The final method in Java is used as a non-access modifier applicable only to a variable, a method, or a class. It is used to restrict a user in Java.
The following are different contexts where the final is used:
- Variable
- Method
- Class

Characteristics of final keyword in Java:
In Java, the final keyword is used to indicate that a variable, method, or class cannot be modified or extended. Here are some of its characteristics:
- Final variables: When a variable is declared as final, its value cannot be changed once it has been initialized. This is useful for declaring constants or other values that should not be modified.
- Final methods: When a method is declared as final, it cannot be overridden by a subclass. This is useful for methods that are part of a class’s public API and should not be modified by subclasses.
- Final classes: When a class is declared as final, it cannot be extended by a subclass. This is useful for classes that are intended to be used as is and should not be modified or extended.
- Initialization: Final variables must be initialized either at the time of declaration or in the constructor of the class. This ensures that the value of the variable is set and cannot be changed.
- Performance: The use of a final can sometimes improve performance, as the compiler can optimize the code more effectively when it knows that a variable or method cannot be changed.
- Security: The final can help improve security by preventing malicious code from modifying sensitive data or behavior.
Overall, the final keyword is a useful tool for improving code quality and ensuring that certain aspects of a program cannot be modified or extended. By declaring variables, methods, and classes as final, developers can write more secure, robust, and maintainable code.
Java Final Variable
When a variable is declared with the final keyword, its value can’t be changed, essentially, a constant. This also means that you must initialize a final variable.
If the final variable is a reference, this means that the variable cannot be re-bound to reference another object, but the internal state of the object pointed by that reference variable can be changed i.e. you can add or remove elements from the final array or final collection.
It is good practice to represent final variables in all uppercase, using underscore to separate words.
Example:
Java
public class ConstantExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Define a constant variable PI
final double PI = 3.14159;
// Print the value of PI
System.out.println("Value of PI: " + PI);
}
}
Output:
Value of PI: 3.14159
Different Methods of Using Final Variable
Let’s see different methods that we can use final variable in Java.
1. final Variable
Example:
// Final variable
final int THRESHOLD = 5;
2. Blank final Variable
Example:
// Blank final variable
final int THRESHOLD;
3. Static Blank final Variable
Example:
// Final static variable PI
static final double PI = 3.141592653589793;
4. Static final Variable
Example:
// Blank final static variable
static final double PI;
Initializing a final Variable
We must initialize a final variable, otherwise, the compiler will throw a compile-time error. A final variable can only be initialized once, either via an initializer or an assignment statement. There are three ways to initialize a final variable:
- You can initialize a final variable when it is declared. This approach is the most common. A final variable is called a blank final variable if it is not initialized while declaration. Below are the two ways to initialize a blank final variable.
- A blank final variable can be initialized inside an instance-initializer block or the constructor. If you have more than one constructor in your class then it must be initialized in all of them, otherwise, a compile-time error will be thrown.
- A blank final static variable can be initialized inside a static block.
Let us see these two different ways of initializing a final variable
Example:
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate Different
// Ways of Initializing a final Variable
// Main class
class GFG {
// a final variable
// direct initialize
final int THRESHOLD = 5;
// a blank final variable
final int CAPACITY;
// another blank final variable
final int MINIMUM;
// a final static variable PI
// direct initialize
static final double PI = 3.141592653589793;
// a blank final static variable
static final double EULERCONSTANT;
// instance initializer block for
// initializing CAPACITY
{
CAPACITY = 25;
}
// static initializer block for
// initializing EULERCONSTANT
static{
EULERCONSTANT = 2.3;
}
// constructor for initializing MINIMUM
// Note that if there are more than one
// constructor, you must initialize MINIMUM
// in them also
public GFG()
{
MINIMUM = -1;
}
}
There was no main method in the above code as it was simply for illustration purposes to get a better understanding to draw conclusions:
Observation 1: When to use a final variable?
The only difference between a normal variable and a final variable is that we can re-assign the value to a normal variable but we cannot change the value of a final variable once assigned. Hence final variables must be used only for the values that we want to remain constant throughout the execution of the program.
Observation 2: Reference final variable.
When a final variable is a reference to an object, then this final variable is called the reference final variable. For example, a final StringBuffer variable looks defined below as follows:
final StringBuffer sb;
As we all know a final variable cannot be re-assign. But in the case of a reference final variable, the internal state of the object pointed by that reference variable can be changed. Note that this is not re-assigning.
This property of the final is called non-transitivity. To understand what is meant by the internal state of the object as shown in the below example as follows:
Example 1:
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate
// Reference of Final Variable
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating an object of StringBuilder class
// Final reference variable
final StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("Geeks");
// Printing the element in StringBuilder object
System.out.println(sb);
// changing internal state of object reference by
// final reference variable sb
sb.append("ForGeeks");
// Again printing the element in StringBuilder
// object after appending above element in it
System.out.println(sb);
}
}
OutputGeeks
GeeksForGeeks
The non-transitivity property also applies to arrays, because arrays are objects in Java. Arrays with the final keyword are also called final arrays.
Note: As discussed above, a final variable cannot be reassign, doing it will throw compile-time error.
Example 2:
Java
// Java Program to Demonstrate Re-assigning
// Final Variable will throw Compile-time Error
// Main class
class GFG {
// Declaring and customly initializing
// static final variable
static final int CAPACITY = 4;
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
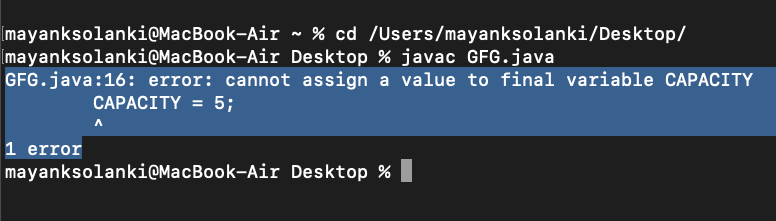
// Re-assigning final variable
// will throw compile-time error
CAPACITY = 5;
}
}
Output:
Remember: When a final variable is created inside a method/constructor/block, it is called local final variable, and it must initialize once where it is created. See below program for local final variable.
Example:
Java
// Java program to demonstrate
// local final variable
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String args[])
{
// Declaring local final variable
final int i;
// Now initializing it with integer value
i = 20;
// Printing the value on console
System.out.println(i);
}
}
Remember these key points as perceived before moving forward as listed below as follows:
- Note the difference between C++ const variables and Java final variables. const variables in C++ must be assigned a value when declared. For final variables in Java, it is not necessary as we see in the above examples. A final variable can be assigned value later, but only once.
- final with foreach loop: final with for-each statement is a legal statement.
Example:
Java
// Java Program to demonstrate Final
// with for-each Statement
// Main class
class GFG {
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Declaring and initializing
// custom integer array
int arr[] = { 1, 2, 3 };
// final with for-each statement
// legal statement
for (final int i : arr)
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
}
Output explanation: Since the “i” variable goes out of scope with each iteration of the loop, it is re-declared each iteration, allowing the same token (i) to be used to represent multiple variables.
Example:
Java
public class Example {
public static void main(String[] args) {
final int VALUE = 10; // declaring a final variable
System.out.println("The value is: " + VALUE);
// VALUE = 20; // uncommenting this line will cause a compiler error
// System.out.println("The new value is: " + VALUE);
final String MESSAGE = "Hello, world!"; // declaring a final variable
System.out.println(MESSAGE);
MyClass myObj = new MyClass();
myObj.printMessage();
myObj.printFinalMessage();
// MyOtherClass extends MyClass {} // uncommenting this line will cause a compiler error
}
}
class MyClass {
final String message = "Hello!"; // declaring a final instance variable
void printMessage() {
System.out.println(message);
}
void printFinalMessage() {
final String finalMessage = "Hello, final!";
System.out.println(finalMessage);
}
}
final class MyOtherClass { // declaring a final class
// ...
}
OutputThe value is: 10
Hello, world!
Hello!
Hello, final!
Java Final classes
When a class is declared with the final keyword in Java, it is called a final class. A final class cannot be extended(inherited).
There are two uses of a final class:
Usage 1: One is definitely to prevent inheritance, as final classes cannot be extended. For example, all Wrapper Classes like Integer, Float, etc. are final classes. We can not extend them.
final class A
{
// methods and fields
}
// The following class is illegal
class B extends A
{
// COMPILE-ERROR! Can't subclass A
}
Usage 2: The other use of final with classes is to create an immutable class like the predefined String class. One can not make a class immutable without making it final.
Java Final Method
When a method is declared with final keyword, it is called a final method in Java. A final method cannot be overridden.
The Object class does this—a number of its methods are final. We must declare methods with the final keyword for which we are required to follow the same implementation throughout all the derived classes.
Illustration: Final keyword with a method
class A
{
final void m1()
{
System.out.println("This is a final method.");
}
}
class B extends A
{
void m1()
{
// Compile-error! We can not override
System.out.println("Illegal!");
}
}
Advantages of final Keyword in Java:
The final keyword in Java provides several advantages, including:
- Ensuring immutability: When a variable or reference is marked as final, its value cannot be changed once it is assigned. This helps ensure that data is immutable and cannot be accidentally or maliciously modified.
- Improving performance: The use of the final can sometimes help improve performance, as the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) can optimize code more effectively when it knows that certain values or references cannot be changed.
- Making code easier to understand: By declaring variables, methods, or classes as final, developers can make their code easier to understand and reason about. When a value or reference is marked as final, it is clear that it will not change, which can simplify code analysis and debugging.
- Promoting code reuse: By declaring methods as final, developers can prevent subclasses from overriding them. This can help promote code reuse and reduce duplication, as subclasses must use the parent class’s implementation of the method.
- Enhancing security: The use of final can help enhance security by preventing malicious code from modifying sensitive data or behavior.
Overall, the final keyword is a useful tool for improving code quality and ensuring that certain aspects of a program cannot be modified. By declaring variables, methods, and classes as final, developers can write more secure, robust, and maintainable code.
For more examples and behavior of final methods and final classes, please see Using final with inheritance. Please see the abstract in java article for differences between the final and the abstract.
Related Interview Question(Important): Difference between final, finally, and finalize in Java
Conclusion
The final Keyword in Java is a method to make user-restricted variables, methods, or classes. In this tutorial, we cover Java’s final keyword in detail and understand all its contexts.
The contexts are explained with Java programs in examples, providing a complete understanding of the subject.
Java Final Keyword – FAQs
What is a final method in Java?
A final method in Java is a method declared with the final keyword, meaning that its implementation cannot be overridden by subclasses.
Is final method inherited?
No, in Java a final method can not be inherited by a subclass. This means that a subclass can not override a final method.
What is the final keyword and static keyword in Java?
Final Keyword: It is used to declare variables, methods, or classes as unmodifiable.
Static keyword: It is used to declare class members (variables and methods) that belong to the class itself, not individual objects.
Can we write final keyword with a string in Java?
Yes, you can declare a variable with final keyword and assign string literal to it.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...