Data Communication Tutorial
Last Updated :
08 Sep, 2023
Data communication plays an important role in today’s interconnected world and enables the exchange of information between devices and networks. Whether you’re sending an email, making a video call, or browsing the web, data communication ensures that information flows smoothly.
This Data Communication tutorial is designed for both beginners and experienced professionals, covering basic and advanced concepts of data communication. It includes topics such as the basics of data communication, OSI Model, TCP/IP Model, addressing, and more.
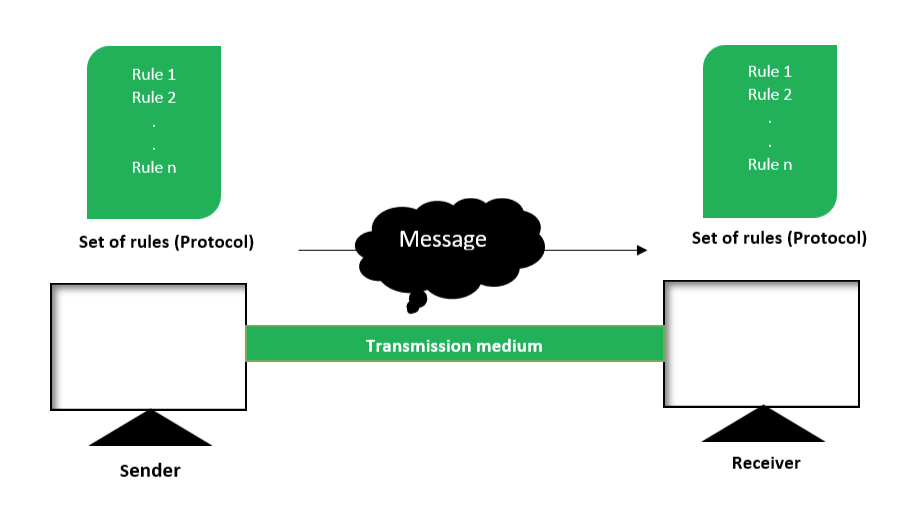
What is Data Communication?
Data communication refers to the process of transmitting and receiving data between two or more devices over a communication channel. It involves the conversion of data into signals that can be transmitted and then decoding those signals at the receiving end. Effective data communication requires the use of appropriate protocols, encoding techniques, and hardware devices.
Components of Data Communication
Data communication systems consist of several components that work together to enable the transfer of data. These components include:
- Sender: The device or system that initiates the data transmission.
- Receiver: The device or system that receives the transmitted data.
- Medium/Channel: The physical pathway through which data is transmitted, such as cables or wireless connections.
- Protocol: A set of rules and conventions that govern the transmission and reception of data.
- Modem: Short for modulator-demodulator, a device that converts digital signals into analog signals for transmission and vice versa.
Types of Data Transmission
Data transmission can occur in two primary ways:
- Serial Transmission: In serial transmission, data is transmitted bit by bit over a single communication channel. It is commonly used for long-distance communication and is more reliable but slower compared to parallel transmission.
- Parallel Transmission: In parallel transmission, multiple bits are transmitted simultaneously over separate communication channels. It allows for faster data transfer but is more susceptible to errors in long-distance transmissions.
Basics of Data Communication
OSI Model
TCP/IP Model
Addressing
- Physical Addresses
- Logical Addresses
- Port Addresses
- Specific Addresses
Data and Signals
Transmission of Signals
Multiplexing
Error Detection and Correction
Channelization
Logical Addressing
Network Security
Applications of Data Communication
Computer systems and other devices are connected to form a network. They provide numerous advantages:
- Video conferences
- Parallel computing
- Resource sharing such as printers and storage devices
- Exchange of information by means of e-Mails and FTP
- Information sharing by using the Web or the Internet
- Interaction with other users using dynamic web pages
- IP phones
- Instant messaging
FAQs on Data Communication
Q.1 What is the importance of data communication?
Data communication is important for connecting devices and for the transfer of information in the digital world and various technologies and services we dependent in daily life.
Q.2 How does data transmission occur?
Data transmission occurs through various mediums such as cables, wireless connections, or optical fibers. The data is encoded, transmitted, received, and decoded using protocols and devices.
Q.3 What are the benefits of wireless data communication?
Wireless data communication provides mobility, flexibility, and convenience. It allows devices to connect and communicate without the limitations of physical cables.
Q.4 How does data communication ensure security?
Data communication provide encryption, authentication, and other security measures to protect data from unauthorized access, interception, and tampering.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...