Access and Non Access Modifiers in Java
Last Updated :
05 May, 2022
Java provides a rich set of modifiers. They are used to control access mechanisms and also provide information about class functionalities to JVM. They are divided into two categories namely:
- Access modifiers
- Non-access modifiers

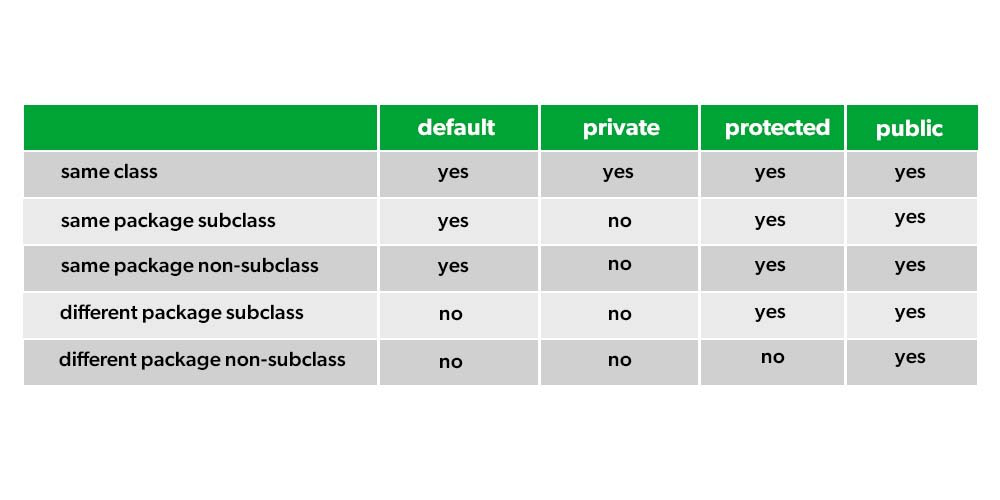
Java’s access modifiers are public, private, and protected. Java also defines a default access level (called package-private).
- public: When a member of a class is modified by public, then that member can be accessed by any other code.
- private: When a member of a class is specified as private, then that member can only be accessed by other members of its class.
- default: It is also referred to as no modifier. Whenever we do not use any access modifier it is treated as default where this allows us to access within a class, within a subclass, and also non-sun class within a package but when the package differs now be it a subclass or non-class we are not able to access.
- protected: With the above default keyword we were facing an issue as we are getting closer to the real world with the above default modifier but there was a constriction as we are not able to access class sub-class from a different package. So protected access modifier allows not only to access class be it subclass or non-sub class but allows us to access subclass of the different package which brings us very close to a real-world and hence strong understanding of inheritance is required for understanding and implementing this keyword.
Types of Access Modifiers
Note: Now you can understand why main( ) has always been preceded by the public modifier. It is called by code that is outside the program—that is, by the Java run-time system. When no access modifier is used, then by default the member of a class is public within its own package, but cannot be accessed outside of its package. protected applies only when inheritance is involved.
class GFG
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Insert your code here
}
}
In java, we have 7 non-access modifiers. They are used with classes, methods, variables, constructors, etc to provide information about their behavior to JVM. They are as follows:
- static
- final
- abstract
- synchronized
- transient
- volatile
- native
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...