Class 11 NCERT Solutions- Chapter 13 Limits And Derivatives – Exercise 13.1 | Set 1
Last Updated :
07 Apr, 2021
Evaluate the following limits in Exercises 1 to 22.
Question 1: 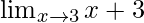
Solution:
In 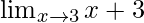 , as x⇢3
, as x⇢3
Put x = 3, we get
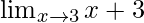 = 3+3
= 3+3
= 6
Question 2: 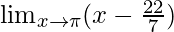
Solution:
In 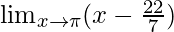 , as x⇢π
, as x⇢π
Put x = π, we get
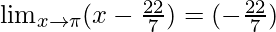
= 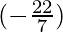
Question 3: 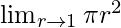
Solution:
In 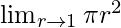 , as r⇢1
, as r⇢1
Put r = 1, we get
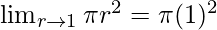
= π
Question 4: 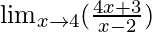
Solution:
In 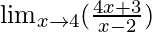 , as x⇢4
, as x⇢4
Put x = 4, we get
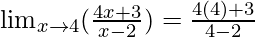
= 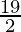
Question 5: 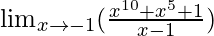
Solution:
In 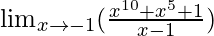 , as x⇢-1
, as x⇢-1
Put x = -1, we get
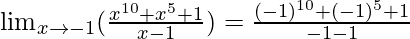
= 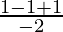
= 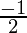
Question 6: 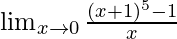
Solution:
In 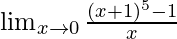 , as x⇢0
, as x⇢0
Put x = 0, we get
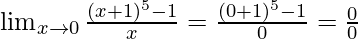
As, this limit becomes undefined
Now, let’s take x+1=p and x = p-1, to make it equivalent to theorem.
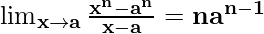
As, x⇢0 ⇒ p⇢1
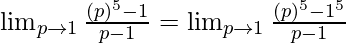
Here, n=5 and a = 1.
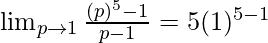
= 5(1)4
= 5
Question 7: 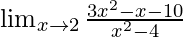
Solution:
In 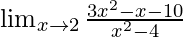 , as x⇢2
, as x⇢2
Put x = 2, we get
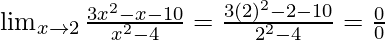
As, this limit becomes undefined
Now, let’s Factorise the numerator and denominator, we get
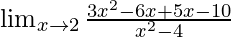
= 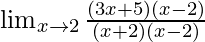
Cancelling (x-2), we have
= 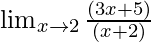
Put x = 2, we get
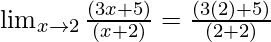
= 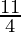
Question 8: 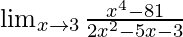
Solution:
In 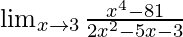 , as x⇢3
, as x⇢3
Put x = 3, we get
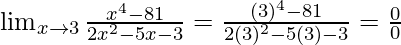
As, this limit becomes undefined
Now, let’s Factorise the numerator and denominator, we get
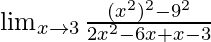
= 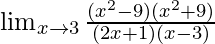
= 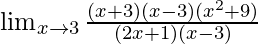
Cancelling (x-3), we have
= 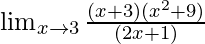
Put x = 3, we get
= 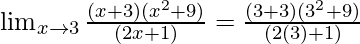
= 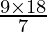
= 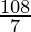
Question 9: 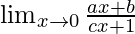
Solution:
In 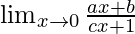 , as x⇢0
, as x⇢0
Put x = 0, we get
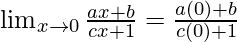
= b
Question 10: 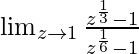
Solution:
In 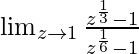 , as z⇢1
, as z⇢1
Put z = 1, we get
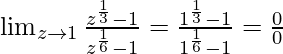
Let’s take 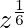 = p and
= p and 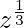 = p2,
= p2,
As, z⇢1 ⇒ p⇢1
= 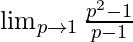
Now, let’s Factorise the numerator, we get
= 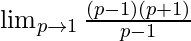
Cancelling (p-1), we have
= 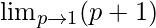
Put p = 1, we get
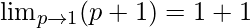
= 2
Question 11: 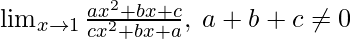
Solution:
In 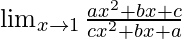 , as x⇢1
, as x⇢1
Put x = 1, we get
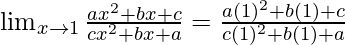
= 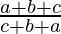
= 1 (As it is given a+b+c≠0)
Question 12: 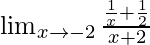
Solution:
In 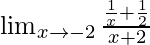 , as x⇢-2
, as x⇢-2
Firstly, lets simplify the equation
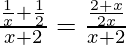
Cancelling (x+2),we get
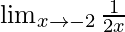
Put x = -2, we get
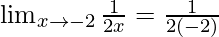
= 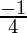
Question 13: 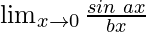
Solution:
In 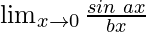 , as x⇢0
, as x⇢0
Put x = 0, we get
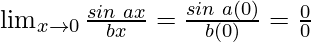
As, this limit becomes undefined
Now, let’s multiply and divide the equation by a, to make it equivalent to theorem.
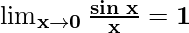
Hence, we have
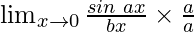
= 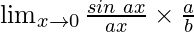
= 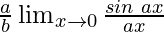
As x⇢0, then ax⇢0
= 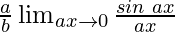
By using the theorem, we get
= 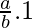
= 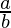
Question 14: 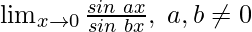
Solution:
In 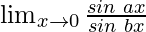 , as x⇢0
, as x⇢0
Put x = 0, we get
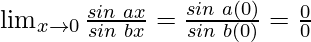
As, this limit becomes undefined
Now, let’s multiply and divide the numerator by ax and denominator by bx to make it equivalent to theorem.
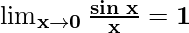
Hence, we have
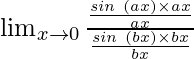
= 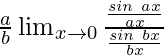
= 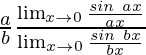
By using the theorem, we get
= 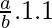
= 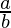
Question 15: 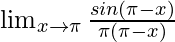
Solution:
In 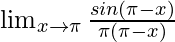 , as x⇢π
, as x⇢π
Put x = π, we get
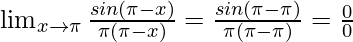
As, this limit becomes undefined
Now, let’s take π-x=p
As, x⇢π ⇒ p⇢0
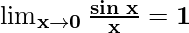
= 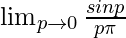
= 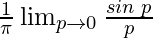
By using the theorem, we get
= 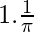
= 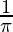
Question 16: 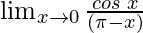
Solution:
In 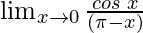 , as x⇢0
, as x⇢0
Put x = 0, we get
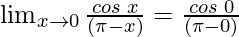
= 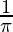
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...