Random Forest Regression is a versatile machine-learning technique for predicting numerical values. It combines the predictions of multiple decision trees to reduce overfitting and improve accuracy. Python’s machine-learning libraries make it easy to implement and optimize this approach.
Ensemble Learning
Ensemble learning is a machine learning technique that combines the predictions from multiple models to create a more accurate and stable prediction. It is an approach that leverages the collective intelligence of multiple models to improve the overall performance of the learning system.
Types of Ensemble Methods
There are various types of ensemble learning methods, including:
- Bagging (Bootstrap Aggregating): This method involves training multiple models on random subsets of the training data. The predictions from the individual models are then combined, typically by averaging.
- Boosting: This method involves training a sequence of models, where each subsequent model focuses on the errors made by the previous model. The predictions are combined using a weighted voting scheme.
- Stacking: This method involves using the predictions from one set of models as input features for another model. The final prediction is made by the second-level model.
Random Forest
A random forest is an ensemble learning method that combines the predictions from multiple decision trees to produce a more accurate and stable prediction. It is a type of supervised learning algorithm that can be used for both classification and regression tasks.
Every decision tree has high variance, but when we combine all of them in parallel then the resultant variance is low as each decision tree gets perfectly trained on that particular sample data, and hence the output doesn’t depend on one decision tree but on multiple decision trees. In the case of a classification problem, the final output is taken by using the majority voting classifier. In the case of a regression problem, the final output is the mean of all the outputs. This part is called Aggregation.
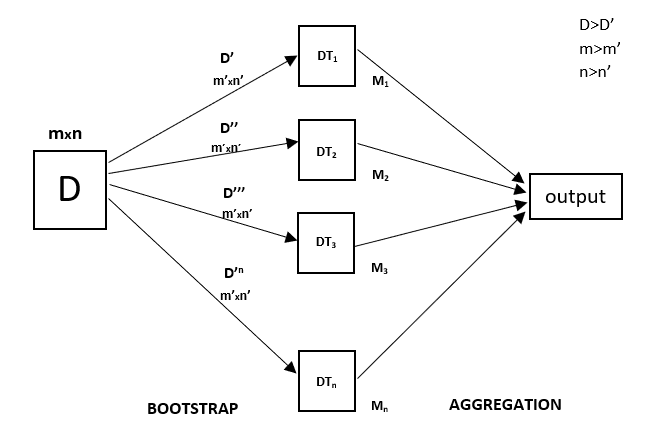
Random Forest Regression Model Working
What is Random Forest Regression?
Random Forest Regression in machine learning is an ensemble technique capable of performing both regression and classification tasks with the use of multiple decision trees and a technique called Bootstrap and Aggregation, commonly known as bagging. The basic idea behind this is to combine multiple decision trees in determining the final output rather than relying on individual decision trees.
Random Forest has multiple decision trees as base learning models. We randomly perform row sampling and feature sampling from the dataset forming sample datasets for every model. This part is called Bootstrap.
We need to approach the Random Forest regression technique like any other machine learning technique.
- Design a specific question or data and get the source to determine the required data.
- Make sure the data is in an accessible format else convert it to the required format.
- Specify all noticeable anomalies and missing data points that may be required to achieve the required data.
- Create a machine-learning model.
- Set the baseline model that you want to achieve
- Train the data machine learning model.
- Provide an insight into the model with test data
- Now compare the performance metrics of both the test data and the predicted data from the model.
- If it doesn’t satisfy your expectations, you can try improving your model accordingly or dating your data, or using another data modeling technique.
- At this stage, you interpret the data you have gained and report accordingly.
Random Forest Regression in Python
We will be using a similar sample technique in the below example. Below is a step-by-step sample implementation of Random Forest Regression, on the dataset that can be downloaded here- https://bit.ly/417n3N5
Python libraries make it very easy for us to handle the data and perform typical and complex tasks with a single line of code.
- Pandas – This library helps to load the data frame in a 2D array format and has multiple functions to perform analysis tasks in one go.
- Numpy – Numpy arrays are very fast and can perform large computations in a very short time.
- Matplotlib/Seaborn – This library is used to draw visualizations.
- Sklearn – This module contains multiple libraries having pre-implemented functions to perform tasks from data preprocessing to model development and evaluation.
- RandomForestRegressor – This is the regression model that is based upon the Random Forest model or the ensemble learning that we will be using in this article using the sklearn library.
- sklearn: This library is the core machine learning library in Python. It provides a wide range of tools for preprocessing, modeling, evaluating, and deploying machine learning models.
- LabelEncoder: This class is used to encode categorical data into numerical values.
- KNNImputer: This class is used to impute missing values in a dataset using a k-nearest neighbors approach.
- train_test_split: This function is used to split a dataset into training and testing sets.
- StandardScaler: This class is used to standardize features by removing the mean and scaling to unit variance.
- f1_score: This function is used to evaluate the performance of a classification model using the F1 score.
- RandomForestRegressor: This class is used to train a random forest regression model.
- cross_val_score: This function is used to perform k-fold cross-validation to evaluate the performance of a model
Step-1: Import Libraries
Here we are importing all the necessary libraries required.
Python3
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
import sklearn
import warnings
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
from sklearn.impute import KNNImputer
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
from sklearn.metrics import f1_score
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
|
Step-2: Import Dataset
Now let’s load the dataset in the panda’s data frame. For better data handling and leveraging the handy functions to perform complex tasks in one go.
Python3
df= pd.read_csv('Salaries.csv')
print(df)
|
Output:
Position Level Salary
0 Business Analyst 1 45000
1 Junior Consultant 2 50000
2 Senior Consultant 3 60000
3 Manager 4 80000
4 Country Manager 5 110000
5 Region Manager 6 150000
6 Partner 7 200000
7 Senior Partner 8 300000
8 C-level 9 500000
9 CEO 10 1000000
Here the .info() method provides a quick overview of the structure, data types, and memory usage of the dataset.
Output:
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 10 entries, 0 to 9
Data columns (total 3 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 Position 10 non-null object
1 Level 10 non-null int64
2 Salary 10 non-null int64
dtypes: int64(2), object(1)
memory usage: 372.0+ bytes
Step-3: Data Preparation
Here the code will extracts two subsets of data from the Dataset and stores them in separate variables.
- Extracting Features: It extracts the features from the DataFrame and stores them in a variable named
X.
- Extracting Target Variable: It extracts the target variable from the DataFrame and stores it in a variable named
y.
Python3
X = df.iloc[:,1:2].values
y = df.iloc[:,2].values
|
Step-4: Random Forest Regressor Model
The code processes categorical data by encoding it numerically, combines the processed data with numerical data, and trains a Random Forest Regression model using the prepared data.
Python3
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestRegressor
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
Check for and handle categorical variables
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
x_categorical = df.select_dtypes(include=['object']).apply(label_encoder.fit_transform)
x_numerical = df.select_dtypes(exclude=['object']).values
x = pd.concat([pd.DataFrame(x_numerical), x_categorical], axis=1).values
regressor = RandomForestRegressor(n_estimators=10, random_state=0, oob_score=True)
regressor.fit(x, y)
|
Step-5: Make predictions and Evaluation
The code evaluates the trained Random Forest Regression model:
- out-of-bag (OOB) score, which estimates the model’s generalization performance.
- Makes predictions using the trained model and stores them in the ‘predictions’ array.
- Evaluates the model’s performance using the Mean Squared Error (MSE) and R-squared (R2) metrics.
Out of Bag Score in RandomForest
Bag score or OOB score is the type of validation technique that is mainly used in bagging algorithms to validate the bagging algorithm. Here a small part of the validation data is taken from the mainstream of the data and the predictions on the particular validation data are done and compared with the other results.
The main advantage that the OOB score offers is that here the validation data is not seen by the bagging algorithm and that is why the results on the OOB score are the true results that indicated the actual performance of the bagging algorithm.
To get the OOB score of the particular Random Forest algorithm, one needs to set the value “True” for the OOB_Score parameter in the algorithm.
Python3
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
oob_score = regressor.oob_score_
print(f'Out-of-Bag Score: {oob_score}')
predictions = regressor.predict(x)
mse = mean_squared_error(y, predictions)
print(f'Mean Squared Error: {mse}')
r2 = r2_score(y, predictions)
print(f'R-squared: {r2}')
|
Output:
Out-of-Bag Score: 0.644879832593859
Mean Squared Error: 2647325000.0
R-squared: 0.9671801245316117
Step-6: Visualization
Now let’s visualize the results obtained by using the RandomForest Regression model on our salaries dataset.
- Creates a grid of prediction points covering the range of the feature values.
- Plots the real data points as blue scatter points.
- Plots the predicted values for the prediction grid as a green line.
- Adds labels and a title to the plot for better understanding.
Python3
import numpy as np
X_grid = np.arange(min(X),max(X),0.01)
X_grid = X_grid.reshape(len(X_grid),1)
plt.scatter(X,y, color='blue')
plt.plot(X_grid, regressor.predict(X_grid),color='green')
plt.title("Random Forest Regression Results")
plt.xlabel('Position level')
plt.ylabel('Salary')
plt.show()
|
Output:

Step-7: Visualizing a Single Decision Tree from the Random Forest Model
The code visualizes one of the decision trees from the trained Random Forest model. Plots the selected decision tree, displaying the decision-making process of a single tree within the ensemble.
Python3
from sklearn.tree import plot_tree
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
tree_to_plot = regressor.estimators_[0]
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plot_tree(tree_to_plot, feature_names=df.columns.tolist(), filled=True, rounded=True, fontsize=10)
plt.title("Decision Tree from Random Forest")
plt.show()
|
Output:
 Applications of Random Forest Regression
Applications of Random Forest Regression
The Random forest regression has a wide range of real-world problems, including:
- Predicting continuous numerical values: Predicting house prices, stock prices, or customer lifetime value.
- Identifying risk factors: Detecting risk factors for diseases, financial crises, or other negative events.
- Handling high-dimensional data: Analyzing datasets with a large number of input features.
- Capturing complex relationships: Modeling complex relationships between input features and the target variable.
Advantages of Random Forest Regression
- It is easy to use and less sensitive to the training data compared to the decision tree.
- It is more accurate than the decision tree algorithm.
- It is effective in handling large datasets that have many attributes.
- It can handle missing data, outliers, and noisy features.
Disadvantages of Random Forest Regression
- The model can also be difficult to interpret.
- This algorithm may require some domain expertise to choose the appropriate parameters like the number of decision trees, the maximum depth of each tree, and the number of features to consider at each split.
- It is computationally expensive, especially for large datasets.
- It may suffer from overfitting if the model is too complex or the number of decision trees is too high.
Conclusion
Random Forest Regression has become a powerful tool for continuous prediction tasks, with advantages over traditional decision trees. Its capability to handle high-dimensional data, capture complex relationships, and reduce overfitting has made it a popular choice for a variety of applications. Python’s scikit-learn library enables the implementation, optimization, and evaluation of Random Forest Regression models, making it an accessible and effective technique for machine learning practitioners.
Frequently Asked Question(FAQ’s)
1. What is Random Forest Regression Python?
Random Forest Regression Python is an ensemble learning method that uses multiple decision trees to make predictions. It is a powerful and versatile algorithm that is well-suited for regression tasks.
2. What is the use of random forest regression?
Random Forest Regression can be used to predict a variety of target variables, including prices, sales, customer churn, and more. It is a robust algorithm that is not easily overfitted, making it a good choice for real-world applications.
3. What is the difference between random forest and regression?
Random Forest is an ensemble learning method, while regression is a type of supervised learning algorithm. Random Forest uses multiple decision trees to make predictions, while regression uses a single model to make predictions.
4. How do you tune the hyperparameters of Random Forest Regression?
There are several methods for tuning the hyperparameters of Random Forest Regression, such as:
- Grid search: Grid search involves systematically trying different combinations of hyperparameter values to find the best combination.
- Random search: Random search randomly samples different combinations of hyperparameter values to find a good combination.
5. Why is random forest better than regression?
Random Forest is generally more accurate and robust than regression. It is also less prone to overfitting, which means that it is more likely to generalize well to new data.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...