Class 11 NCERT Solutions- Chapter 5 Complex Numbers And Quadratic Equations – Exercise 5.3
Last Updated :
10 Mar, 2021
Solve each of the following equations:
Question 1. x2 + 3 = 0
Solution:
We have,
x2 + 3 = 0 or x2 + 0 × x + 3 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = 1 , b = 0 and c = 3
D = (0)2 – 4*(1)*(3)
D = -12
Since , x = 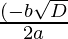
Therefore ,
x = 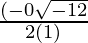
x = 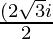
x = ± √3 i
Hence , the solution of x2 + 3 = 0 is ± √3 i
Question 2. 2x2 + x + 1 = 0
Solution:
We have,
2x2 + x + 1 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = 2 , b = 1 and c = 1
D = (1)2 – 4*(2)*(1)
D = -7
Since , x = 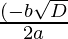
Therefore ,
x = 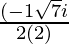
x = 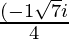
Hence , the solution of 2x2 + x + 1 = 0 is 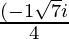 .
.
Question 3. x2 + 3x + 9 = 0
Solution:
We have,
x2 + 3x + 9 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = 1 , b = 3 and c = 9
D = (3)2 – 4*(1)*(9)
D = -27
Since , x = 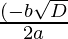
Therefore ,
x = 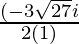
x = 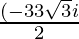
Hence , the solution of x2 + 3x + 1 = 0 is 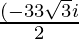 .
.
Question 4. -x2+ x – 2 = 0
Solution:
We have,
-x2 + x – 2 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = -1 , b = 1 and c = -2
D = (1)2 – 4*(-1)*(-2)
D = -7
Since , x = 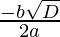
Therefore ,
x = 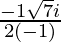
x = 
Hence , the solution of -x2 + x – 2= 0 is 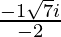 .
.
Question 5. x2 + 3x + 5 = 0
Solution:
We have,
x2 + 3x + 5 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = 1 , b = 3 and c = 5
D = (3)2 – 4*(1)*(5)
D = -11
Since , x = 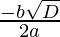
Therefore ,
x = 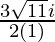
x = 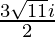
Hence , the solution of -x2 + x – 2= 0 is 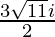 .
.
Question 6. x2 – x + 2 = 0
Solution:
We have,
x2 – x + 2 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = 1 , b = -1 and c = 2
D = (-1)2 – 4*(1)*(2)
D = -7
Since , x = 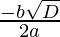
Therefore ,
x = 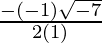
x = 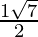
Hence , the solution of -x2 + x – 2= 0 is 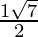 .
.
Question 7. √2x2 + x + √2 = 0
Solution:
We have,
√2x2 + x + √2 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = √2 , b = 1 and c = √2
D = (1)2 – 4*(√2)*(√2)
D = -7
Since , x = 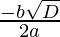
Therefore ,
x = 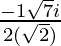
Hence , the solution of -x2 + x – 2= 0 is 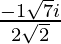 .
.
Question 8. √3x2 – √2x + 3√3 = 0
Solution:
We have,
√3x2 – √2x + 3√3 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = √3 , b = -√2 and c = 3√3
D = (-√2)2 – 4*(√3)*(3√3)
D = -34
Since , x = 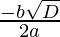
Therefore ,
x = 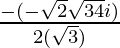
x = 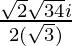
Hence , the solution of -x2 + x – 2= 0 is 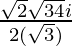 .
.
Question 9. x2 + x + 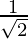 = 0
= 0
Solution:
We have,
x2 + x + 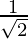 = 0 or √2x2 + √2x + 1 = 0 —(1)
= 0 or √2x2 + √2x + 1 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = √2 , b = √2 and c = 1
D = (√2)2 – 4*(√2)*(1)
D = 2 – 4√2 = 2 ( 1 – 2√2 )
Since , x = 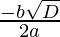
Therefore ,
x = 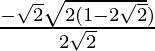
x = 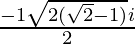
x = 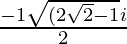
Hence , the solution of -x2 + x – 2= 0 is 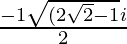 .
.
Question 10. x2 + 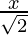 + 1 = 0
+ 1 = 0
Solution:
We have,
x2 + 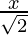 + 1 = 0 or √2x2 + x + √2 = 0 —(1)
+ 1 = 0 or √2x2 + x + √2 = 0 —(1)
Discriminant, D = b2 – 4ac
from (1) , a = √2 , b = 1 and c = √2
D = (1)2 – 4*(√2)*(√2)
D = -7
Since , x = 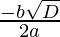
Therefore ,
x = 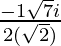
x = 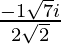
Hence , the solution of x2 + 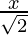 + 1 = 0 is
+ 1 = 0 is 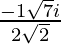 .
.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...