Difference between Substitution Cipher Technique and Transposition Cipher Technique
Last Updated :
16 May, 2023
Both Substitution cipher technique and Transposition cipher technique are the types of Traditional cipher which are used to convert the plain text into cipher text.
Substitution Cipher Technique:
In Substitution Cipher Technique plain text characters are replaced with other characters, numbers and symbols as well as in substitution Cipher Technique, character’s identity is changed while its position remains unchanged.
Transposition Cipher Technique:
Transposition Cipher Technique rearranges the position of the plain text’s characters. In transposition Cipher Technique, The position of the character is changed but character’s identity is not changed.
Transposition cipher is a type of encryption technique where the positions of the letters in the plaintext message are rearranged to form a ciphertext message. This technique does not alter the letters themselves but rather the order in which they appear.
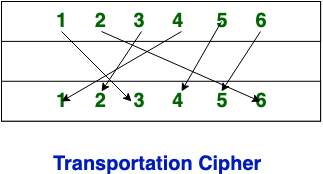
Difference between Substitution Cipher Technique and Transposition Cipher Technique:
| S.NO |
Substitution Cipher Technique |
Transposition Cipher Technique |
| 1. |
In substitution Cipher Technique, plain text characters are replaced with other characters, numbers and symbols. |
In transposition Cipher Technique, plain text characters are rearranged with respect to the position. |
| 2. |
Substitution Cipher’s forms are: Mono alphabetic substitution cipher and poly alphabetic substitution cipher. |
Transposition Cipher’s forms are: Key-less transposition cipher and keyed transposition cipher. |
| 3. |
In substitution Cipher Technique, character’s identity is changed while its position remains unchanged. |
While in transposition Cipher Technique, The position of the character is changed but character’s identity is not changed. |
| 4. |
In substitution Cipher Technique, The letter with low frequency can detect plain text. |
While in transposition Cipher Technique, The Keys which are nearer to correct key can disclose plain text. |
| 5. |
The example of substitution Cipher is Caesar Cipher, monoalphabetic cipher, and polyalphabetic cipher. |
The example of transposition Cipher is Rail Fence Cipher, columnar transposition cipher, and route cipher. |
| 6. |
Involves replacing plaintext letters or groups of letters with ciphertext letters or groups of letters according to a specific algorithm or key. |
Involves rearranging the order of the plaintext letters or groups of letters according to a specific algorithm or key. |
| 7. |
The frequency distribution of the plaintext letters is typically obscured, but patterns can still be detected with statistical analysis. |
The frequency distribution of the plaintext letters remains the same, but the order is scrambled, making it difficult to detect patterns with statistical analysis. |
| 8. |
Vulnerable to frequency analysis attacks, where the most commonly used letters or letter combinations in the language can be identified and used to deduce the key. |
Less vulnerable to frequency analysis attacks, but still susceptible to attacks such as brute force and known plaintext attacks. |
| 9. |
Relatively easy to understand and implement, making it suitable for simple applications.
|
Can be more difficult to implement and understand, but can be more secure than substitution ciphers for certain applications. |
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...