A Triangle is a polygon with three sides and three corners. The corners are also known as vertices, and the sides that connect them are called edges. The interior of a triangle is a two-dimensional region. A triangle is the simplest form of a Polygon.
- Triangles can be classified based on their angles: Acute-angled, Obtuse-angled, and Right-angled.
- Triangles can be classified based on their sides: Equilateral, Isosceles, and Scalene.
Triangles are fundamental geometric shapes that play a crucial role in various fields, from mathematics and architecture to engineering and art. In this comprehensive guide, we delve into the world of triangles, uncovering their diverse properties, types, and real-world applications.
Let’s learn more about what are triangles in maths, their definition, types of triangles, formulas, examples, and practice problems in the article.
What are Triangles in Maths?
A triangle is a polygon with three sides and three angles. It is denoted by the symbol △. In a triangle, any two-sided joint is called a vertex. There are three vertices of triangle. It is one of the basic figures used in mathematics. There are various properties of the triangle which are discussed below.
Triangles Definition
Triangles are polygons with three sides. The word “Tri” means three and therefore a figure with 3 angles is a triangle. It is formed with the help of three-line segments intersecting each other, a triangle has 3 vertices, 3 edges, and 3 angles. It is a 2-dimensional polygon in Euclidean geometry.
A triangle is a fundamental geometric shape that consists of three straight sides and three angles. It is a polygon with the fewest number of sides.
Triangle Shape
A triangle is a 2-Dimensional closed figure with three sides and three angles. It is the simplest polygon and is widely used in geometry and mathematics.
Triangle shape is one of the most common shapes which we observe in our daily life. We observe traffic signals, snacks, cloth hangers, etc. which are shaped like triangles
Parts of a Triangle
A triangle as the name suggests has three angles thus it is called a “tri” angle. It contains various parts. A triangle has 3 angles, 3 vertices, and 3 sides.
In the triangle, ABC given in the image below shows the vertices, sides, and interior angles of triangle.
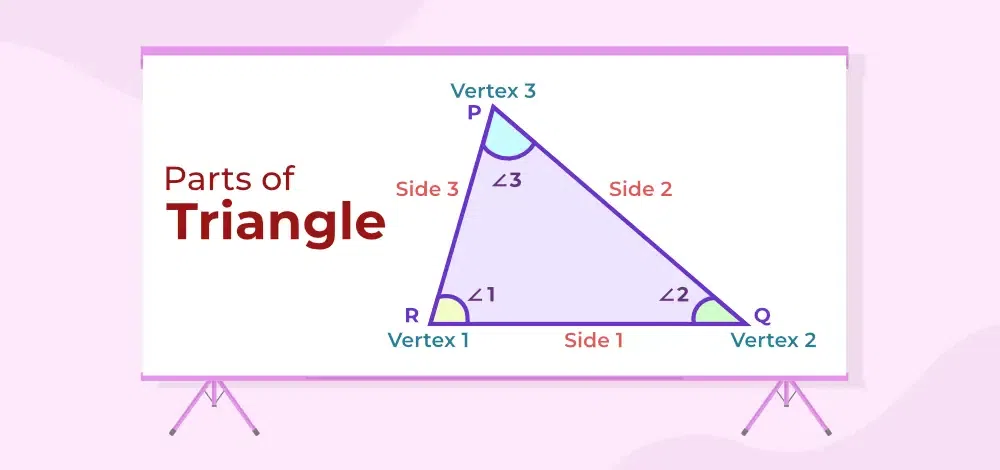
Parts of Triangle
- Three Angles of the triangle are, ∠ABC, ∠BCA, and ∠CAB.
- Three sides of the triangles are side AB, side BC, and side CA
- There are three vertices of triangle, which are A, B and C.
Angles in a Triangle
A triangle has three angles, an angle is formed when two sides of the triangle meet at a common point, this common point is known as the vertex. The sum of the three interior angles is equal to 180 degrees.
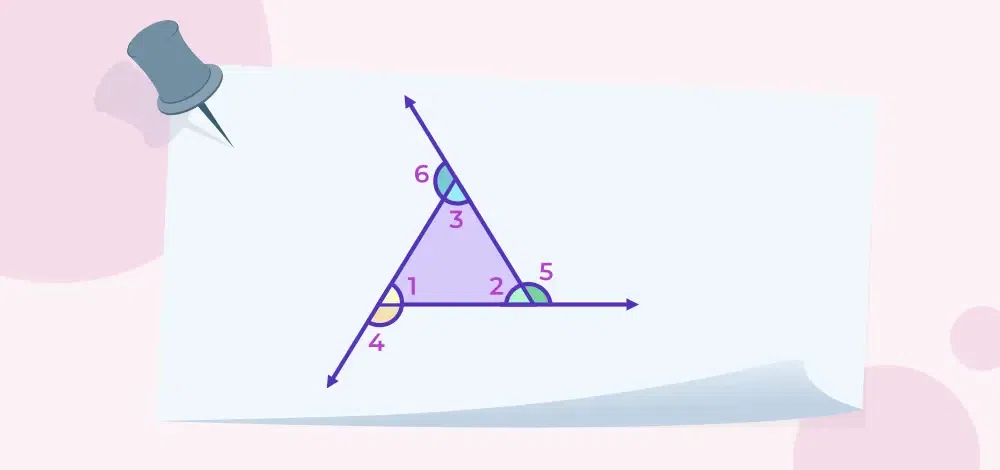
Angles of Triangle
Let’s take the triangle with the interior angles at ∠1, ∠2, and ∠3 and their respective exterior angle at, ∠4, ∠5 and ∠6
Now, using the triangle sum property
∠1 + ∠2 + ∠3 = 180°
When the sides are extended outwards in a triangle, then it forms three exterior angles. The sum of the interior and exterior angles pair of a triangle is always supplementary. Also, the sum of all three exterior angles of a triangle is 360 degrees.
Now,
∠4 + ∠5 + ∠6 = 360°
Examples of Triangles
Various examples of triangles that we observed in our daily life include sandwiches, racks in billiards, tiles, and others. It is one of the fundamental shapes of nature and various shapes can be studied easily by dividing it into various triangles.
Some real-life examples of triangles are Nachos, Tiles, Photo frames, and others.
Properties of Triangles
Various properties of triangles are,
- Angle Sum Property: The sum of all three interior angles is always 180°. Therefore. In the Triangle ΔABC shown above, ∠A+ ∠B+ ∠C= 180°, the interior angles of a triangle will be greater than 0° and less than 180°.
- A Triangle has 3 sides, 3 vertices, and 3 angles.
- Exterior angle property: The Exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of Interior opposite and non-adjacent angles (also referred to as remote interior angles). In the above shown ΔABC, ∠ACD= ∠ABC+ ∠BAC
- The sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side. For example, AB+ BC> AC or BC+ AC> AB.
- The side opposite the largest angle is the largest side of the triangle. For instance, in a right-angled triangle, the side opposite 90° is the longest side.
- The perimeter of a figure is defined by the overall length the figure is covering. Hence, the perimeter of a triangle is equal to the sum of lengths on all three sides of the triangle. Perimeter of ΔABC= (AB + BC + AC)
- The difference between the length of any two sides is always lesser than the third side. For example, AB-BC< AC or BC-AC< AB
- For similar triangles, the angles of the two triangles have to be congruent to each other and the respective sides should be proportional.
- Area of Triangle: 1/2× base × height
Types of Triangles
Classification of triangles is done based on the following characteristics:
- Types of Triangles Based on Sides
- Types of Triangles Based on Angles
Types of Triangles Based on Sides
On the basis of sides, there are 3 types of triangles:
- Scalene Triangle
- Isosceles Triangle
- Equilateral Triangle
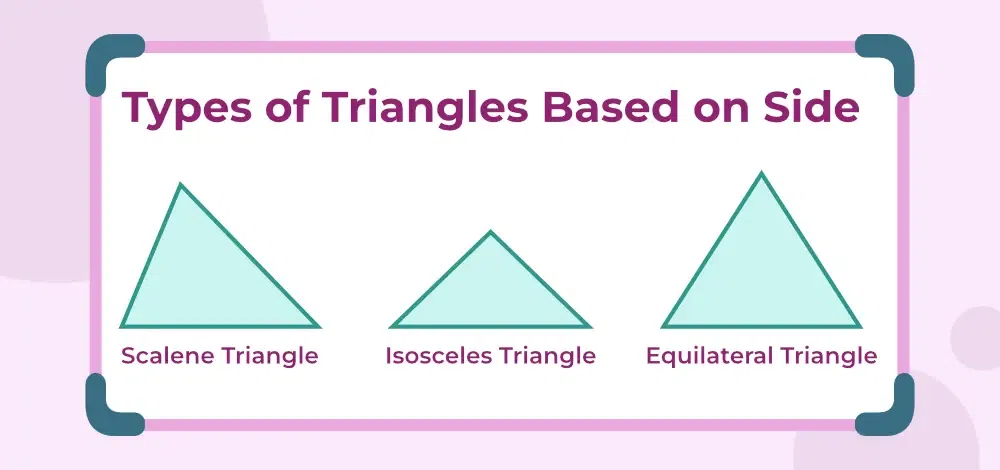
Types of Triangles Based on Sides
Equilateral Triangle
In an Equilateral triangle, all three sides are equal to each other as well as all three interior angles of the equilateral triangle are equal.
Since all the interior angles are equal and the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is 180° (one of the Properties of the Triangle). We can calculate the individual angles of an equilateral triangle.
∠A+ ∠B+ ∠C = 180°
∠A = ∠B = ∠C
Therefore, 3∠A = 180°
∠A= 180/3 = 60°
Hence, ∠A = ∠B = ∠C = 60°
Properties of Equilateral Triangle
- All sides are equal.
- All angles are equal and are equal to 60°
- There exist three lines of symmetry in an equilateral triangle
- The angular bisector, altitude, median, and perpendicular line are all same and here it is AE.
- The orthocentre and centroid are the same.
Equilateral Triangle Formulas
The basic formulas for equilateral triangles are:
where, a is Side of Triangle
Isosceles Triangle
In an Isosceles triangle, two sides are equal and the two angles opposite to the sides are also equal. It can be said that any two sides are always congruent. Area of Isosceles triangle is calculated by using the formula for the area of the triangle as discussed above.
Properties of Isosceles Triangle
- Two sides of the isosceles triangle are always equal
- Third side is referred to as the base of the triangle and the height is calculated from the base to the opposite vertex
- Opposite angles corresponding to the two equal sides are also equal to each other.
Scalene Triangle
In a Scalene triangle, all sides and all angles are unequal. Imagine drawing a triangle randomly and none of its sides is equal, all angles differ from each other too.
Properties of Scalene Triangle
- None of the sides are equal to each other.
- Interior angles of the scalene triangle are all different.
- No line of symmetry exists.
- No point of symmetry can be seen.
- Interior angles may be acute, obtuse, or right angles in nature (this is the classification based on angles).
- Smallest side is opposite the smallest angle and the largest side is opposite the largest angle (general property).
Types of Triangles Based on Angles
On the basis of angles, there are 3 types of triangles:
- Acute Angled Triangle
- Obtuse Angled Triangle
- Right Angled Triangle
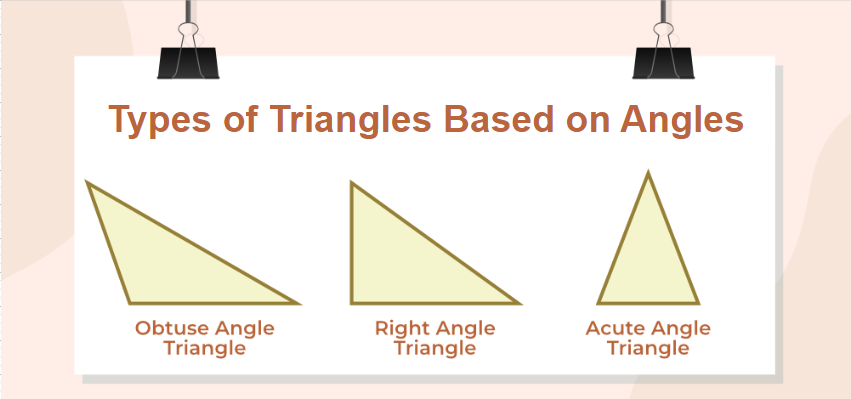
Types of Triangles Based on Angles
Acute Angled Triangle
In Acute angle triangles, all the angles are greater than 0° and less than 90°. So, it can be said that all 3 angles are acute in nature (angles are lesser than 90°)
Properties of Acute Angled Triangles
- All the interior angles are always less than 90° with different lengths of their sides.
- The line that goes from the base to the opposite vertex is always perpendicular.
Obtuse Angled Triangle
In an obtuse angle Triangle, one of the 3 sides will always be greater than 90°, and since the sum of all three sides is 180°, the rest of the two sides will be less than 90° (angle sum property).
Properties of Obtuse Angled Triangle
- One of the three angles is always greater than 90°.
- Sum of the remaining two angles is always less than 90° (angle sum property).
- Circumference and the orthocentre of the obtuse angle lie outside the triangle.
- Incentre and centroid lie inside the triangle.
Right Angled Triangle
When one angle of a triangle is exactly 90°, then the triangle is known as the Right Angle Triangle.
Properties of Right-angled Triangle
- A Right-angled Triangle must have one angle exactly equal to 90°, it may be scalene or isosceles but since one angle has to be 90°, hence, it can never be an equilateral triangle.
- Side opposite 90° is called Hypotenuse.
- Sides are adjacent to the 90° are base and perpendicular.
- Pythagoras Theorem: It is a special property for Right-angled triangles. It states that the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the base and perpendicular i.e. AC2 = AB2 + BC2
Angle Sum Property of a Triangle
Angle Sum Property of a Triangle states that “The sum of three angles in a Triangle is 180°”. It basically means, if there is a Triangle named ABC with three angles ∠A, ∠B and ∠C then as per Angle Sum Property of a Triangle,
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
Triangle’s Angle Sum Property implies that:
- If two angles are given then third angle can be found by subtracting the sum of two angles from 180°
- There can be only one right angle in a Triangle
- There can be only one obtuse angle in a Triangle
- In a triangle Right Angle and Obtuse Angle can’t be together
- All the three angles of a Triangle can be acute angle
Triangle – Line of Symmetry
Line of Symmetry of a triangle is a line that divides the triangle into two equal parts such that each part completely coincides the other. There can be a maximum of three lines of symmetry in a Triangle and a minimum of zero line of symmetry in a Triangle depending upon the type of triangle
- There are three lines of symmetry in an Equilateral Triangle
- There is only one line of symmetry in an Isosceles Triangle
- There is zero line of symmetry in a Scalene Triangle
In geometry, for every two-dimensional shape (2D shape), there are always two basic measurements that we need to find out, i.e., the area and perimeter of that shape. Therefore, the triangle has two basic formulas which help us to determine its area and perimeter. Let us discuss the formulas in detail.
Perimeter of Triangle
Perimeter of a triangle is defined as the sum of all three sides of a triangle. Suppose a triangle with sides a, b, and c is given then its perimeter is given by:
Perimeter of triangle = a + b + c
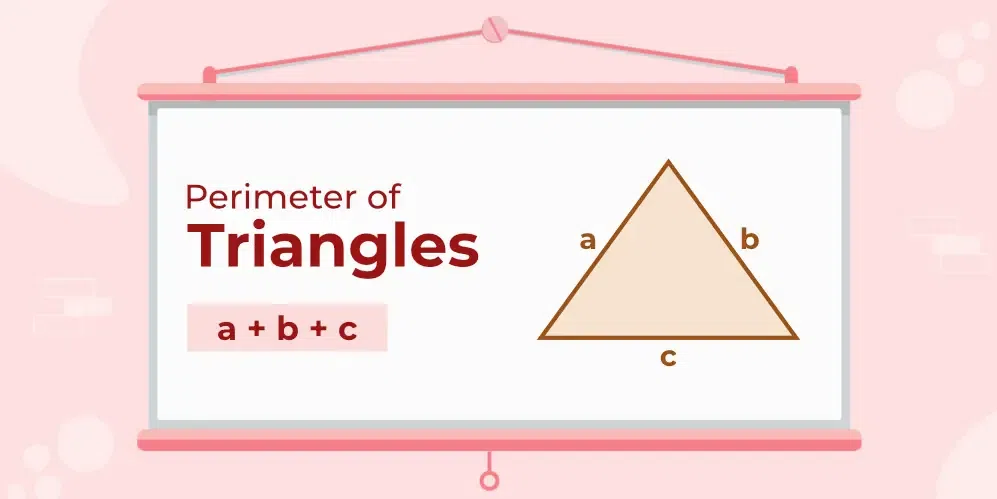
Perimeter of Triangle
Area of a Triangle
Area of a triangle is the total area covered by the triangle boundary. It is equal to half the product of its base and height. Area of a triangle is measured in square units. If the base of a triangle is b and its height is h then its area is given by:
Area of Triangle = 1/2 × b × h
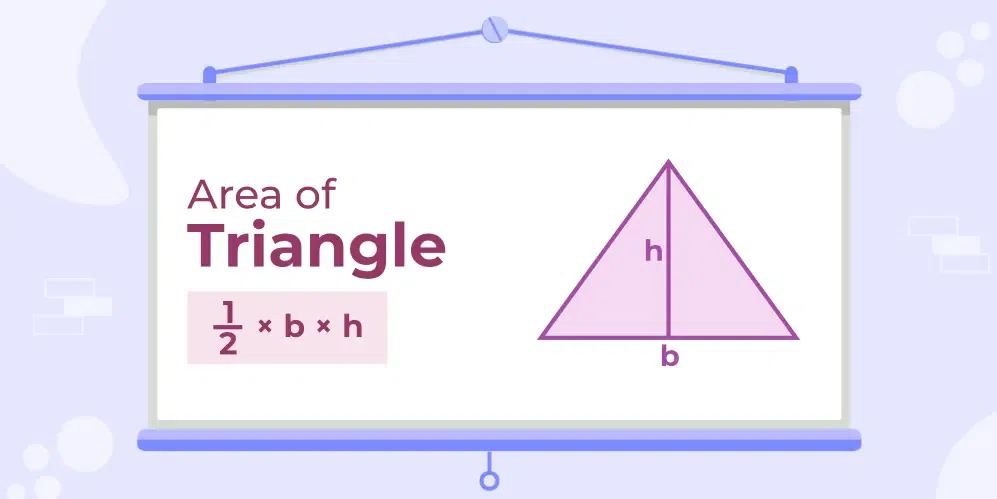
Area of Triangle
Heron’s Formula is used to find the area of a triangle when the measurement of its three sides are given. Suppose a triangle with sides a, b, and c units is given then its area is calculated using the steps discussed below:
Steps to Find Area Using Herons Formula
Step 1: Mark all the dimensions of the given triangle.
Step 2: Calculate the semi-perimeter (s) using the formula s = (a+b+c) / 2
Step 3: Use the formula for finding area Area;
A = √[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)]
where,
a, b, and c are the sides of a triangle
Also check: How to Find Area of Triangle, Formulas, Examples
Congruent Triangles
Definition: Two triangles are said to be congruent if their corresponding angles are equal, and their corresponding sides have the same lengths. The term “congruent” is derived from the Latin word “congruere,” meaning “to agree”.
Ways to Prove Triangle Congruence:
Several methods are employed to establish the congruence of triangles:
- Side-Angle-Side (SAS): If two triangles have two sides and the included angle equal, they are congruent.
- Side-Side-Side (SSS): If the three sides of one triangle are equal to the three sides of another triangle, the triangles are congruent.
- Angle-Side-Angle (ASA): If two triangles have two angles and the included side equal, they are congruent.
- Angle-Angle-Side (AAS): If two triangles have two angles and a non-included side equal, they are congruent.
- Hypotenuse-Leg (HL): In right-angled triangles, if the hypotenuse and one leg of one triangle are equal to the hypotenuse and corresponding leg of another triangle, they are congruent.
Properties of Congruent Triangles:
- Corresponding angles are equal.
- Corresponding sides are of the same length.
- Congruent triangles have equal perimeter and equal area.
- Congruence is reflexive, symmetric, and transitive.
Applications of Congruent Triangles:
- Construction: Congruent triangles are employed in construction, ensuring accuracy in replicating shapes.
- Architectural Design: Architects use the concept of congruent triangles to create symmetrical and aesthetically pleasing structures.
- Robotics: In robotics, understanding the congruence of triangles is essential for precise movement and coordination.
- Engineering: Engineers use congruent triangles in designing and analysing structures to ensure stability and balance.
Similar Triangles
Definition: Similar triangles are triangles that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size. In other words, their corresponding angles are equal, and their corresponding sides are in proportion.
Properties of Similar Triangles
- Corresponding Angles: Corresponding angles of similar triangles are congruent.
- Proportional Sides: Corresponding sides of similar triangles are in proportion. This means that if two triangles are similar, the ratio of the lengths of their corresponding sides is constant.
- Equal Ratios: The ratios of corresponding sides are equal. For example, if two sides of one triangle are in a ratio of 2:3 to the corresponding sides of another triangle, then all sides of the triangles are in this ratio.
Formula of Similar Triangles
The formula to determine if two triangles are similar is known as the “Angle-Angle (AA) Similarity Criterion” or “AA Postulate.” It states that if two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
Another important formula related to similar triangles is the “Side-Side-Side (SSS) Similarity Criterion.” It states that if the corresponding sides of two triangles are in proportion, then the triangles are similar.
Rules of Similar Triangles
- AA Similarity: If two angles of one triangle are congruent to two angles of another triangle, then the triangles are similar.
- SSS Similarity: If the corresponding sides of two triangles are in proportion, then the triangles are similar.
- SAS Similarity: If two sides of one triangle are in proportion to two sides of another triangle, and the included angles are congruent, then the triangles are similar.
Applications of Similar Triangles
Similar triangles are extensively used in various fields such as:
- Geometry and trigonometry
- Engineering, architecture, and construction for scaling and proportioning structures
- Computer graphics and image processing for resizing and transformations
- Navigation and surveying for measuring distances and angles
Triangle Class 9
In Class 9, Triangle is an important chapter. Let’s learn the important concepts of Triangle Class 9.
Median of Triangle
A median is a line segment that that joins vertex of the triangle with the midpoint of opposite sides of the triangle. A median of a triangle bisects the side which it joins
Altitude of Triangle
Altitude of Triangle is the perpendicular distance from the base of the triangle to its apex vertex.
Centroid of Triangle
Centroid is the point inside a triangle where all the medians of a triangle meet each other. Centroid of a Triangle divides the median into 2:1.
Circumcentre of a Triangle
Circumcentre of a Triangle is the point where all the perpendicular bisectors of sides of triangle.
Orthocentre of a Triangle
Orthocentre of a Triangle is the point where all the altitude of a triangle meet each other.
Incentre of a Triangle
Incentre of a Triangle is a point where all the angle bisectors of a triangle meet each other.
Fun Facts about Triangles
Below are 10 interesting facts about Triangles that find real life significance:
- Strong and Stable: Triangles are incredibly strong for their size because they distribute stress evenly throughout their shape. This is why bridges, trusses, and even airplane wings are often built using triangular frameworks.
- Minimal Materials: Because triangles are so strong, they can be built using less material compared to other shapes for the same level of stability. This makes them a lightweight and efficient choice in construction.
- Stacking Efficiency: Triangles, especially equilateral ones, can be packed together very efficiently. This is useful for things like creating stable and space-saving containers for fruits and vegetables.
- Direction Indicators: Triangles are universally recognized as pointing arrows. This makes them ideal for road signs, warning labels, and directional markers, ensuring clear communication.
- Musical Harmony: The basic principles of harmony in music rely on the perfect fifth, which has a frequency ratio of 3:2. This ratio can be visualized as a 30-60-90 degree triangle, making triangles a foundational concept in musical theory.
- Tooth Shape Efficiency: Our premolar teeth have triangular cusps that are perfect for grinding and tearing food. The triangular shape allows for maximum surface area and efficient chewing.
- Aerodynamic Design: The triangular shape plays a role in aerodynamics. The delta wing, a triangular airplane wing design, is known for its stability and maneuverability at high speeds.
- Facial Recognition: Our brains use triangles to recognize faces. The triangular arrangement of eyes, nose, and mouth helps us quickly identify and differentiate faces.
- Fracture Lines: Even in breaking, triangles can be helpful! Cracks in glass or other materials often propagate in triangular patterns, which can help predict how something might break and potentially prevent accidents.
- Building Blocks of Life: The basic building block of DNA, the double helix, can be visualized as two intertwined triangles representing the sugar-phosphate backbones. This triangular structure is essential for storing and transmitting genetic information.
Triangles Solved Examples
Example 1: In a triangle ∠ACD = 120°, and ∠ABC = 60°. Find the type of Triangle.
Solution:
In the above figure, we can say, ∠ACD = ∠ABC + ∠BAC (Exterior angle Property)
120° = 60° + ∠BAC
∠BAC = 60°
∠A + ∠B + ∠C = 180°
∠C OR ∠ACB = 60°
Since all the three angles are 60°, the triangle is an Equilateral Triangle.
Example 2: The triangles with sides of 5 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm are given. Find the area and perimeter of the Triangle.
Solution:
Given, the sides of a triangle are 5 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm
Perimeter of the triangle = (5 + 5 + 6) = 16 cm
Semi Perimeter = 16 / 2 = 8 cm
Area of Triangle = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c) (Using Heron’s Formula)
= √8(8 – 5)(8 – 5)(8 – 6)
= √144 = 12 cm2
Example 3: In the Right-angled triangle, ∠ACB = 60°, and the length of the base is given as 4cm. Find the area of the Triangle.
Solution:
Using trigonometric formula of tan60°,
tan60° = AB / BC = AB /4
AB = 4√3cm
Area of Triangle ABC = 1/2
= 1/2 × 4 × 4√3
= 8√3 cm2
Example 4: In ΔABC if ∠A+ ∠B = 55°. ∠B + ∠C = 150°, Find angle B separately.
Solution:
Angle Sum Property of a Triangle says ∠A+ ∠B+ ∠C= 180°
Given:
∠A+ ∠B = 55°
∠B+ ∠C = 150°
Adding the above 2 equations,
∠A+ ∠B+ ∠B+ ∠C= 205°
180°+ ∠B= 205°
∠B = 25°
Also Read:
Triangles – Practice Problems
1. Determine the type of triangle based on its angles:
a) A triangle with angles 45°, 45°, and 90°.
b) A triangle with angles 60°, 60°, and 60°.
2. Calculate the area of the following triangles:
a) A right-angled triangle with a base of 6 units and a height of 8 units.
b) An equilateral triangle with a side length of 10 units.
c) A triangle with sides of lengths 7 units, 24 units, and 25 units (Hint: This is a Pythagorean triple).
3. Find the perimeter of the following triangles:
a) A scalene triangle with side lengths 5 cm, 6 cm, and 7 cm.
b) An isosceles triangle with a base of 12 meters and congruent sides of 9 meters each.
Practice Questions on Triangles
Answer the following MCQs (Here only one answer is correct)
1. Which of the following statements is true about an equilateral triangle?
- All angles are equal
- All sides are equal
- One angle is 90 degrees
- It has no equal sides or angles
2. In a right-angled triangle, the side opposite the right angle is called:
- Hypotenuse
- Adjacent side
- Opposite side
- Base
3. What is the sum of the interior angles of a triangle?
- 90 degrees
- 180 degrees
- 270 degrees
- 360 degrees
4. Pythagorean Theorem is applicable to which type of triangle?
- Equilateral triangle
- Isosceles triangle
- Right-angled triangle
- Scalene triangle
5. What is the name of the triangle where all angles are less than 90 degrees?
- Acute-angled triangle
- Right-angled triangle
- Obtuse-angled triangle
- Isosceles triangle
6. In an isosceles triangle, which sides are of equal length?
- Base and height
- Adjacent sides
- Opposite sides
- Base and one of the other two sides
7. The angle sum property of a triangle states that the sum of all angles in a triangle is:
- 90 degrees
- 180 degrees
- 270 degrees
- 360 degrees
8. What is the name of a triangle with all sides of different lengths?
- Equilateral triangle
- Isosceles triangle
- Scalene triangle
- Right-angled triangle
9. The exterior angle of a triangle is equal to the sum of:
- Two interior angles
- Three interior angles
- Four interior angles
- None of the above
10. If one angle of a triangle is 120 degrees, what is the measure of the other two angles, assuming it is not a right-angled triangle?
- 30 degrees each
- 60 degrees each
- 45 degrees each
- 90 degrees each
FAQs on Triangles
What is a Triangle in Maths?
A triangle is a polygon, with three sides and three vertices. A triangle also has three angles and the sum of all three angles of the triangle is 180 degrees.
What are the Triangle Formulas?
The main triangle formulas are,
Area of triangle
A = [(½) b × h
Perimeter of a triangle
P = (a + b + c)
How many Types of Triangles are there in Maths?
The six basic types of triangles are,
- Acute angle triangles
- Obtuse angle triangles
- Right angle triangles
- Scalene Triangles
- Isosceles triangles
- Equilateral triangles
What are the Properties of Triangles?
Some of the important properties of triangles are:
- Sum of all three angles of the triangle is equal to 180 degrees.
- Equal angles have equal sides opposite them.
- Sum of the length of any two sides of a triangle is always greater than the third side.
What is the difference between Scalene, Isosceles, and Equilateral Triangles?
On the basis of sides triangles are of three types:
- Scalene Triangle: A triangle with all three sides unequal is called a Scalene triangle.
- Isosceles Triangle: A triangle in which any two sides are equal is an Isosceles triangle.
- Equilateral Triangle: A triangle with all three sides equal is called an Equilateral triangle.
What is the difference between an Acute Triangle, an Obtuse Triangle, and a Right Triangle?
On the basis of angles triangles are of three types:
- Acute Triangle: A triangle with all three angles as acute angles is called an acute angle triangle.
- Obtuse Triangle: A triangle with any one angle as an obtuse angle is called an obtuse angle triangle.
- Right Triangle: A triangle with any one angle as a right angle is called a right angle triangle.
What is the Triangle where Two Sides are Equal?
A triangle where two sides are equal is called an Isosceles triangle.
What is an Equilateral Triangle?
An equilateral triangle is a type of triangle that has three equal sides and three equal angles. In an equilateral triangle:
- Side Lengths: All three sides are of the same length.
- Angle Measures: All three angles are of the same measure, and each angle in an equilateral triangle measures 60 degrees.
What is an Isosceles Triangle?
An isosceles triangle is a type of triangle that has two sides of equal length and two angles of equal measure. In an isosceles triangle:
- Side Lengths: At least two sides are of the same length, making them congruent.
- Angle Measures: The angles opposite the equal sides are also congruent, meaning they have the same measure.
How many Triangles are in a Star?
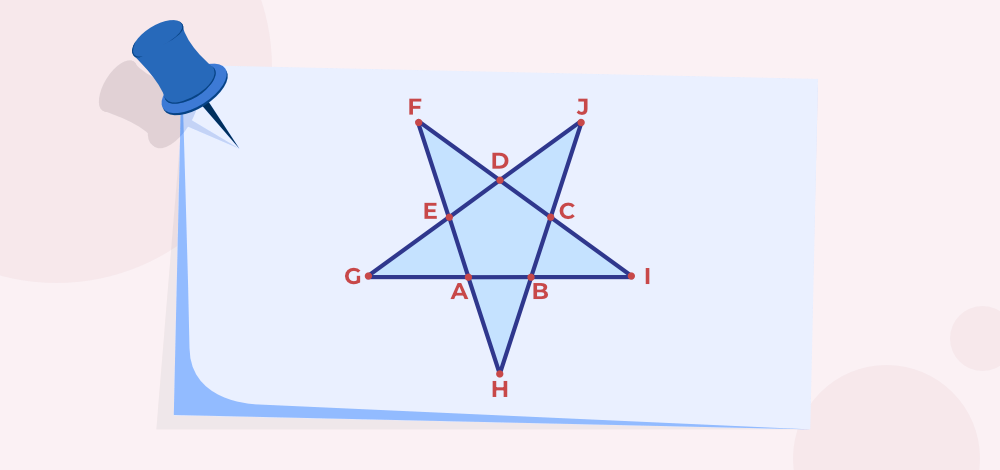
A star has 10 triangles that are,
∆ABH, ∆BIC, ∆CJD, ∆DFE, ∆EGA, ∆DGI, ∆GJB, ∆FAI, ∆JGB and ∆EHJ
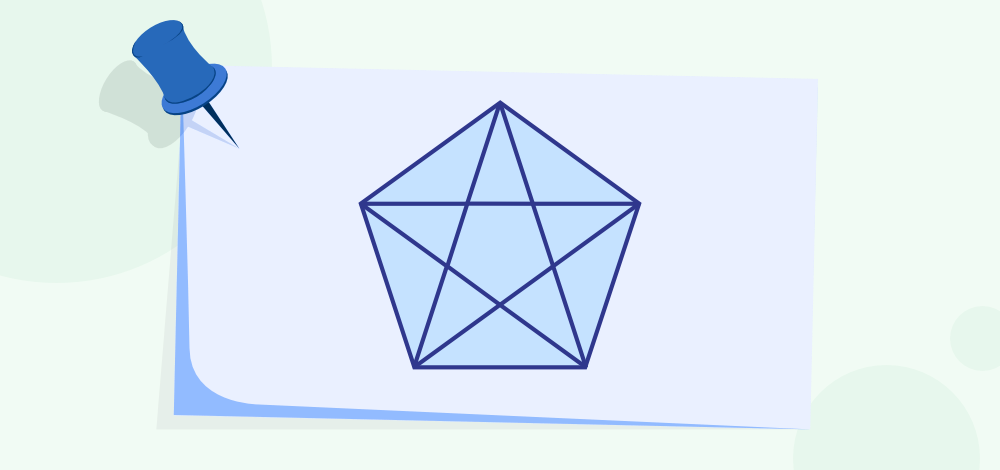
How many Triangles can a Pentagon be divided into?
A pentagon is divided into six different triangles which are made using the vertices of the Pentagon.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...