Count Unique Paths in matrix
Last Updated :
21 Sep, 2023
The problem is to count all unique possible paths from the top left to the bottom right of a M X N matrix with the constraints that from each cell you can either move only to the right or down
Examples:
Input: M = 2, N = 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two paths
(0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (1, 1)
(0, 0) -> (1, 0) -> (1, 1)
Input: M = 2, N = 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three paths
(0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (0, 2) -> (1, 2)
(0, 0) -> (0, 1) -> (1, 1) -> (1, 2)
(0, 0) -> (1, 0) -> (1, 1) -> (1, 2)
Count all possible paths from top left to the bottom right of a M X N matrix using Recursion:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can recursively move to right and down from the start until we reach the destination and then add up all valid paths to get the answer.
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Create a recursive function with parameters as row and column index
- Call this recursive function for N-1 and M-1
- In the recursive function
- If N == 1 or M == 1 then return 1
- else call the recursive function with (N-1, M) and (N, M-1) and return the sum of this
- Print the answer
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
if (m == 1 || n == 1)
return 1;
return numberOfPaths(m - 1, n)
+ numberOfPaths(m, n - 1);
}
int main()
{
cout << numberOfPaths(3, 3);
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
if (m == 1 || n == 1)
return 1;
return numberOfPaths(m - 1, n)
+ numberOfPaths(m, n - 1);
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Python3
def numberOfPaths(m, n):
if(m == 1 or n == 1):
return 1
return numberOfPaths(m-1, n) + numberOfPaths(m, n-1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
m = 3
n = 3
print(numberOfPaths(m, n))
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
if (m == 1 || n == 1)
return 1;
return numberOfPaths(m - 1, n)
+ numberOfPaths(m, n - 1);
}
static public void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function numberOfPaths(m, n)
{
if (m == 1 || n == 1)
return 1;
return numberOfPaths(m - 1, n) + numberOfPaths(m, n - 1);
}
document.write(numberOfPaths(3, 3)+"<br>");
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function numberOfPaths($m, $n)
{
if ($m == 1 || $n == 1)
return 1;
return numberOfPaths($m - 1, $n) +
numberOfPaths($m, $n - 1);
}
echo numberOfPaths(3, 3);
?>
|
Time Complexity: O(2N)
Auxiliary Space: O(N + M)
Count all possible paths from top left to the bottom right of a M X N matrix using Memoization:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
As the above recursive solution has overlapping subproblems so we can declare a 2-D array to save the values for different states of the recursive function and later on use the values of this dp array to get the answer for already solved subproblems
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Declare a 2-D array of size N X M
- Create a recursive function with parameters as row and column index and 2-D array
- Call this recursive function for N-1 and M-1
- In the recursive function
- If N == 1 or M == 1 then return 1
- If the value of this recursive function is not stored in the 2-D array then call the recursive function for (N-1, M, dp) and (N, M-1, dp) and assign the sum of answers of these functions in the 2-D array and return this value
- else return the value of this function stored in the 2-D array
- Print the answer
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int numberOfPaths(int n, int m, int DP[4][4])
{
if (n == 1 || m == 1)
return DP[n][m] = 1;
if (DP[n][m] == 0)
DP[n][m] = numberOfPaths(n - 1, m, DP)
+ numberOfPaths(n, m - 1, DP);
return DP[n][m];
}
int main()
{
int DP[4][4] = { 0 };
memset(DP, 0, sizeof(DP));
cout << numberOfPaths(3, 3, DP);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.util.*;
public class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int n, int m, int DP[][])
{
if (n == 1 || m == 1)
return DP[n][m] = 1;
if (DP[n][m] == 0)
DP[n][m] = numberOfPaths(n - 1, m, DP)
+ numberOfPaths(n, m - 1, DP);
return DP[n][m];
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
int DP[][] = new int[4][4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
DP[i][j] = 0;
}
}
System.out.println(numberOfPaths(3, 3, DP));
}
}
|
Python3
def numberOfPaths(n, m, DP):
if (n == 1 or m == 1):
DP[n][m] = 1
return 1
if (DP[n][m] == 0):
DP[n][m] = numberOfPaths(n - 1, m, DP) + numberOfPaths(n, m - 1, DP)
return DP[n][m]
if __name__ == '__main__':
DP = [[0 for i in range(4)] for j in range(4)]
print(numberOfPaths(3, 3, DP))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int n, int m, int[, ] DP)
{
if (n == 1 || m == 1)
return DP[n, m] = 1;
if (DP[n, m] == 0)
DP[n, m] = numberOfPaths(n - 1, m, DP)
+ numberOfPaths(n, m - 1, DP);
return DP[n, m];
}
public static void Main()
{
int[, ] DP = new int[4, 4];
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
DP[i, j] = 0;
}
}
Console.WriteLine(numberOfPaths(3, 3, DP));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let DP = new Array(4);
for(let i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
DP[i] = new Array(4);
for(let j = 0; j < 4; j++) {
DP[i][j] = 0;
}
}
function numberOfPaths(n, m, DP){
if(n == 1 || m == 1)
return DP[n][m] = 1;
if(DP[n][m] == 0)
DP[n][m] = numberOfPaths(n - 1, m,DP) + numberOfPaths(n, m - 1,DP);
return DP[n][m];
}
document.write(numberOfPaths(3, 3,DP));
</script>
|
Time Complexity: O(N * M)
Auxiliary Space: (N * M)
Count all possible paths from the top left to the bottom right of a M X N matrix using DP:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
So this problem has both properties (see this and this) of a dynamic programming problem. Like other typical Dynamic Programming(DP) problems, recomputations of the same subproblems can be avoided by constructing a temporary array count[][] in a bottom-up manner using the above recursive formula
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Declare a 2-D array count of size M * N
- Set value of count[i][0] equal to 1 for 0 <= i < M as the answer of subproblem with a single column is equal to 1
- Set value of count[0][j] equal to 1 for 0 <= j < N as the answer of subproblem with a single row is equal to 1
- Create a nested for loop for 0 <= i < M and 0 <= j < N and assign count[i][j] equal to count[i-1][j] + count[i][j-1]
- Print value of count[M-1][N-1]
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int count[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
count[i][0] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
count[0][j] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
count[i][j]
= count[i - 1][j]
+ count[i][j - 1];
}
return count[m - 1][n - 1];
}
int main()
{
cout << numberOfPaths(3, 3);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int count[][] = new int[m][n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
count[i][0] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
count[0][j] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
count[i][j]
= count[i - 1][j]
+ count[i]
[j - 1];
}
return count[m - 1][n - 1];
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Python3
def numberOfPaths(m, n):
count = [[0 for x in range(n)] for y in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
count[i][0] = 1
for j in range(n):
count[0][j] = 1
for i in range(1, m):
for j in range(1, n):
count[i][j] = count[i-1][j] + count[i][j-1]
return count[m-1][n-1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
m = 3
n = 3
print(numberOfPaths(m, n))
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int[, ] count = new int[m, n];
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
count[i, 0] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
count[0, j] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
count[i, j]
= count[i - 1, j]
+ count[i,
j - 1];
}
return count[m - 1, n - 1];
}
static public void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function numberOfPaths(m , n)
{
var count = Array(m).fill(0).map(x => Array(n).fill(0));
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
count[i][0] = 1;
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
count[0][j] = 1;
for (i = 1; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 1; j < n; j++)
count[i][j] = count[i - 1][j] + count[i][j - 1];
}
return count[m - 1][n - 1];
}
document.write(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function numberOfPaths($m, $n)
{
$count = array();
for ($i = 0; $i < $m; $i++)
$count[$i][0] = 1;
for ($j = 0; $j < $n; $j++)
$count[0][$j] = 1;
for ($i = 1; $i < $m; $i++)
{
for ($j = 1; $j < $n; $j++)
$count[$i][$j] = $count[$i - 1][$j] +
$count[$i][$j - 1];
}
return $count[$m - 1][$n - 1];
}
echo numberOfPaths(3, 3);
?>
|
Time Complexity: O(M * N) – Due to nested for loops.
Auxiliary Space: O(M * N) – We have used a 2D array of size M x N
Space optimization of the above approach:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
We can space optimize the above dp approach as for calculating the values of the current row we require only previous row
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Declare an array dp of size N
- Set dp[0] = 1
- Create a nested for loop for 0 <= i < M and 0 <= j < N and add dp[j-1] to dp[j]
- Print value of dp[n – 1]
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int dp[n] = { 1 };
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
int main() { cout << numberOfPaths(3, 3); }
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
public static void main(String args[])
{
System.out.println(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Python3
def numberOfPaths(p, q):
dp = [1 for i in range(q)]
for i in range(p - 1):
for j in range(1, q):
dp[j] += dp[j - 1]
return dp[q - 1]
if __name__ == '__main__':
print(numberOfPaths(3, 3))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.Write(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function numberOfPaths(m , n)
{
dp = Array.from({length: n}, (_, i) => 0);
dp[0] = 1;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++) {
for (j = 1; j < n; j++) {
dp[j] += dp[j - 1];
}
}
return dp[n - 1];
}
document.write(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function numberOfPaths($m, $n)
{
$dp = array();
$dp[0] = 1;
for ($i = 0; $i < $m; $i++)
{
for ($j = 1; $j < $n; $j++)
{
$dp[$j] += $dp[$j - 1];
}
}
return $dp[$n - 1];
}
echo numberOfPaths(3, 3);
?>
|
Time Complexity: O(M * N), The program uses nested loops to fill the 1D array “dp”. The outer loop runs “m” times, and the inner loop runs “n-1” times. Therefore, the time complexity of the program is O(M*N).
Auxiliary Space: O(N), The program uses a 1D array “dp” of size “n” to store the results of subproblems. Hence, the space complexity of the program is O(N).
This code is contributed by Vivek Singh
Note: the count can also be calculated using the formula (M-1 + N-1)!/(M-1)! * (N-1)!
Count all possible paths from top left to the bottom right of a M X N matrix using combinatorics:
To solve the problem follow the below idea:
In this approach, We have to calculate m+n-2Cn-1 here which will be (m+n-2)! / (n-1)! (m-1)!
m = number of rows, n = number of columns
Total number of moves in which we have to move down to reach the last row = m – 1 (m rows, since we are starting from (1, 1) that is not included)
Total number of moves in which we have to move right to reach the last column = n – 1 (n column, since we are starting from (1, 1) that is not included)
Down moves = (m – 1)
Right moves = (n – 1)
Total moves = Down moves + Right moves = (m – 1) + (n – 1)
Now think of moves as a string of ‘R’ and ‘D’ characters where ‘R’ at any ith index will tell us to move ‘Right’ and ‘D’ will tell us to move ‘Down’. Now think of how many unique strings (moves) we can make where in total there should be (n – 1 + m – 1) characters and there should be (m – 1) ‘D’ character and (n – 1) ‘R’ character?
Choosing positions of (n – 1) ‘R’ characters results in the automatic choosing of (m – 1) ‘D’ character positions
The number of ways to choose positions for (n – 1) ‘R’ character = Total positions C n – 1 = Total positions C m – 1 = (n – 1 + m – 1) != 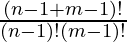
Another way to think about this problem:
Count the Number of ways to make an N digit Binary String (String with 0s and 1s only) with ‘X’ zeros and ‘Y’ ones (here we have replaced ‘R’ with ‘0’ or ‘1’ and ‘D’ with ‘1’ or ‘0’ respectively whichever suits you better)
Follow the below steps to solve the problem:
- Declare a variable path equal to 1
- Create a for loop from i equal to n to (m + n – 1)
- Set path equal to path * i
- Set path equal to path divided by (i – n + 1)
- Return path
Below is the implementation of the above approach:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int path = 1;
for (int i = n; i < (m + n - 1); i++) {
path *= i;
path /= (i - n + 1);
}
return path;
}
int main()
{
cout << numberOfPaths(3, 3);
return 0;
}
|
Java
import java.io.*;
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int path = 1;
for (int i = n; i < (m + n - 1); i++) {
path *= i;
path /= (i - n + 1);
}
return path;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Python3
def numberOfPaths(m, n):
path = 1
for i in range(n, (m + n - 1)):
path *= i
path //= (i - n + 1)
return path
print(numberOfPaths(3, 3))
|
C#
using System;
class GFG {
static int numberOfPaths(int m, int n)
{
int path = 1;
for (int i = n; i < (m + n - 1); i++) {
path *= i;
path /= (i - n + 1);
}
return path;
}
public static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
function numberOfPaths(m , n)
{
var path = 1;
for (i = n; i < (m + n - 1); i++) {
path *= i;
path = parseInt(path/(i - n + 1));
}
return path;
}
document.write(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
</script>
|
PHP
<?php
function numberOfPaths($m, $n)
{
$path = 1;
for ($i = $n; $i < ($m + $n - 1); $i++)
{
$path *= $i;
$path /= ($i - $n + 1);
}
return $path;
}
{
echo(numberOfPaths(3, 3));
}
|
Time Complexity: O(M), The time complexity is O(M), where M is the maximum of m and n. This is because the for loop iterates M times, and each iteration involves a constant number of arithmetic operations.
Auxiliary Space: O(1), The space complexity of the program is also O(1), which means that it uses a constant amount of memory regardless of the input size. This is because the program does not create any data structures or arrays that grow with the input size, and all calculations are done using only a few variables.
Like Article
Suggest improvement
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...