Heap Sort – Data Structures and Algorithms Tutorials
Last Updated :
29 Mar, 2024
Heap sort is a comparison-based sorting technique based on Binary Heap data structure. It is similar to the selection sort where we first find the minimum element and place the minimum element at the beginning. Repeat the same process for the remaining elements.
Heap Sort Algorithm
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
First convert the array into heap data structure using heapify, then one by one delete the root node of the Max-heap and replace it with the last node in the heap and then heapify the root of the heap. Repeat this process until size of heap is greater than 1.
- Build a heap from the given input array.
- Repeat the following steps until the heap contains only one element:
- Swap the root element of the heap (which is the largest element) with the last element of the heap.
- Remove the last element of the heap (which is now in the correct position).
- Heapify the remaining elements of the heap.
- The sorted array is obtained by reversing the order of the elements in the input array.
Detailed Working of Heap Sort
To understand heap sort more clearly, let’s take an unsorted array and try to sort it using heap sort.
Consider the array: arr[] = {4, 10, 3, 5, 1}.
Build Complete Binary Tree: Build a complete binary tree from the array.
.webp)
Heap sort algorithm | Build Complete Binary Tree
Transform into max heap: After that, the task is to construct a tree from that unsorted array and try to convert it into max heap.
- To transform a heap into a max-heap, the parent node should always be greater than or equal to the child nodes
- Here, in this example, as the parent node 4 is smaller than the child node 10, thus, swap them to build a max-heap.
- Now, 4 as a parent is smaller than the child 5, thus swap both of these again and the resulted heap and array should be like this:
.webp)
Heap sort algorithm | Max Heapify constructed binary tree
Perform heap sort: Remove the maximum element in each step (i.e., move it to the end position and remove that) and then consider the remaining elements and transform it into a max heap.
- Delete the root element (10) from the max heap. In order to delete this node, try to swap it with the last node, i.e. (1). After removing the root element, again heapify it to convert it into max heap.
- Resulted heap and array should look like this:
.webp)
Heap sort algorithm | Remove maximum from root and max heapify
- Repeat the above steps and it will look like the following:
.webp)
Heap sort algorithm | Remove next maximum from root nad max heapify
- Now remove the root (i.e. 3) again and perform heapify.
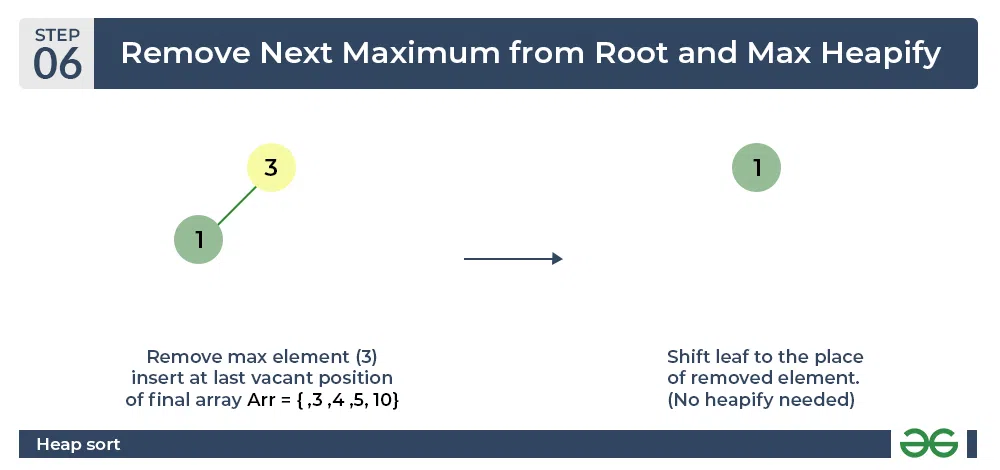
Heap sort algorithm | Repeat previous step
- Now when the root is removed once again it is sorted. and the sorted array will be like arr[] = {1, 3, 4, 5, 10}.
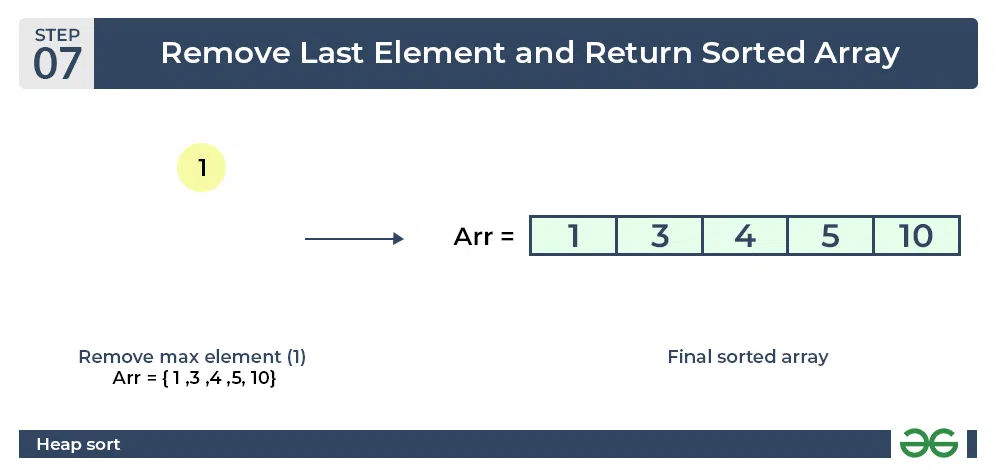
Heap sort algorithm | Final sorted array
Implementation of Heap Sort
C++
// C++ program for implementation of Heap Sort
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i
// which is an index in arr[].
// n is size of heap
void heapify(int arr[], int N, int i)
{
// Initialize largest as root
int largest = i;
// left = 2*i + 1
int l = 2 * i + 1;
// right = 2*i + 2
int r = 2 * i + 2;
// If left child is larger than root
if (l < N && arr[l] > arr[largest])
largest = l;
// If right child is larger than largest
// so far
if (r < N && arr[r] > arr[largest])
largest = r;
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
swap(arr[i], arr[largest]);
// Recursively heapify the affected
// sub-tree
heapify(arr, N, largest);
}
}
// Main function to do heap sort
void heapSort(int arr[], int N)
{
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for (int i = N / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, N, i);
// One by one extract an element
// from heap
for (int i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
swap(arr[0], arr[i]);
// call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// A utility function to print array of size n
void printArray(int arr[], int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
cout << arr[i] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
heapSort(arr, N);
cout << "Sorted array is \n";
printArray(arr, N);
}
// Heap Sort in C
#include <stdio.h>
// Function to swap the position of two elements
void swap(int* a, int* b)
{
int temp = *a;
*a = *b;
*b = temp;
}
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i
// which is an index in arr[].
// n is size of heap
void heapify(int arr[], int N, int i)
{
// Find largest among root,
// left child and right child
// Initialize largest as root
int largest = i;
// left = 2*i + 1
int left = 2 * i + 1;
// right = 2*i + 2
int right = 2 * i + 2;
// If left child is larger than root
if (left < N && arr[left] > arr[largest])
largest = left;
// If right child is larger than largest
// so far
if (right < N && arr[right] > arr[largest])
largest = right;
// Swap and continue heapifying
// if root is not largest
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
swap(&arr[i], &arr[largest]);
// Recursively heapify the affected
// sub-tree
heapify(arr, N, largest);
}
}
// Main function to do heap sort
void heapSort(int arr[], int N)
{
// Build max heap
for (int i = N / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, N, i);
// Heap sort
for (int i = N - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
swap(&arr[0], &arr[i]);
// Heapify root element
// to get highest element at
// root again
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// A utility function to print array of size n
void printArray(int arr[], int N)
{
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
printf("\n");
}
// Driver's code
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
// Function call
heapSort(arr, N);
printf("Sorted array is\n");
printArray(arr, N);
}
// This code is contributed by _i_plus_plus_.
// Java program for implementation of Heap Sort
public class HeapSort {
public void sort(int arr[])
{
int N = arr.length;
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for (int i = N / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, N, i);
// One by one extract an element from heap
for (int i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i which is
// an index in arr[]. n is size of heap
void heapify(int arr[], int N, int i)
{
int largest = i; // Initialize largest as root
int l = 2 * i + 1; // left = 2*i + 1
int r = 2 * i + 2; // right = 2*i + 2
// If left child is larger than root
if (l < N && arr[l] > arr[largest])
largest = l;
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (r < N && arr[r] > arr[largest])
largest = r;
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
int swap = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = swap;
// Recursively heapify the affected sub-tree
heapify(arr, N, largest);
}
}
/* A utility function to print array of size n */
static void printArray(int arr[])
{
int N = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
System.out.println();
}
// Driver's code
public static void main(String args[])
{
int arr[] = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = arr.length;
// Function call
HeapSort ob = new HeapSort();
ob.sort(arr);
System.out.println("Sorted array is");
printArray(arr);
}
}
// C# program for implementation of Heap Sort
using System;
public class HeapSort {
public void sort(int[] arr)
{
int N = arr.Length;
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for (int i = N / 2 - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, N, i);
// One by one extract an element from heap
for (int i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
int temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i which is
// an index in arr[]. n is size of heap
void heapify(int[] arr, int N, int i)
{
int largest = i; // Initialize largest as root
int l = 2 * i + 1; // left = 2*i + 1
int r = 2 * i + 2; // right = 2*i + 2
// If left child is larger than root
if (l < N && arr[l] > arr[largest])
largest = l;
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (r < N && arr[r] > arr[largest])
largest = r;
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
int swap = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = swap;
// Recursively heapify the affected sub-tree
heapify(arr, N, largest);
}
}
/* A utility function to print array of size n */
static void printArray(int[] arr)
{
int N = arr.Length;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
Console.Write(arr[i] + " ");
Console.Read();
}
// Driver's code
public static void Main()
{
int[] arr = { 12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7 };
int N = arr.Length;
// Function call
HeapSort ob = new HeapSort();
ob.sort(arr);
Console.WriteLine("Sorted array is");
printArray(arr);
}
}
// This code is contributed
// by Akanksha Rai(Abby_akku)
// JavaScript program for implementation
// of Heap Sort
function sort( arr)
{
var N = arr.length;
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for (var i = Math.floor(N / 2) - 1; i >= 0; i--)
heapify(arr, N, i);
// One by one extract an element from heap
for (var i = N - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// Move current root to end
var temp = arr[0];
arr[0] = arr[i];
arr[i] = temp;
// call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify(arr, i, 0);
}
}
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i which is
// an index in arr[]. n is size of heap
function heapify(arr, N, i)
{
var largest = i; // Initialize largest as root
var l = 2 * i + 1; // left = 2*i + 1
var r = 2 * i + 2; // right = 2*i + 2
// If left child is larger than root
if (l < N && arr[l] > arr[largest])
largest = l;
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if (r < N && arr[r] > arr[largest])
largest = r;
// If largest is not root
if (largest != i) {
var swap = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[largest];
arr[largest] = swap;
// Recursively heapify the affected sub-tree
heapify(arr, N, largest);
}
}
/* A utility function to print array of size n */
function printArray(arr)
{
var N = arr.length;
for (var i = 0; i < N; ++i)
document.write(arr[i] + " ");
}
var arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7];
var N = arr.length;
sort(arr);
document.write( "Sorted array is");
printArray(arr, N);
// This code is contributed by SoumikMondal
<?php
// Php program for implementation of Heap Sort
// To heapify a subtree rooted with node i which is
// an index in arr[]. n is size of heap
function heapify(&$arr, $N, $i)
{
$largest = $i; // Initialize largest as root
$l = 2*$i + 1; // left = 2*i + 1
$r = 2*$i + 2; // right = 2*i + 2
// If left child is larger than root
if ($l < $N && $arr[$l] > $arr[$largest])
$largest = $l;
// If right child is larger than largest so far
if ($r < $N && $arr[$r] > $arr[$largest])
$largest = $r;
// If largest is not root
if ($largest != $i)
{
$swap = $arr[$i];
$arr[$i] = $arr[$largest];
$arr[$largest] = $swap;
// Recursively heapify the affected sub-tree
heapify($arr, $N, $largest);
}
}
// main function to do heap sort
function heapSort(&$arr, $N)
{
// Build heap (rearrange array)
for ($i = $N / 2 - 1; $i >= 0; $i--)
heapify($arr, $N, $i);
// One by one extract an element from heap
for ($i = $N-1; $i > 0; $i--)
{
// Move current root to end
$temp = $arr[0];
$arr[0] = $arr[$i];
$arr[$i] = $temp;
// call max heapify on the reduced heap
heapify($arr, $i, 0);
}
}
/* A utility function to print array of size n */
function printArray(&$arr, $N)
{
for ($i = 0; $i < $N; ++$i)
echo ($arr[$i]." ") ;
}
// Driver's program
$arr = array(12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7);
$N = sizeof($arr)/sizeof($arr[0]);
// Function call
heapSort($arr, $N);
echo 'Sorted array is ' . "\n";
printArray($arr , $N);
// This code is contributed by Shivi_Aggarwal
?>
# Python program for implementation of heap Sort
# To heapify subtree rooted at index i.
# n is size of heap
def heapify(arr, N, i):
largest = i # Initialize largest as root
l = 2 * i + 1 # left = 2*i + 1
r = 2 * i + 2 # right = 2*i + 2
# See if left child of root exists and is
# greater than root
if l < N and arr[largest] < arr[l]:
largest = l
# See if right child of root exists and is
# greater than root
if r < N and arr[largest] < arr[r]:
largest = r
# Change root, if needed
if largest != i:
arr[i], arr[largest] = arr[largest], arr[i] # swap
# Heapify the root.
heapify(arr, N, largest)
# The main function to sort an array of given size
def heapSort(arr):
N = len(arr)
# Build a maxheap.
for i in range(N//2 - 1, -1, -1):
heapify(arr, N, i)
# One by one extract elements
for i in range(N-1, 0, -1):
arr[i], arr[0] = arr[0], arr[i] # swap
heapify(arr, i, 0)
# Driver's code
if __name__ == '__main__':
arr = [12, 11, 13, 5, 6, 7]
# Function call
heapSort(arr)
N = len(arr)
print("Sorted array is")
for i in range(N):
print("%d" % arr[i], end=" ")
# This code is contributed by Mohit Kumra
OutputSorted array is
5 6 7 11 12 13
Complexity Analysis of Heap Sort
Time Complexity: O(N log N)
Auxiliary Space: O(log n), due to the recursive call stack. However, auxiliary space can be O(1) for iterative implementation.
Important points about Heap Sort:
- Heap sort is an in-place algorithm.
- Its typical implementation is not stable but can be made stable (See this)
- Typically 2-3 times slower than well-implemented QuickSort. The reason for slowness is a lack of locality of reference.
Advantages of Heap Sort:
- Efficient Time Complexity: Heap Sort has a time complexity of O(n log n) in all cases. This makes it efficient for sorting large datasets. The log n factor comes from the height of the binary heap, and it ensures that the algorithm maintains good performance even with a large number of elements.
- Memory Usage – Memory usage can be minimal (by writing an iterative heapify() instead of a recursive one). So apart from what is necessary to hold the initial list of items to be sorted, it needs no additional memory space to work
- Simplicity – It is simpler to understand than other equally efficient sorting algorithms because it does not use advanced computer science concepts such as recursion.
Disadvantages of Heap Sort:
- Costly: Heap sort is costly as the constants are higher compared to merge sort even if the time complexity is O(n Log n) for both.
- Unstable: Heap sort is unstable. It might rearrange the relative order.
- Efficient: Heap Sort is not very efficient when working with highly complex data.
Frequently Asked Questions Related to Heap Sort
Q1. What are the two phases of Heap Sort?
The heap sort algorithm consists of two phases. In the first phase, the array is converted into a max heap. And in the second phase, the highest element is removed (i.e., the one at the tree root) and the remaining elements are used to create a new max heap.
Q2. Why Heap Sort is not stable?
The heap sort algorithm is not a stable algorithm because we swap arr[i] with arr[0] in heapSort() which might change the relative ordering of the equivalent keys.
Q3. Is Heap Sort an example of the “Divide and Conquer” algorithm?
Heap sort is NOT at all a Divide and Conquer algorithm. It uses a heap data structure to efficiently sort its element and not a “divide and conquer approach” to sort the elements.
Q4. Which sorting algorithm is better – Heap sort or Merge Sort?
The answer lies in the comparison of their time complexity and space requirements. The Merge sort is slightly faster than the Heap sort. But on the other hand merge sort takes extra memory. Depending on the requirement, one should choose which one to use.
Q5. Why is Heap sort better than Selection sort?
Heap sort is similar to selection sort, but with a better way to get the maximum element. It takes advantage of the heap data structure to get the maximum element in constant time
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...