Implementation of Micro Instructions Sequencer
Last Updated :
19 Sep, 2023
The address is used by a microprogram sequencer to decide which microinstruction has to be performed next. Microprogram sequencing is the name of the total procedure. The addresses needed to step through a control store’s microprogram are created by a sequencer, also known as a microsequencer.
The control unit’s main job is to communicate with the computer’s memory, input/output device, and ALU on how to respond to or carry out a set of instructions. Processing is not done within the Control unit itself. It only directs and manages the task. It serves as the computer’s supervisor, regulating all operations including retrieving instructions from main memory and putting them to use.
Micro Instructions Sequencer
Micro Instructions Sequencer is a combination of all hardware for selecting the next micro-instruction address. The micro-instruction in control memory contains a set of bits to initiate micro-operations in computer registers and other bits to specify the method by which the address is obtained.
Implementation of Micro Instructions Sequencer
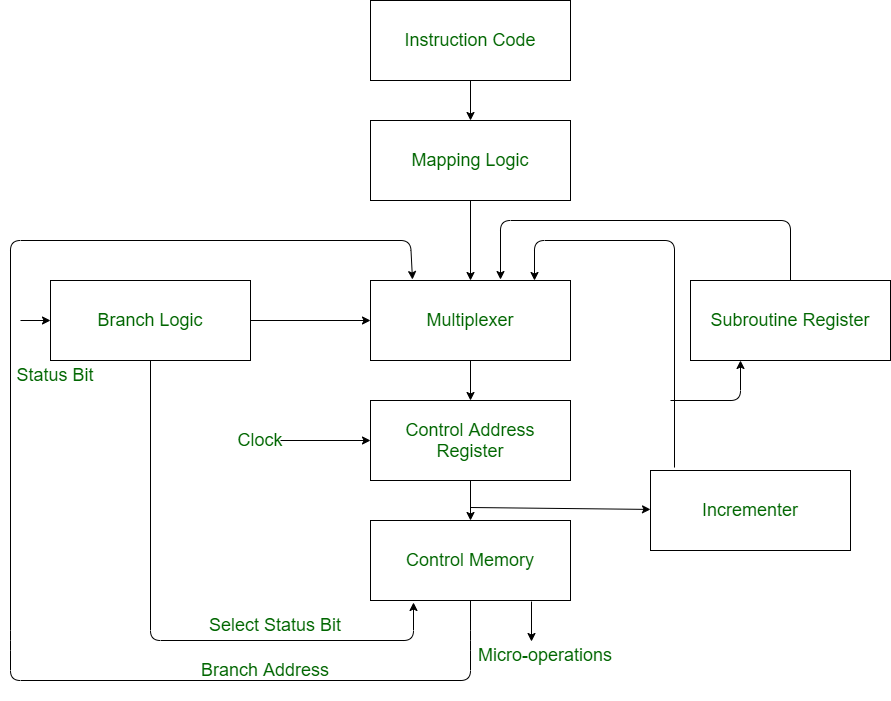
- Control Address Register(CAR) : Control address register receives the address from four different paths. For receiving the addresses from four different paths, Multiplexer is used.
- Multiplexer : Multiplexer is a combinational circuit which contains many data inputs and single data output depending on control or select inputs.
- Branching : Branching is achieved by specifying the branch address in one of the fields of the micro instruction. Conditional branching is obtained by using part of the micro-instruction to select a specific status bit in order to determine its condition.
- Mapping Logic : An external address is transferred into control memory via a mapping logic circuit.
- Incrementer : Incrementer increments the content of the control address register by one, to select the next micro-instruction in sequence.
- Subroutine Register (SBR) : The return address for a subroutine is stored in a special register called Subroutine Register whose value is then used when the micro-program wishes to return from the subroutine.
- Control Memory : Control memory is a type of memory which contains addressable storage registers. Data is temporarily stored in control memory. Control memory can be accessed quicker than main memory.
Design of Micro-programmed Controller Unit
A set of micro-instructions make up microprogramming. Three micro-operation phases are primarily present in each micro-instruction. F1, F2, F3, respectively. We also have the condition, branch, and address fields in addition to these three.
A 3X8 decoder decodes the F1, F2, and F3 fields because they are all 3 bits in size. We receive 8 outputs from the F1 micro-operation phase. One of these eight outputs is still unutilized.
Like the F1 procedure, the F2 operation produces a total of 7 outputs.
Only six operations can be carried out in the F3 micro-operation phase (one is left unfinished, and the other is saved for later use).
Therefore, we can complete 20 micro-operations in total (7+7+6).
Out of 20 operations, the diagram above shows 5 micro-operations.
The ALU is attached to F2 output number 3. It applies the AND operation to the contents of the data register and accumulator, then transfers the outcome to the accumulator. This is how it is written: ACAC AND DR
And we give the matching accumulator a clock pulse. The ability to load it onto the accumulator is enabled.
Output 1 of F1 adds data register and accumulator using an ALU, then sends the outcome to the accumulator.
The DRTAR operation, or transfer of the contents of the data register to the address register, is carried out by output 5 of F1. However, the data register’s size is 16 bits, while the the rightmost significant 12 bits of the data register are moved to the address register since the address register only has a capacity of 12 bits.
Transferring the contents of the programme counter to the address register is what output 6 of F1 does.
FAQs on Micro Instructions Sequencer
1. How is the sequencing of microinstructions controlled?
The sequencing of microinstructions is controlled by a combination of logic circuits and address counters. The current address points to the next microinstruction to be executed. Branching and conditional execution can modify this sequence.
2. What is the role of the control unit logic?
The control unit logic is responsible for reading the current microinstruction from the microinstruction memory and decoding its fields to generate the appropriate control signals for various components of the computer.
3. How do you connect the microinstruction sequencer to other components?
The microinstruction sequencer interfaces with the computer’s registers, ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), memory, and other components. Each microinstruction’s control signals activate or deactivate specific operations within these components.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...