Supernetting in Network Layer
Last Updated :
13 Mar, 2024
Supernetting is the opposite of Subnetting. In subnetting, a single big network is divided into multiple smaller subnetworks. In Supernetting, multiple networks are combined into a bigger network termed a Supernetwork or Supernet. In this article, we’ll explore the purpose and advantages of supernetting, along with essential considerations for its implementation.
What is Supernetting?
Supernetting is the process of aggregating routes to multiple smaller networks. Thus saving storage space in the routing table, simplifying routing decisions, and reducing route advertisements to neighboring gateways. Supernetting has helped address the increasing size of routing tables as the Internet has expanded. Supernetting is mainly used in Route Summarization, where routes to multiple networks with similar network prefixes are combined into a single routing entry, with the routing entry pointing to a Super network, encompassing all the networks. This in turn significantly reduces the size of routing tables and also the size of routing updates exchanged by routing protocols.
More specifically,
- When multiple networks are combined to form a bigger network, it is termed super-netting
- Super netting is used in route aggregation to reduce the size of routing tables and routing table updates
Important Points for Supernetting
- All the Networks should be contiguous.
- The block size of every network should be equal and must be in form of 2n.
- First Network id should be exactly divisible by whole size of supernet.
Example: Suppose 4 small networks of class C:
200.1.0.0,
200.1.1.0,
200.1.2.0,
200.1.3.0
Build a bigger network that has a single Network Id.
Explanation: Before Supernetting routing table will look like as:
| Network Id |
Subnet Mask |
Interface |
| 200.1.0.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
A |
| 200.1.1.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
B |
| 200.1.2.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
C |
| 200.1.3.0 |
255.255.255.0 |
D |
First, let’s check whether three conditions are satisfied or not:
- Contiguous: You can easily see that all networks are contiguous all having size 256 IP Addresses( or 254 Hosts )..
Range of first Network from 200.1.0.0 to 200.1.0.255. If you add 1 in last IP address of first network that is 200.1.0.255 + 0.0.0.1, you will get the next network id which is 200.1.1.0. Similarly, check that all network are contiguous.
- Equal size of all network: As all networks are of class C, so all of them have a size of 256 which is in turn equal to 28.
- First IP address exactly divisible by total size: When a binary number is divided by 2n then last n bits are the remainder. Hence in order to prove that first IP address is exactly divisible by while size of Supernet Network. You can check that if last n (n here refers to the number of bits required to represent the Total Size of the Supernet) bits are 0 or not.
In the given example first IP is 200.1.0.0 and whole size of supernet is 4*28 = 210. If last 10 bits of first IP address are zero then IP will be divisible.
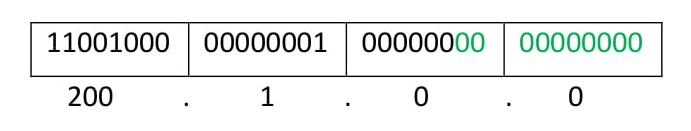
Last 10 bits of first IP address are zero (highlighted by green color). So 3rd condition is also satisfied.
Advantages of Supernetting
- Control and reduce network traffic
- Helpful to solve the problem of lacking IP addresses
- Minimizes the routing table i.e, it cannot cover a different area of the network when combined and all the networks should be in the same class and all IP should be contiguous
Conclusion
In conclusion, supernetting is a networking technique that consolidates multiple smaller networks into a larger one, simplifying routing and reducing the size of routing tables. It’s a valuable tool in managing the growth of internet routing tables and optimizing network performance. However, it requires careful consideration of network characteristics and adherence to specific conditions for effective implementation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q.1: Can supernetting be used in IPv6 networks, or is it primarily for IPv4?
Answer:
Supernetting can be used in both IPv4 and IPv6 networks. While it’s more commonly associated with IPv4 due to its longer adoption history, the principles apply to both IP versions.
Q.2: Can supernetting be applied in cloud-based or virtualized networks?
Answer:
Yes, supernetting principles can be applied to cloud-based and virtualized networks to optimize routing and reduce the complexity of routing tables, improving overall network performance.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...