Types of Polygons classify all polygons based on various parameters. As we know, a polygon is a closed figure consisting only of straight lines on its edges. In other words, polygons are closed figures made up of more than 2 line segments on a 2-dimensional plane. The word Polygon is made up of two words, the first is “poly” which means many and the second is “gons” which means sides, thus polygon means many sides. Polygons are made with two components, the first is the vertex and the second is an edge.
In this article, we will discuss the classification of Polygons which include, convex and concave polygons, simple and complex polygons, regular and irregular polygons, etc. So let’s start learning about the various types of polygons in this article.
How many Types of Polygons?
Polygons can be classified based on various different parameters, some of these parameters are:
- Based on Boundary of the Polygon
- Based on the Side Length
- Based on Interior Angle
- Based on Sides
Area of a polygon can be easily calculated using polygon formula. Let’s discuss types of polygons based on these parameters in detail as follows:
Types of Polygons Based on Boundary of the Polygon
- Simple Polygon
- Complex Polygon
Simple Polygon
A simple Polygon is a closed geometric shape which is constructed using non-intersecting line segments. In simple words, a two-dimensional figure with sides that do not intersect with each other is called a simple polygon. Some of the common examples of simple polygons are triangles, squares, rectangles, pentagons, hexagons, and many more.
Complex Polygon
A complex polygon is a two-dimensional geometric shape that has sides consisting of straight line segments and may have self-intersections or holes. Unlike simple polygons, which do not cross themselves, complex polygons can have edges that intersect each other within the polygon’s boundary, resulting in a more intricate and irregular shape.
Complex polygons can be formed by combining simple polygons or by adding cut-outs (holes) within a simple polygon. These cut-outs create regions within the polygon that are not part of the main boundary. The inclusion of self-intersections and holes makes complex polygons more challenging to work with and analyse compared to simple polygons.
Types of Polygons Based on the Side Length
Based on the length of sides, the polygons are classified as follows:
Regular Polygon
If all the sides and interior angles of the polygon are equal or if a polygon is equiangular and equilateral, then the polygon will be known as a regular polygon. Example square, rhombus, equilateral triangle, etc.
Irregular Polygon
If all the sides and the interior angles of the polygon are of different measure, then the polygon will be known as an irregular polygon. For example scalene triangle, rectangle, kite, etc.
Types of Polygons Based on Interior Angle
Based on the measurement of interior angles the polygons are classified as follows:
Convex Polygon
If all the interior angles of a polygon are strictly less than 180° or if a line segment between two points on the boundary does not go outside the polygon, then the polygon will be known as a convex polygon.

Concave Polygon
If one or more interior angles of a polygon are more than 180° degrees or a polygon contains at least one reflex interior angle, then the polygon will be known as a concave polygon. This polygon can have at least four sides.
.png)
Types of Polygons Based on Sides
Polygons are classified based on the number of sides or vertices they have. So, some of the polygons are:
- Triangles
- Quadrilateral
- Pentagon
- Hexagon
- So on . . .
All of these polygons are given in the following table:
|
Polygon
|
Shape |
No. of sides
|
No. of Diagonal
|
No. of vertices
|
Interior Angle
|
Exterior Angle
|
|
Triangle
|
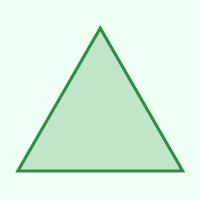 |
3
|
0
|
3
|
60°
|
120°
|
|
Quadrilateral
|
 |
4
|
2
|
4
|
90°
|
90°
|
|
Pentagon
|
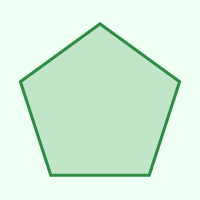 |
5
|
5
|
5
|
108°
|
72°
|
|
Hexagon
|
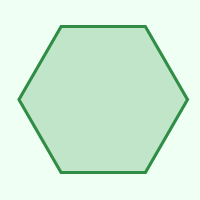 |
6
|
9
|
6
|
120°
|
60°
|
|
Heptagon
|
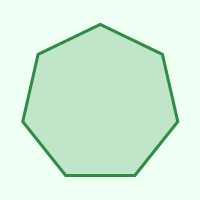 |
7
|
14
|
7
|
128.571°
|
51.429°
|
|
Octagon
|
 |
8
|
20
|
8
|
135°
|
45°
|
|
Nonagon
|
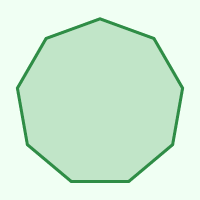 |
9
|
27
|
9
|
140°
|
40°
|
|
Decagon
|
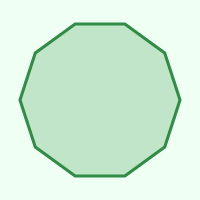 |
10
|
35
|
10
|
144°
|
36°
|
|
Hendecagon
|
 |
11
|
44
|
11
|
147.273°
|
32.727°
|
|
Dodecagon
|
 |
12
|
54
|
12
|
150°
|
30°
|
|
Triskaidecagon
|
 |
13
|
65
|
13
|
158.308°
|
27.692°
|
|
Tetrakaidecagon
|
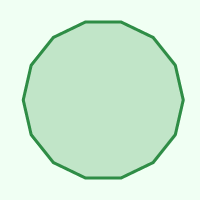 |
14
|
77
|
14
|
154.286°
|
25.714°
|
|
Pentadecagon
|
 |
15
|
90
|
15
|
156°
|
24°
|
Triangles(3-gon)
A triangle is a polygon, it is formed with the help of three-line segments intersecting each other, so a triangle has 3 vertices, 3 edges, and 3 angles. The triangles are classified into different types, based on the sides and angles.
Some properties of the triangle:
- Area of Triangle: 1/2× base × height
- In a triangle, the sum of all the interior angles of a triangle is 180o.
- The side opposite to the largest angle is the largest side of the triangle.
- The perimeter of a triangle is equal to the sum of the lengths of all three sides of the triangle.
Types: Based on Sides
- Equilateral triangle: If a triangle has all sides equal and angles of equal measure then such types of triangles are known as equilateral triangles.
- Isosceles triangle: If any triangle having any 2 sides equal and angles opposite to the equal sides are equal, then such types of triangles are known as isosceles triangles.
- Scalene triangle: If a triangle has all the 3 sides unequal, then such type of triangles are known as a scalene triangle.

Types: Based on the Angle
- Acute Angled Triangle: A triangle with an angle less than 90° is known as an acute-angle triangle.
- Right Angled Triangle: If any one of the three angles of a triangle is equal to 90° then such type of triangle is known as a right-angle triangle.
- Obtuse Angled Triangle: If any one angle of a triangle is greater than 90°, then such type of triangle is known as an obtuse-angle triangle.

Quadrilaterals (4-gon)
A Quadrilateral is nothing but a polygon having at least 4 sides. A polygon is formed by enclosing four line segments such that they meet at each other at vertices to make 4 or more angles. Examples of Quadrilateral are Square, Rectangle, Parallelogram, Rhombus, Trapezium.
Some properties of a quadrilateral:
- It has four sides.
- It has four vertices.
- In a quadrilateral, the sum of all the interior angles is 360o.

Apart from triangle and quadrilateral there are also other polygons but they don’t have much use in real life.
Read More,
Sample Problems on Types of Polygon
Question 1. Find the exterior angle of a regular hexagon.
Solution:
As we know that, hexagon has 6 sides therefore
Exterior Angle = 360o / n = 360o / 6
Exterior Angle = 60o

Question 2. Find the interior angle of a regular pentagon.
Solution:
As we know that pentagon has 5 sides, therefore
Exterior Angle = 360o / 5 = 72o
Interior Angle = 180o – 72o = 108o
Question 3. Find each interior angle of a regular decagon.
Solution:
As we know that, decagon has ten sides.
Using angle sum formula,
As we know that,
S = (n − 2) × 180°
Here, n = 10
Therefore,
Sum of angles of decagon = (10 − 2) × 180°
= 8 × 180° = 1440°
As we know that all the interior angles are equal of a regular decagon,
Therefore, the measure of each interior angle of regular decagon = sum of interior angles / number of sides
Interior angle = 1440 / 10 = 144°
Hence, Sum of Interior Angle of decagon is 1440° and each interior angle is of 144°.
Question 4. Find the value of x in the given figure:

Solution:
As we know that the sum of angles os a quadrilateral = 360o
so, 55o + 124o + 70o + x = 360o
249o + x = 360o
x = 111o
Question 5. Find the value of x in the given figure:

Solution:
As we know that the sum of exterior angles = 360o
So, 120o + 125 + x = 360o
245o + x = 360o
x = 360o – 245o
x = 115o
FAQs on Types of Polygons
1. What is a Polygon?
A polygon is a closed two-dimensional shape with straight sides. It is formed by connecting several line segments, known as edges and the endpoints of those edges are called vertices.
2. How are Polygons Classified based on the Number of Sides they have?
Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they possess. Common classifications include:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- Nonagon: 9 sides
- Decagon: 10 sides
- and so on…
3. What is a Regular Polygon?
A regular polygon is a polygon with all sides of equal length and all angles of equal measure. For example, a regular pentagon has five sides of equal length and five angles of equal measure.
4. Can a Polygon have Concave Sides?
Yes, a polygon can have concave sides. A concave polygon has at least one interior angle greater than 180 degrees, causing one or more sides to “sink inward.”
5. How do you Identify Convex and Concave Polygons?
If the interior angles of any polygon are greater than 180° then the polygon is concave, and if all the interior angles are less than 180° then the polygon is convex.
6. What is a Regular Convex Polygon?
A regular convex polygon is a polygon that is both convex and regular i.e., it has all sides of equal length and all interior angles of equal measure and less than 180°.
7. Are there any Polygons with an Infinite Number of Sides?
Yes, a polygon with an infinite number of sides is called a circle as a circle can be considered a polygon as it meets the definition of a closed two-dimensional shape with straight sides where a number of edges approaches infinity
8. Can a Polygon have Curved Sides?
No, by definition, a polygon has straight sides, thus any shape with curve sides is not a polygon.
9. What is the Sum of the Interior Angles of a Polygon?
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon can be calculated using the formula (n – 2) × 180°, where ‘n’ represents the number of sides of the polygon.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...