Find if an array of strings can be chained to form a circle | Set 1
Last Updated :
15 Feb, 2023
Given an array of strings, find if the given strings can be chained to form a circle. A string X can be put before another string Y in circle if the last character of X is same as first character of Y.
Examples:
Input: arr[] = {"geek", "king"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
Note that the last character of first string is same
as first character of second string and vice versa is
also true.
Input: arr[] = {"for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "for", "rig", "geek"
and "kaf"
Input: arr[] = {"aab", "bac", "aaa", "cda"}
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "aaa", "aab", "bac"
and "cda"
Input: arr[] = {"aaa", "bbb", "baa", "aab"};
Output: Yes, the given strings can be chained.
The strings can be chained as "aaa", "aab", "bbb"
and "baa"
Input: arr[] = {"aaa"};
Output: Yes
Input: arr[] = {"aaa", "bbb"};
Output: No
Input : arr[] = ["abc", "efg", "cde", "ghi", "ija"]
Output : Yes
These strings can be reordered as, “abc”, “cde”, “efg”,
“ghi”, “ija”
Input : arr[] = [“ijk”, “kji”, “abc”, “cba”]
Output : No
The idea is to create a directed graph of all characters and then find if there is an eulerian circuit in the graph or not.
Graph representation of some string arrays are given in below diagram,
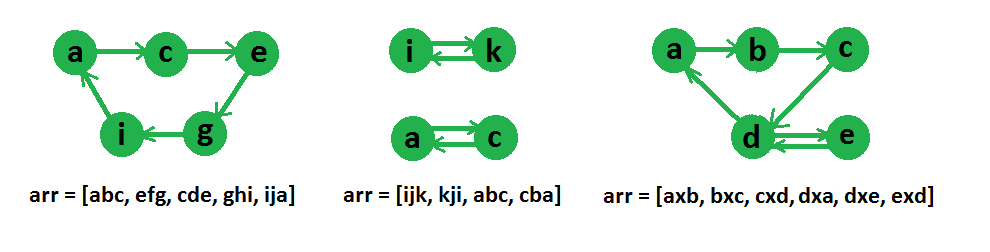
If there is an eulerian circuit, then chain can be formed, otherwise not.
Note that a directed graph has eulerian circuit only if in degree and out degree of every vertex is same, and all non-zero degree vertices form a single strongly connected component.
Following are detailed steps of the algorithm.
- Create a directed graph g with number of vertices equal to the size of alphabet. We have created a graph with 26 vertices in the below program.
- Do following for every string in the given array of strings.
- …..a) Add an edge from first character to last character of the given graph.
- If the created graph has eulerian circuit, then return true, else return false.
Following are C++ and Python implementations of the above algorithm.
C++
#include<iostream>
#include <list>
#define CHARS 26
using namespace std;
class Graph
{
int V;
list<int> *adj;
int *in;
public:
Graph(int V);
~Graph() { delete [] adj; delete [] in; }
void addEdge(int v, int w) { adj[v].push_back(w); (in[w])++; }
bool isEulerianCycle();
bool isSC();
void DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[]);
Graph getTranspose();
};
Graph::Graph(int V)
{
this->V = V;
adj = new list<int>[V];
in = new int[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
in[i] = 0;
}
bool Graph::isEulerianCycle()
{
if (isSC() == false)
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
void Graph::DFSUtil(int v, bool visited[])
{
visited[v] = true;
list<int>::iterator i;
for (i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
if (!visited[*i])
DFSUtil(*i, visited);
}
Graph Graph::getTranspose()
{
Graph g(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
list<int>::iterator i;
for(i = adj[v].begin(); i != adj[v].end(); ++i)
{
g.adj[*i].push_back(v);
(g.in[v])++;
}
}
return g;
}
bool Graph::isSC()
{
bool visited[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
int n;
for (n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj[n].size() > 0)
break;
DFSUtil(n, visited);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
Graph gr = getTranspose();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].size() > 0 && visited[i] == false)
return false;
return true;
}
bool canBeChained(string arr[], int n)
{
Graph g(CHARS);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
string s = arr[i];
g.addEdge(s[0]-'a', s[s.length()-1]-'a');
}
return g.isEulerianCycle();
}
int main()
{
string arr1[] = {"for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"};
int n1 = sizeof(arr1)/sizeof(arr1[0]);
canBeChained(arr1, n1)? cout << "Can be chained \n" :
cout << "Can't be chained \n";
string arr2[] = {"aab", "abb"};
int n2 = sizeof(arr2)/sizeof(arr2[0]);
canBeChained(arr2, n2)? cout << "Can be chained \n" :
cout << "Can't be chained \n";
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
class GFG{
static final int CHARS = 26;
int V;
List<List<Integer>> adj;
int[] in;
GFG(int V)
{
this.V = V;
in = new int[V];
adj = new ArrayList<>(CHARS);
for(int i = 0; i < CHARS; i++)
{
adj.add(i, new ArrayList<>());
}
}
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj.get(v).add(w);
in[w]++;
}
boolean isEulerianCycle()
{
if (!isSC())
return false;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj.get(i).size() != in[i])
return false;
return true;
}
boolean isSC()
{
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
int n;
for(n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj.get(n).size() > 0)
break;
DFSUtil(n, visited);
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj.get(i).size() > 0 && !visited[i])
return false;
GFG gr = getTranspose();
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj.get(i).size() > 0 && !visited[i])
return false;
return true;
}
void DFSUtil(int v, boolean[] visited)
{
visited[v] = true;
for(Integer i : adj.get(v))
if (!visited[i])
{
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
GFG getTranspose()
{
GFG g = new GFG(V);
for(int v = 0; v < V; v++)
{
for(Integer i : adj.get(v))
{
g.adj.get(i).add(v);
g.in[v]++;
}
}
return g;
}
static boolean canBeChained(String[] arr, int n)
{
GFG g = new GFG(CHARS);
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
String s = arr[i];
g.addEdge(s.charAt(0) - 'a',
s.charAt(s.length() - 1) - 'a');
}
return g.isEulerianCycle();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
String[] arr1 = { "for", "geek",
"rig", "kaf" };
int n1 = arr1.length;
System.out.println((canBeChained(arr1, n1) ?
"Can be chained " :
"Can't be chained "));
String[] arr2 = { "aab", "abb" };
int n2 = arr2.length;
System.out.println((canBeChained(arr2, n2) ?
"Can be chained " :
"Can't be chained "));
}
}
|
Python3
CHARS = 26
class Graph(object):
def __init__(self, V):
self.V = V
self.adj = [[] for x in range(V)]
self.inp = [0] * V
def addEdge(self, v, w):
self.adj[v].append(w)
self.inp[w]+=1
def isSC(self):
visited = [False] * self.V
n = 0
for n in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[n]) > 0:
break
self.DFSUtil(n, visited)
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[i]) > 0 and visited[i] == False:
return False
gr = self.getTranspose()
for i in range(self.V):
visited[i] = False
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited)
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[i]) > 0 and visited[i] == False:
return False
return True
def isEulerianCycle(self):
if self.isSC() == False:
return False
for i in range(self.V):
if len(self.adj[i]) != self.inp[i]:
return False
return True
def DFSUtil(self, v, visited):
visited[v] = True
for i in range(len(self.adj[v])):
if not visited[self.adj[v][i]]:
self.DFSUtil(self.adj[v][i], visited)
def getTranspose(self):
g = Graph(self.V)
for v in range(self.V):
for i in range(len(self.adj[v])):
g.adj[self.adj[v][i]].append(v)
g.inp[v]+=1
return g
def canBeChained(arr, n):
g = Graph(CHARS)
for i in range(n):
s = arr[i]
g.addEdge(ord(s[0])-ord('a'), ord(s[len(s)-1])-ord('a'))
return g.isEulerianCycle()
arr1 = ["for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"]
n1 = len(arr1)
if canBeChained(arr1, n1):
print ("Can be chained")
else:
print ("Cant be chained")
arr2 = ["aab", "abb"]
n2 = len(arr2)
if canBeChained(arr2, n2):
print ("Can be chained")
else:
print ("Can't be chained")
|
C#
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
public class GFG {
static readonly int CHARS = 26;
int V;
List<List<int> > adj;
int[] ind;
GFG(int V)
{
this.V = V;
ind = new int[V];
adj = new List<List<int> >(CHARS);
for (int i = 0; i < CHARS; i++) {
adj.Add(new List<int>());
}
}
void addEdge(int v, int w)
{
adj[v].Add(w);
ind[w]++;
}
bool isEulerianCycle()
{
if (!isSC())
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count != ind[i])
return false;
return true;
}
bool isSC()
{
bool[] visited = new bool[V];
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
int n;
for (n = 0; n < V; n++)
if (adj[n].Count > 0)
break;
DFSUtil(n, visited);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count > 0 && !visited[i])
return false;
GFG gr = getTranspose();
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
visited[i] = false;
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
if (adj[i].Count > 0 && !visited[i])
return false;
return true;
}
void DFSUtil(int v, bool[] visited)
{
visited[v] = true;
foreach(int i in adj[v]) if (!visited[i])
{
DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
GFG getTranspose()
{
GFG g = new GFG(V);
for (int v = 0; v < V; v++) {
foreach(int i in adj[v])
{
g.adj[i].Add(v);
g.ind[v]++;
}
}
return g;
}
static bool canBeChained(String[] arr, int n)
{
GFG g = new GFG(CHARS);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String s = arr[i];
g.addEdge(s[0] - 'a', s[s.Length - 1] - 'a');
}
return g.isEulerianCycle();
}
static public void Main()
{
String[] arr1 = { "for", "geek", "rig", "kaf" };
int n1 = arr1.Length;
Console.WriteLine((canBeChained(arr1, n1)
? "Can be chained "
: "Can't be chained "));
String[] arr2 = { "aab", "abb" };
int n2 = arr2.Length;
Console.WriteLine((canBeChained(arr2, n2)
? "Can be chained "
: "Can't be chained "));
}
}
|
Javascript
let CHARS = 26;
class Graph {
constructor(V) {
this.V = V;
this.adj = Array.from(Array(V), () => new Array());
this.in = new Array(V);
for (let i = 0; i < V; i++) {
this.in[i] = 0;
}
}
addEdge(v, w) {
this.adj[v].push(w);
this.in[w]++;
}
isEulerianCycle() {
if (this.isSC() == false) return false;
for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
if (this.adj[i].length != this.in[i]) return false;
return true;
}
isSC() {
let visited = new Array(this.V);
for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) visited[i] = false;
let n;
for (n = 0; n < this.V; n++) if (this.adj[n].length > 0) break;
this.DFSUtil(n, visited);
for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
if (this.adj[i].length > 0 && visited[i] == false) return false;
let gr = this.getTranspose();
for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++) visited[i] = false;
gr.DFSUtil(n, visited);
for (let i = 0; i < this.V; i++)
if (this.adj[i].length > 0 && visited[i] == false) return false;
return true;
}
DFSUtil(v, visited) {
visited[v] = true;
for (let j in this.adj[v]) {
let i = this.adj[v][j];
if (!visited[i]) {
this.DFSUtil(i, visited);
}
}
}
getTranspose() {
let g = new Graph(this.V);
for (let v = 0; v < this.V; v++) {
for (let j in this.adj[v]) {
let i = this.adj[v][j];
g.adj[i].push(v);
g.in[v]++;
}
}
return g;
}
}
function canBeChained(arr, n) {
let g = new Graph(CHARS);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
let s = arr[i];
g.addEdge(
s[0].charCodeAt() - "a".charCodeAt(),
s[s.length - 1].charCodeAt() - "a".charCodeAt()
);
}
return g.isEulerianCycle();
}
let arr1 = ["for", "geek", "rig", "kaf"];
let n1 = arr1.length;
canBeChained(arr1, n1)
? console.log("Can be chained")
: console.log("Can't be chained");
let arr2 = ["aab", "abb"];
let n2 = arr2.length;
canBeChained(arr2, n2)
? console.log("Can be chained")
: console.log("Can't be chained");
|
Output
Can be chained
Can't be chained
Time Complexity: O(n*m) where n is max of sizes of arr1 and arr2 and m is maximum size word in arr1 or arr2.
Auxiliary space: O(max(n,m))
Find if an array of strings can be chained to form a circle | Set 2
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...