What is Routing Loop and How to Avoid Routing Loop?
Last Updated :
25 Jul, 2022
Routing is a procedure that helps the packet choose an optimal path to reach its destination as soon as possible. For example, a device can be a router, which is used to handle traffic within networks. Optimal network routing methods help maintain your network operating efficiently at help in some ways i.e. faster data access and preventing overload of bandwidth.
Routing Loop
A routing loop is an issue that occurs when the routers forward packets such that the same single packet ends up back at the same router repeatedly in the network because of the unusual behavior of the routing table when the data packets keep getting routed again and again between two or more routers.
For example, it’s where traffic is being received from one connection or one device (a router typically or a layer 3 switch) it sees traffic coming from an interface and it sends this traffic to this host and then that host receives the traffic and it sends this traffic to the interface and it is receiving traffic from the host and it is sending it right back to host so essentially the traffic goes in a loop.
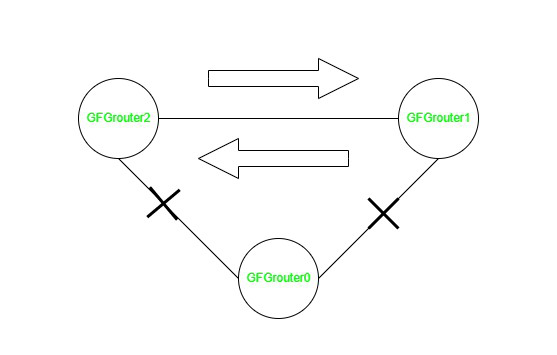
Routing Loop Example
In the above image, the GFG Router2 is sending the data traffic to GFG Router1 and it is sending back it to GFG Router2 which cause the loop there is a term called TTL which is a time to live on a packet and it tells up to how many hops this packet can live.
Whenever a routing loop is developed due to some fault in the routing table the data packets are delivered in between two routers again and again until the time to live expires and then the packet has to be deleted that’s why the routing loop is bad.
How routing loops affect network performance?
If a routing loop exists then there is some problem in the routing table which is called the poisoning of the routing table which can cause high damage to networks like a failure of the network or slowness in the network as inaccurate data is being added to the routing table and this causes abundance loss of data packets and the waste of bandwidth.
If there are two hosts and the network trying to communicate or a big file is to be transferred via this network and there’s a routing loop also. Due to the presence of a routing loop every packet just keeps getting replicated so that it starts putting load and strain on the network and at some point, a network outage can occur because of these routing loops.
How to avoid Routing loops?
The following techniques are used to avoid Routing Loops.
1. Split Horizon
A split horizon is a technique to avoid routing loops by disabling the router from sending information about a failed route in the routing table through the same interface that it learned about the route from. This method includes Routing Information Protocol (RIP), The virtual private LAN service (VPLS), and Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP).
2. Hold-down Timers
It is a method that is used to prevent regular update messages from reinstating a route that may have gone bad. Imagine a router receives an update from a neighbor indicating that a previously accessible network is not working and is inaccessible then the hold-down timer will start if a new update arrives from a neighbor with a better metric then hold down is removed and data is passed otherwise it will ignore that new update.
Disadvantages:
- Never going to deliver the packet
- It causes Route Poisoning and Counts to infinity problem
- Wasting of bandwidth
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...