Abstract Class in Java
Last Updated :
26 Sep, 2023
In Java, abstract class is declared with the abstract keyword. It may have both abstract and non-abstract methods(methods with bodies). An abstract is a Java modifier applicable for classes and methods in Java but not for Variables. In this article, we will learn the use of abstract classes in Java.
What is Abstract Class in Java?
Java abstract class is a class that can not be initiated by itself, it needs to be subclassed by another class to use its properties. An abstract class is declared using the “abstract” keyword in its class definition.
Illustration of Abstract class
abstract class Shape
{
int color;
// An abstract function
abstract void draw();
}
In Java, the following some important observations about abstract classes are as follows:
- An instance of an abstract class can not be created.
- Constructors are allowed.
- We can have an abstract class without any abstract method.
- There can be a final method in abstract class but any abstract method in class(abstract class) can not be declared as final or in simpler terms final method can not be abstract itself as it will yield an error: “Illegal combination of modifiers: abstract and final”
- We can define static methods in an abstract class
- We can use the abstract keyword for declaring top-level classes (Outer class) as well as inner classes as abstract
- If a class contains at least one abstract method then compulsory should declare a class as abstract
- If the Child class is unable to provide implementation to all abstract methods of the Parent class then we should declare that Child class as abstract so that the next level Child class should provide implementation to the remaining abstract method
Examples of Java Abstract Class
1. Example of Abstract Class that has Abstract method
Below is the implementation of the above topic:
Java
abstract class Sunstar {
abstract void printInfo();
}
class Employee extends Sunstar {
void printInfo()
{
String name = "avinash";
int age = 21;
float salary = 222.2F;
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(salary);
}
}
class Base {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Sunstar s = new Employee();
s.printInfo();
}
}
|
2. Abstract Class having constructor, data member, and methods
Elements abstract class can have
- data member
- abstract method
- method body (non-abstract method)
- constructor
- main() method.
Below is the implementation of the above topic:
Java
import java.io.*;
abstract class Subject {
Subject() {
System.out.println("Learning Subject");
}
abstract void syllabus();
void Learn(){
System.out.println("Preparing Right Now!");
}
}
class IT extends Subject {
void syllabus(){
System.out.println("C , Java , C++");
}
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Subject x=new IT();
x.syllabus();
x.Learn();
}
}
|
Output
Learning Subject
C , Java , C++
Preparing Right Now!
Properties of Abstract class
Let us elaborate on these observations and do justify them with help of clean java programs as follows.
Observation 1
In Java, just like in C++ an instance of an abstract class cannot be created, we can have references to abstract class type though. It is as shown below via the clean Java program.
Example
Java
abstract class Base {
abstract void fun();
}
class Derived extends Base {
void fun()
{
System.out.println("Derived fun() called");
}
}
class Main {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Base b = new Derived();
b.fun();
}
}
|
Output
Derived fun() called
Observation 2
Like C++, an abstract class can contain constructors in Java. And a constructor of an abstract class is called when an instance of an inherited class is created. It is as shown in the program below as follows:
Example:
Java
abstract class Base {
Base()
{
System.out.println("Base Constructor Called");
}
abstract void fun();
}
class Derived extends Base {
Derived()
{
System.out.println("Derived Constructor Called");
}
void fun()
{
System.out.println("Derived fun() called");
}
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Derived d = new Derived();
d.fun();
}
}
|
Output
Base Constructor Called
Derived Constructor Called
Derived fun() called
Observation 3
In Java, we can have an abstract class without any abstract method. This allows us to create classes that cannot be instantiated but can only be inherited. It is as shown below as follows with help of a clean java program.
Example:
Java
abstract class Base {
void fun()
{
System.out.println(
"Function of Base class is called");
}
}
class Derived extends Base {
}
class Main {
public static void main(String args[])
{
Derived d = new Derived();
d.fun();
}
}
|
Output
Function of Base class is called
Observation 4
Abstract classes can also have final methods (methods that cannot be overridden)
Example:
Java
abstract class Base {
final void fun()
{
System.out.println("Base fun() called");
}
}
class Derived extends Base {
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
{
Base b = new Derived();
b.fun();
}
}
}
|
Observation 5
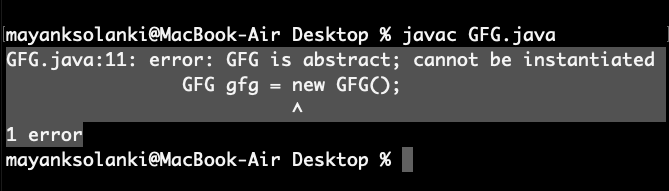
For any abstract java class we are not allowed to create an object i.e., for an abstract class instantiation is not possible.
Java
abstract class GFG {
public static void main(String args[])
{
GFG gfg = new GFG();
}
}
|
Output:
Observation 6
Similar to the interface we can define static methods in an abstract class that can be called independently without an object.
Java
abstract class Helper {
static void demofun()
{
System.out.println("Geeks for Geeks");
}
}
public class GFG extends Helper {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Helper.demofun();
}
}
|
Observation 7
We can use the abstract keyword for declaring top-level classes (Outer class) as well as inner classes as abstract
Java
import java.io.*;
abstract class B {
abstract class C {
abstract void myAbstractMethod();
}
}
class D extends B {
class E extends C {
void myAbstractMethod()
{
System.out.println(
"Inside abstract method implementation");
}
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[])
{
D outer = new D();
D.E inner = outer.new E();
inner.myAbstractMethod();
}
}
|
Output
Inside abstract method implementation
Observation 8
If a class contains at least one abstract method then compulsory that we should declare the class as abstract otherwise we will get a compile-time error ,If a class contains at least one abstract method then, implementation is not complete for that class, and hence it is not recommended to create an object so in order to restrict object creation for such partial classes we use abstract keyword.
Java
import java.io.*;
abstract class Demo {
abstract void m1();
}
class Child extends Demo {
public void m1()
{
System.out.print("Hello");
}
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Child c = new Child();
c.m1();
}
}
|
Observation 9
If the Child class is unable to provide implementation to all abstract methods of the Parent class then we should declare that Child class as abstract so that the next level Child class should provide implementation to the remaining abstract method.
Java
import java.io.*;
abstract class Demo {
abstract void m1();
abstract void m2();
abstract void m3();
}
abstract class FirstChild extends Demo {
public void m1() {
System.out.println("Inside m1");
}
}
class SecondChild extends FirstChild {
public void m2() {
System.out.println("Inside m2");
}
public void m3() {
System.out.println("Inside m3");
}
}
class GFG {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
SecondChild s = new SecondChild();
s.m1();
s.m2();
s.m3();
}
}
|
Output
Inside m1
Inside m2
Inside m3
In C++, if a class has at least one pure virtual function, then the class becomes abstract. Unlike C++, in Java, a separate keyword abstract is used to make a class abstract.
Conclusion
Points to remember from this article are mentioned below:
- An abstract class is a class that can not be initiated by itself, it needs to be subclassed by another class to use its properties.
- An abstract class can be created using “abstract” keywords.
- We can have an abstract class without any abstract method.
FAQs of Abstract class
1. What is an abstract class in Java?
An abstract class in Java is a class that can not be initiated on its own but can be used as a subclass by another class.
2. What is the abstract class purpose?
The main purpose of the abstract class is to create a base class from which many other classes can be derived.
3. What is the main advantage of abstract class?
An abstract class provides the provides of data hiding in Java.
4. Why abstract class is faster than interface?
An abstract class is faster than an interface because the interface involves a search before calling any overridden method in Java whereas abstract class can be directly used.
Also, Read
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...