Fixed and Flooding Routing algorithms
Last Updated :
22 Apr, 2023
In most situations, packets require multiple hops to make a journey towards the destination. Routing is one of the most complex and crucial aspects of packet-switched network design.
Desirable Properties of Routing Algorithms:-
- Correctness and Simplicity
- Robustness: Ability of the network to deliver packets via some route even in the face of failures.
- Stability: The algorithm should converge to equilibrium fast in the face of changing conditions in the network.
- Fairness and Optimality
- Efficiency: Minimum overhead.
Design Parameters of Routing Algorithms :
- Performance Criteria: Number of hops, Cost(Send packet with high bandwidth path as the cost is less), Delay(Size of Queue), Throughput time(Number of packets delivered/time).
- Decision Time: When to decide to route a packet? Per-Packet(Datagram) or Per-session(Virtual-Circuit).
- Decision Place: Who will decide about routing? Each Node(distributed), Central Node (centralized),Originated Node (source) .
- Network Information Source: None, Local, Adjacent node, Nodes along the route, All nodes.
- Network Information Update Time: Continuous, Periodic, Major Load Change, Topology Change.
Routing Strategies :
- Fixed Routing
- Flooding
- Dynamic Routing
- Random Routing
- Flow-based Routing
Fixed Routing –
- A route is selected for each source and destination pair of nodes in the network.
- The route is fixed; changes only if the topology of the network changes.
Fixed Routing: Example (1)
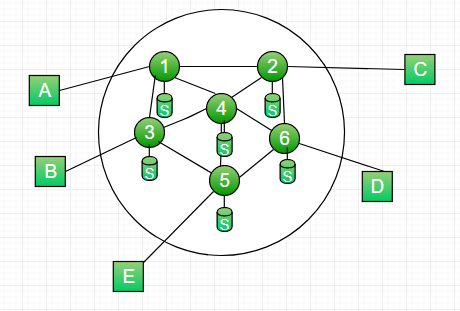
Figure – A simple packet switching network with six nodes (routers)
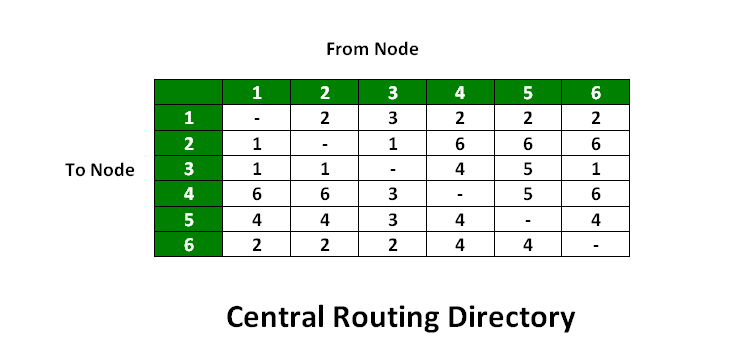
Figure – Central routing table based on least-cost path algorithm
- A Central routing matrix is created based on the least-cost path which is stored in the network control center
- The matrix shows for each source-destination of the route, the identity of the next node on the route.
- Drawback: If the network control center fails, then everything will collapse. Hence it is not reliable.
Fixed Routing: Example (2)
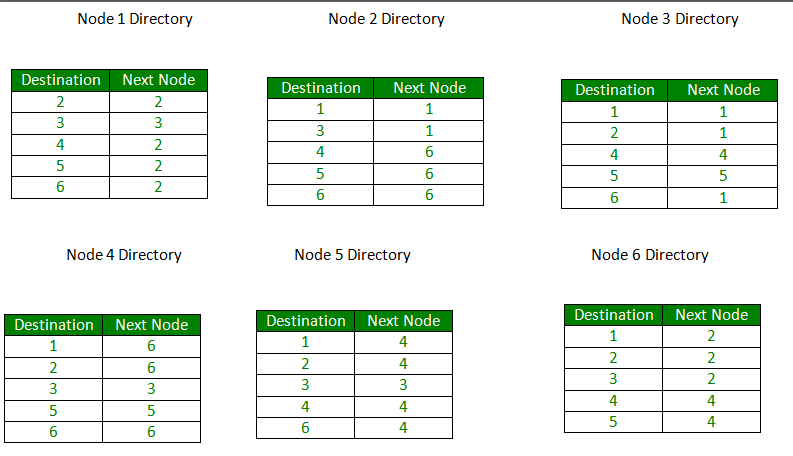
Figure – Routing table stored in different nodes of the network
- Routing Table is created for each node. This is called a distributed routing algorithm
- Routing table can be created using the least-min path or min-hop reach method. Two famous path algorithms
- Dijkstra Algorithm
- Bellman Ford Algorithm
Advantages –
- Simple
- Works well in reliable network with stable load in a reliable network
- Same for virtual circuit and datagram
Disadvantages –
- Lack of flexibility
- Doesn’t react to failure or network congestion
Flooding –
- Requires no network information like topology, load condition, cost of diff. paths
- Every incoming packet to a node is sent out on every outgoing like except the one it arrived on.
- For Example in the above figure
- An incoming packet to (1) is sent out to (2),(3)
- from (2) is sent to (6),(4), and from (3) it is sent to (4),(5)
- from (4) it is sent to (6),(5),(3), from (6) it is sent to (2),(4),(5), from (5) it is sent to (4),(3)
Characteristics –
- All possible routes between Source and Destination are tried. A packet will always get through if the path exists
- As all routes are tried, there will be at least one route which is the shortest
- All nodes directly or indirectly connected are visited
Limitations –
- Flooding generates a vast number of duplicate packets
- Suitable damping mechanism must be used
Hop-Count –
- A hop counter may be contained in the packet header which is decremented at each hop.
with the packet being discarded when the counter becomes zero
- The sender initializes the hop counter. If no estimate is known, it is set to the full diameter of the subnet.
- Keep track of the packets which are responsible for flooding using a sequence number. Avoid sending them out a second time.
Selective Flooding: Routers do not send every incoming packet out on every line, only on those lines that go in approximately in the direction of the destination.
Advantages of Flooding :
- Highly Robust, emergency or immediate messages can be sent (eg military applications)
- Set up the route in virtual circuit
- Flooding always chooses the shortest path
- Broadcast messages to all the nodes
Disadvantages of Flooding :
- Network congestion: Flooding can cause a significant amount of traffic in the network, leading to congestion. This can result in slower network speeds and delays in delivering data packets.
- Wastage of network resources: Flooding uses a lot of network resources, including bandwidth and processing power, to deliver packets. This can result in the wastage of valuable network resources and reduce the overall efficiency of the network.
- Security risks: Flooding can be used as a tool for launching various types of attacks, including denial of service (DoS) attacks. Attackers can flood the network with data packets, which can overload the network and cause it to crash.
- Inefficient use of energy: Flooding can result in an inefficient use of energy in wireless networks. Since all nodes receive every packet, even if they are not the intended recipient, they will still need to process it, which can waste energy and reduce the overall battery life of mobile devices.
- Difficulty in network troubleshooting: Flooding can make it difficult to troubleshoot network issues. Since packets are sent to all nodes, it can be challenging to isolate the cause of a problem when it arises.
Reference –
Data and Computer Communications
Read next article – Routing Protocols Set 1 (Distance Vector Routing)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...