Covariance and Correlation in R Programming
Last Updated :
05 Jul, 2023
Covariance and Correlation are terms used in statistics to measure relationships between two random variables. Both of these terms measure linear dependency between a pair of random variables or bivariate data. They both capture a different component of the relationship, despite the fact that they both provide information about the link between variables. Let’s investigate the theory underlying correlation and covariance:
We can discuss some of the main difference between them as below:In this article, we are going to discuss cov(), cor() and cov2cor() functions in R which use covariance and correlation methods of statistics and probability theory.
Covariance in R Programming Language
In R programming, covariance can be measured using the cov() function. Covariance is a statistical term used to measure the direction of the linear relationship between the data vectors. Mathematically,
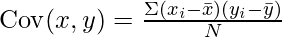
where,
x represents the x data vector
y represents the y data vector
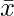 represents mean of x data vector
represents mean of x data vector
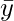 represents mean of y data vector
represents mean of y data vector
N represents total observations
Covariance Syntax in R
Syntax: cov(x, y, method)
where,
- x and y represents the data vectors
- method defines the type of method to be used to compute covariance. Default is “pearson”.
Example:
R
x <- c(1, 3, 5, 10)
y <- c(2, 4, 6, 20)
print(cov(x, y))
print(cov(x, y, method = "pearson"))
print(cov(x, y, method = "kendall"))
print(cov(x, y, method = "spearman"))
|
Output:
[1] 30.66667
[1] 30.66667
[1] 12
[1] 1.666667
Correlation in R Programming Language
cor() function in R programming measures the correlation coefficient value. Correlation is a relationship term in statistics that uses the covariance method to measure how strongly the vectors are related. Mathematically,
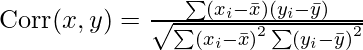
where,
x represents the x data vector
y represents the y data vector
 [Tex]\bar{x} [/Tex]represents mean of x data vector
[Tex]\bar{x} [/Tex]represents mean of x data vector
 [Tex]\bar{y} [/Tex]represents mean of y data vector
[Tex]\bar{y} [/Tex]represents mean of y data vector
Correlation in R
Syntax: cor(x, y, method)
where,
- x and y represents the data vectors
- method defines the type of method to be used to compute covariance. Default is “pearson”.
Example:
R
x <- c(1, 3, 5, 10)
y <- c(2, 4, 6, 20)
print(cor(x, y))
print(cor(x, y, method = "pearson"))
print(cor(x, y, method = "kendall"))
print(cor(x, y, method = "spearman"))
|
Output:
[1] 0.9724702
[1] 0.9724702
[1] 1
[1] 1
Covariance and Correlation For data frame
We cancalculate the covariance and correlation for all columns in data frame.
R
data(iris)
library(dplyr)
data=select(iris,-Species)
cor(data)
cov(data)
|
Output:
> cor(data)
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width
Sepal.Length 1.0000000 -0.1175698 0.8717538 0.8179411
Sepal.Width -0.1175698 1.0000000 -0.4284401 -0.3661259
Petal.Length 0.8717538 -0.4284401 1.0000000 0.9628654
Petal.Width 0.8179411 -0.3661259 0.9628654 1.0000000
> cov(data)
Sepal.Length Sepal.Width Petal.Length Petal.Width
Sepal.Length 0.6856935 -0.0424340 1.2743154 0.5162707
Sepal.Width -0.0424340 0.1899794 -0.3296564 -0.1216394
Petal.Length 1.2743154 -0.3296564 3.1162779 1.2956094
Petal.Width 0.5162707 -0.1216394 1.2956094 0.5810063Conversion of Covariance to Correlation in R
cov2cor() function in R programming converts a covariance matrix into a corresponding correlation matrix.
Syntax: cov2cor(X)
where,
- X and y represents the covariance square matrix
Example:
R
x <- rnorm(2)
y <- rnorm(2)
mat <- cbind(x, y)
X <- cov(mat)
print(X)
print(cor(mat))
print(cov2cor(X))
|
Output:
x y
x 0.0742700 -0.1268199
y -0.1268199 0.2165516
x y
x 1 -1
y -1 1
x y
x 1 -1
y -1 1
Difference between Covariance and Correlation
We can discuss some of the main difference between them as below:
Covariance
| Correlation
|
| Covariance quantifies the interdependence of two variables. It measures the strength of the correlation between changes in one variable and changes in another. | Dividing the covariance by the sum of the standard deviations of the variables, it standardises the covariance. |
| Covariance: Covariance is not scaled, and the units used to quantify the variables affect how much it is worth. Comparing covariances across many datasets or variables is therefore challenging. | Correlation is a standardised measurement that has a range of -1 to 1. It enables meaningful comparisons between several datasets or variables and is independent of the magnitude of the variables. |
| The scales of the variables have an impact on covariance, which is not standardised. As a result, comparing the size of covariances across several datasets or variables is challenging. | By dividing the covariance by the sum of the standard deviations of the variables, correlation standardises the covariance. This enables for meaningful interpretation of the strength and direction of the association and makes correlation values comparable. |
| Understanding the combined variability of two variables and their potential link is helped by covariance. It is frequently used in statistical models, risk analysis, and portfolio analysis. | Correlation is frequently used to assess how strongly two variables are linearly related. It frequently appears in data analysis, regression models, prediction models, and multicollinearity assessments. |
Correlation describes the intensity and direction of the linear link between two variables, whereas covariance shows how much two variables vary together.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...