Cryptography Tutorial
Last Updated :
12 Jul, 2023
Cryptography is a technique of securing communication by converting plain text into unintelligible ciphertext. It involves various algorithms and protocols to ensure data confidentiality, integrity, authentication, and non-repudiation. The two primary types of cryptography are symmetric key cryptography and asymmetric key cryptography and It plays a vital role in ensuring the security and privacy of information in today’s digital world and enables secure online transactions, protects sensitive data stored in databases, and ensures the confidentiality of communication. As technology continues to advance, cryptography remains a crucial tool in the ongoing battle to keep our information safe from hackers.
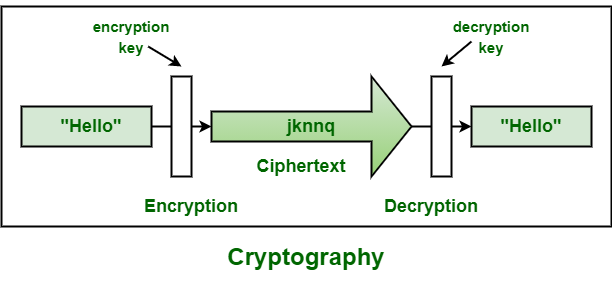
In this Cryptography Tutorial, we’ve covered basics and advanced concepts of Cryptography including symmetric-key cryptography, asymmetric-key cryptography as well as Cryptanalysis, Public Key Cryptography and more. It provides a solid foundation in the core concepts of cryptography, as well as insights into its practical applications.
By the end of this tutorial, you will have a basic understanding of how cryptography works and how it can be used to protect your information.
What is Cryptography?
Cryptography is a technique of securing information and communications through the use of some algorithms so that only those persons for whom the information is intended can understand it and process it.
Cryptography Tutorial Index
Here are the latest topics of cryptography(basics to advanced):
Cryptography – Table of Content
Introduction
Types of Cryptography
Data Encryption Standard (DES)
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES)
Public Key Cryptography Algorithms and RSA
Cryptology, Cryptography and Cryptanalysis
Common Used Cryptography Techniques
Data Integrity in Cryptography
Important Difference b/w topics of Cryptography
Features of Cryptography
Below are some features of cryptography:-
- Confidentiality: Cryptography keeps your sensitive information hidden from hackers by transforming it into an unreadable form.
- Integrity: Cryptography ensures that your data remains intact and unaltered during transmission or storage.
- Authentication: Cryptography helps verify the identity of a sender and confirms the origin of a message.
- Non-repudiation: Cryptography prevents the sender from denying their involvement in a message or transaction.
- Key Management: Cryptography securely manages the keys used for encryption and decryption.
- Scalability: Cryptography can handle different levels of data volume and complexity, from individual messages to large databases.
- Interoperability: Cryptography allows for secure communication between different systems and platforms.
- Adaptability: Cryptography continuously evolves to stay ahead of security threats and technological advancements.
How Cryptography Works?
■ Plaintext: This is the original intelligible message or data that is fed into the algorithm as input.
■ Encryption algorithm: The encryption algorithm performs various substitutions and transformations on the plaintext.

How Cryptography works?
■ Secret key: The secret key is also input to the encryption algorithm. The key is a value independent of the plaintext and of the algorithm. The algorithm will produce a different output depending on the specific key being used at the time. The exact substitutions and transformations performed by the algorithm depend on the key.
■ Ciphertext: Ciphertext is the scrambled message produced as output. It depends on the plaintext and the secret key. For a given message, two different keys will produce two different ciphertexts. The ciphertext is an apparently random stream of data and, as it stands, is unintelligible.
■ Decryption algorithm: This is essentially the encryption algorithm run in reverse. It takes the ciphertext and the secret key and produces the original plaintext.
For Example:- Let’s say you want to send a secret message to your friend. You could write the message on a piece of paper and seal it in an envelope. However, if someone intercepted the envelope, they could open it and read the message. Instead, you could encrypt the message using a cryptographic algorithm. This would transform the message into ciphertext that is unreadable by unauthorized individuals.
You could then send the ciphertext to your friend, who could decrypt it using the same cryptographic algorithm and key. The security of a cryptographic system depends on the strength of the cryptographic algorithm and the secrecy of the keys. If the cryptographic algorithm is weak, then it may be possible to break the encryption and read the plaintext. If the keys are not kept secret, then they may be compromised, which would allow unauthorized individuals to decrypt the ciphertext.
Applications of Cryptography
- Uses: Cryptography finds extensive application in various fields to ensure data security and protect sensitive information.
- Secure Communication: Cryptography enables secure communication channels, such as encrypted messaging apps and virtual private networks (VPNs), to protect conversations and data transmitted over the internet.
- E-commerce and Online Transactions: Cryptography is crucial in securing e-commerce transactions, online banking, and digital payment systems. It protects sensitive financial information, such as credit card details and personal identification numbers (PINs).
- Password Storage: Storing passwords securely is essential to prevent unauthorized access to user accounts. Cryptographic techniques like hashing and salting help protect passwords from being easily compromised in the event of a data breach.
- Digital Rights Management (DRM): Digital Rights Management (DRM) systems use cryptography to enforce copyright protection and prevent unauthorized copying or distribution of digital content, such as e-books, music, and movies.
FAQs on Cryptography
1. What is the purpose of cryptography?
The purpose of cryptography is to secure and protect sensitive information by encoding it in a way that only authorized parties can understand.
2. How does asymmetric key cryptography work?
Asymmetric key cryptography works by using a pair of mathematically related keys: a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
3. Which are the commonly used symmetric key algorithms?
Commonly used symmetric key algorithms include AES (Advanced Encryption Standard), DES (Data Encryption Standard), and 3DES (Triple Data Encryption Standard).
4. Can quantum computers break existing cryptographic systems?
Quantum computers have the potential to break existing cryptographic systems due to their ability to solve certain mathematical problems much faster than traditional computers.
5. How is cryptography used in e-commerce transactions? give answers to these questions in one line
Cryptography is used in e-commerce transactions to encrypt sensitive data, such as credit card information, during transmission to ensure its confidentiality and integrity.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...