Python | Working with Pandas and XlsxWriter | Set – 1
Last Updated :
26 Dec, 2018
Python Pandas is a data analysis library. It can read, filter and re-arrange small and large datasets and output them in a range of formats including Excel.
Pandas writes Excel files using the XlsxWriter modules.
XlsxWriter is a Python module for writing files in the XLSX file format. It can be used to write text, numbers, and formulas to multiple worksheets. Also, it supports features such as formatting, images, charts, page setup, auto filters, conditional formatting and many others.
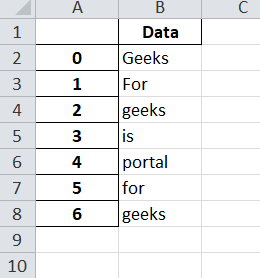
Code #1: Converting a Pandas dataframe to an xlsx file using Pandas and XlsxWriter.
import pandas as pd
df = pd.DataFrame({'Data': ['Geeks', 'For', 'geeks', 'is',
'portal', 'for', 'geeks']})
writer = pd.ExcelWriter('pandasEx.xlsx',
engine ='xlsxwriter')
df.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet1')
writer.save()
|
Output :
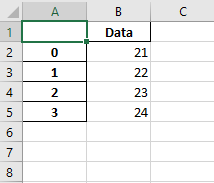
Code #2: Writing multiple dataframes to worksheets using Pandas and XlsxWriter.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [11, 12, 13, 14]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [21, 22, 23, 24]})
df3 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [31, 32, 33, 34]})
writer = pd.ExcelWriter('pandas_multiple.xlsx',
engine ='xlsxwriter')
df1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet1')
df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet2')
df3.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet3')
writer.save()
|
Output :


Code #3: Positioning dataframes in a worksheet using Pandas and XlsxWriter.
import pandas as pd
df1 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [11, 12, 13, 14]})
df2 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [21, 22, 23, 24]})
df3 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [31, 32, 33, 34]})
df4 = pd.DataFrame({'Data': [41, 42, 43, 44]})
writer = pd.ExcelWriter('pandas_positioning.xlsx',
engine ='xlsxwriter')
df1.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet1')
df2.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet1', startcol = 3)
df3.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet1', startrow = 6)
df4.to_excel(writer, sheet_name ='Sheet1',
startrow = 7, startcol = 4,
header = False, index = False)
writer.save()
|
Output :

Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...