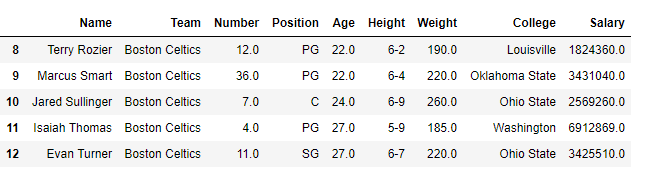
data = pd.read_csv("nba1.1.csv")
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
print(df[[True, False, True, False, True,
False, True, False, True, False,
True, False, True]])
|
Output:
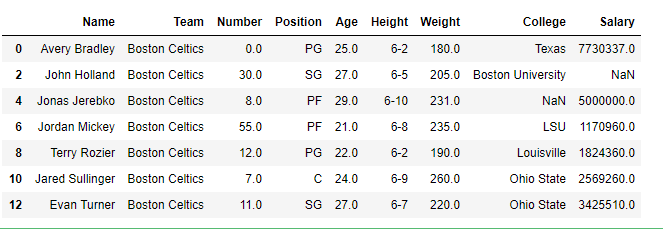
Masking data based on column value:
In a dataframe we can filter a data based on a column value. In order to filter data, we can apply certain conditions on the dataframe using different operators like ==, >, <, <=, >=. When we apply these operators to the dataframe then it produces a Series of True and False. To download the “nba.csv” CSV, click here.
Code #1:
Python
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["BCA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "BCA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict)
print(df['degree'] == 'BCA')
|
Output:

Code #2:
Python
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("nba.csv", index_col ="Name")
print(data['Age'] > 25)
|
Output:
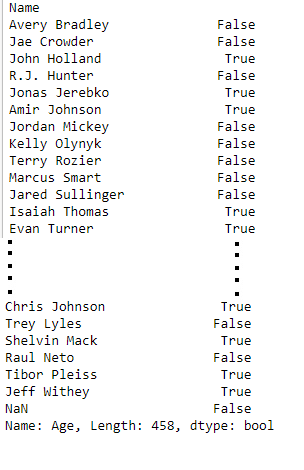
Masking data based on index value :
In a dataframe we can filter a data based on a column value. In order to filter data, we can create a mask based on the index values using different operators like ==, >, <, etc… . To download “nba1.1” CSV file click here.
Code #1:
Python3
import pandas as pd
dict = {'name':["aparna", "pankaj", "sudhir", "Geeku"],
'degree': ["BCA", "BCA", "M.Tech", "BCA"],
'score':[90, 40, 80, 98]}
df = pd.DataFrame(dict, index = [0, 1, 2, 3])
mask = df.index == 0
print(df[mask])
|
Output:
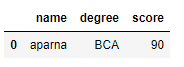
Code #2:
Python3
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("nba1.1.csv")
df = pd.DataFrame(data, index = [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6,
7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12])
mask = df.index > 7
print(df[mask])
|
Output:
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...