Difference Between Skewness and Kurtosis
Last Updated :
23 Jun, 2022
Skewness is an important statistical technique that helps to determine asymmetrical behavior than of the frequency distribution, or more precisely, the lack of symmetry of tails both left and right of the frequency curve. A distribution or dataset is symmetric if it looks the same to the left and right of the center point.
Types of skewness: The following figure describes the classification of skewness:
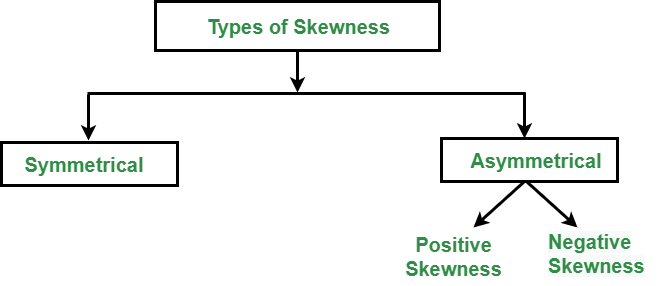
Types of Skewness
1. Symmetric Skewness: A perfect symmetric distribution is one in which frequency distribution is the same on the sides of the center point of the frequency curve. In this, Mean = Median = Mode. There is no skewness in a perfectly symmetrical distribution.
2. Asymmetric Skewness: A asymmetrical or skewed distribution is one in which the spread of the frequencies is different on both the sides of the center point or the frequency curve is more stretched towards one side or value of Mean. Median and Mode falls at different points.
- Positive Skewness: In this, the concentration of frequencies is more towards higher values of the variable i.e. the right tail is longer than the left tail.
- Negative Skewness: In this, the concentration of frequencies is more towards the lower values of the variable i.e. the left tail is longer than the right tail.
Kurtosis:
It is also a characteristic of the frequency distribution. It gives an idea about the shape of a frequency distribution. Basically, the measure of kurtosis is the extent to which a frequency distribution is peaked in comparison with a normal curve. It is the degree of peakedness of a distribution.
Types of kurtosis: The following figure describes the classification of kurtosis:
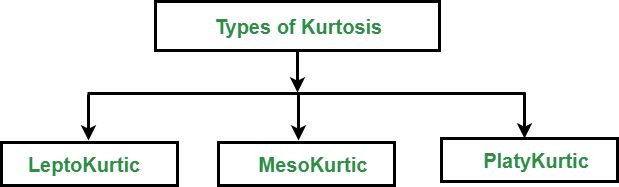
Types of Kurtosis
- Leptokurtic: Leptokurtic is a curve having a high peak than the normal distribution. In this curve, there is too much concentration of items near the central value.
- Mesokurtic: Mesokurtic is a curve having a normal peak than the normal curve. In this curve, there is equal distribution of items around the central value.
- Platykurtic: Platykurtic is a curve having a low peak than the normal curve is called platykurtic. In this curve, there is less concentration of items around the central value.
Difference Between Skewness and Kurtosis
| Sr. No. |
Skewness |
Kurtosis |
| 1. |
It indicates the shape and size of variation on either side of the central value. |
It indicates the frequencies of distribution at the central value. |
| 2. |
The measure differences of skewness tell us about the magnitude and direction of the asymmetry of a distribution. |
It indicates the concentration of items at the central part of a distribution. |
| 3. |
It indicates how far the distribution differs from the normal distribution. |
It studies the divergence of the given distribution from the normal distribution. |
| 4. |
The measure of skewness studies the extent to which deviation clusters is are above or below the average. |
It indicates the concentration of items. |
| 5. |
In an asymmetrical distribution, the deviation below or above an average is not equal. |
No such distribution takes place. |
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...