Java.lang.Thread Class in Java
Last Updated :
13 Mar, 2024
Thread is a line of execution within a program. Each program can have multiple associated threads. Each thread has a priority which is used by the thread scheduler to determine which thread must run first. Java provides a thread class that has various method calls in order to manage the behavior of threads by providing constructors and methods to perform operations on threads.
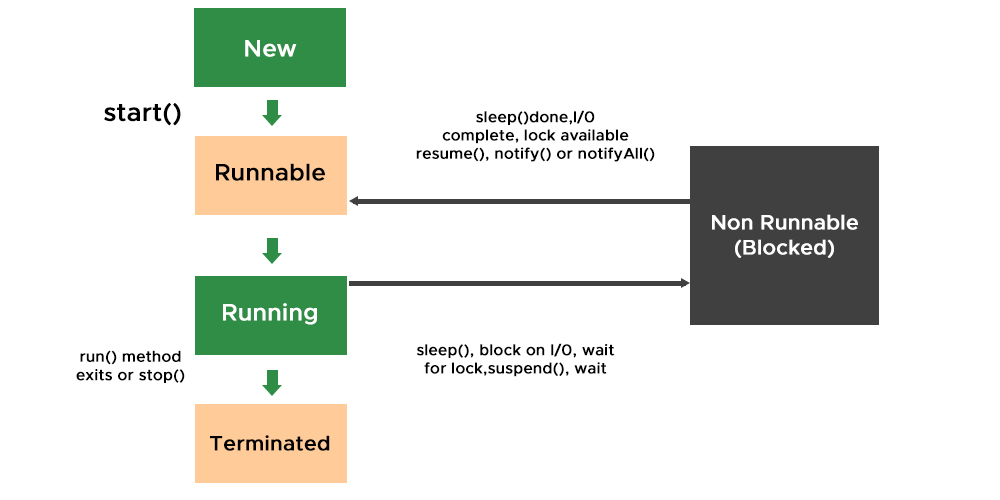
Ways of creating threads
- Creating own class which is extending to parent Thread class
- Implementing the Runnable interface.
Below are the pseudo-codes that one can refer to get a better picture about thread henceforth Thread class.
Illustration 1:
Java
// Way 1
// Creating thread By Extending To Thread class
class MyThread extends Thread {
// Method 1
// Run() method for our thread
public void run()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println(
"Thread is running created by extending to parent Thread class");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of our thread class inside main()
// method
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
// Starting the thread
myThread.start();
}
}
OutputThread is running created by extending to parent Thread class
Illustration 2:
Java
// Way 2
// Creating thread using Runnable interface
class ThreadUsingInterface implements Runnable {
// Method 1
// run() method for the thread
public void run()
{
// Print statement
System.out.println("Thread is created using Runnable interface");
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Creating object of our thread class inside main()
// method
ThreadUsingInterface obj = new ThreadUsingInterface();
// Passing the object to thread in main()
Thread myThread = new Thread(obj);
// Starting the thread
myThread.start();
}
}
OutputThread is created using Runnable interface
Thread Class in Java
A thread is a program that starts with a method() frequently used in this class only known as the start() method. This method looks out for the run() method which is also a method of this class and begins executing the body of the run() method. Here, keep an eye over the sleep() method which will be discussed later below.
Note: Every class that is used as thread must implement Runnable interface and over ride it’s run method.
Syntax:
public class Thread extends Object implements Runnable
Constructors of this class are as follows:
| Constructor | Action Performed |
|---|
| Thread() | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(Runnable target) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(Runnable target, String name) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(String name) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) | Allocates a new Thread object so that it has targeted as its run object, has the specified name as its name, and belongs to the thread group referred to by a group. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name, long stackSize) | Allocates a new Thread object so that it has targeted as its run object, has the specified name as its name, and belongs to the thread group referred to by group, and has the specified stack size. |
| Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) | Allocates a new Thread object. |
Methods of Thread class:
Now let us do discuss all the methods of this class are illustrated as follows:
| Methods | Action Performed |
|---|
| activeCount() | Returns an estimate of the number of active threads in the current thread’s thread group and its subgroups |
| checkAccess() | Determines if the currently running thread has permission to modify this thread |
| clone() | Throws CloneNotSupportedException as a Thread can not be meaningfully cloned |
| currentThread() | Returns a reference to the currently executing thread object |
| dumpStack() | Prints a stack trace of the current thread to the standard error stream |
| enumerate(Thread[] tarray) | Copies into the specified array every active thread in the current thread’s thread group and its subgroups |
| getAllStackTraces() | Returns a map of stack traces for all live threads |
| getContextClassLoader() | Returns the context ClassLoader for this Thread |
| getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler() | Returns the default handler invoked when a thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception |
| getId() | Returns the identifier of this Thread |
| getName() | Returns this thread’s name |
| getPriority() | Returns this thread’s priority |
| getStackTrace() | Returns an array of stack trace elements representing the stack dump of this thread |
| getState() | Returns the state of this thread |
| getThreadGroup() | Returns the thread group to which this thread belongs |
| getUncaughtExceptionHandler() | Returns the handler invoked when this thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception |
| holdsLock(Object obj) | Returns true if and only if the current thread holds the monitor lock on the specified object |
| interrupt() | Interrupts this thread |
| interrupted() | Tests whether the current thread has been interrupted |
| isAlive() | Tests if this thread is alive |
| isDaemon() | Tests if this thread is a daemon thread |
| isInterrupted() | Tests whether this thread has been interrupted |
| join() | Waits for this thread to die |
| join(long millis) | Waits at most millis milliseconds for this thread to die |
| run() | If this thread was constructed using a separate Runnable run object, then that Runnable object’s run method is called; otherwise, this method does nothing and returns |
| setContextClassLoader(ClassLoader cl) | Sets the context ClassLoader for this Thread |
| setDaemon(boolean on) | Marks this thread as either a daemon thread or a user thread |
| setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler( Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) | Set the default handler invoked when a thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception, and no other handler has been defined for that thread |
| setName(String name) | Changes the name of this thread to be equal to the argument name. |
| setUncaughtExceptionHandler( Thread.UncaughtExceptionHandler eh) | Set the handler invoked when this thread abruptly terminates due to an uncaught exception |
| setPriority(int newPriority) | Changes the priority of this thread |
| sleep(long millis) | Causes the currently executing thread to sleep (temporarily cease execution) for the specified number of milliseconds, subject to the precision and accuracy of system timers and schedulers |
| start() | Causes this thread to begin execution; the Java Virtual Machine calls the run method of this thread |
| toString() | Returns a string representation of this thread, including the thread’s name, priority, and thread group |
| yield() | A hint to the scheduler that the current thread is willing to yield its current use of a processor |
Also do remember there are certain methods inherited from class java. lang.Object that are as follows:
- equals() Method
- finalize() Method
- getClass() Method
- hashCode() Method
- notify() Method
- notifyAll() Method
- toString() Method
- wait() Method
Example: Java program to demonstrate usage of Thread class
Java
// Java program Demonstrating Methods of Thread class
// Importing package
package generic;
// Class 1
// Helper class implementing Runnable interface
class Helper implements Runnable {
//
public void run() {
// Try block to check for exceptions
try {
// Print statement
System.out.println("thread2 going to sleep for 5000");
// Making thread sleep for 0.5 seconds
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
// Catch block to handle exception
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Print statement
System.out.println("Thread2 interrupted");
}
}
}
// Class 2
// Helper class extending Runnable interface
public class Test implements Runnable {
// Method 1
// run() method of this class
public void run() {
// Thread run() method
}
// Method 2
// Main driver method
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Making objects of class 1 and 2 in main() method
Test obj = new Test();
Helper obj2 = new Helper();
// Creating 2 threads in main() method
Thread thread1 = new Thread(obj);
Thread thread2 = new Thread(obj2);
// Moving thread to runnable states
thread1.start();
thread2.start();
// Loading thread 1 in class 1
ClassLoader loader = thread1.getContextClassLoader();
// Creating 3rd thread in main() method
Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Helper());
// Getting number of active threads
System.out.println(Thread.activeCount());
thread1.checkAccess();
// Fetching an instance of this thread
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
// Print and display commands
System.out.println(t.getName());
System.out.println("Thread1 name: " + thread1.getName());
System.out.println("Thread1 ID: " + thread1.getId());
// Fetching the priority and state of thread1
System.out.println("Priority of thread1 = " + thread1.getPriority());
// Getting the state of thread 1 using getState() method
// and printing the same
System.out.println(thread1.getState());
thread2 = new Thread(obj2);
thread2.start();
thread2.interrupt();
System.out.println("Is thread2 interrupted? " + thread2.interrupted() );
System.out.println("Is thread2 alive? " + thread2.isAlive());
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
thread1.setDaemon(true);
System.out.println("Is thread1 a daemon thread? " + thread1.isDaemon());
System.out.println("Is thread1 interrupted? " + thread1.isInterrupted());
// Waiting for thread2 to complete its execution
System.out.println("thread1 waiting for thread2 to join");
try {
thread2.join();
}
catch (InterruptedException e) {
// Display the exception along with line number
// using printStackTrace() method
e.printStackTrace();
}
// Now setting the name of thread1
thread1.setName("child thread xyz");
// Print and display command
System.out.println("New name set for thread 1" + thread1.getName());
// Setting the priority of thread1
thread1.setPriority(5);
thread2.yield();
// Fetching the string representation of thread1
System.out.println(thread1.toString());
// Getting list of active thread in current thread's group
Thread[] tarray = new Thread[3];
Thread.enumerate(tarray);
// Display commands
System.out.println("List of active threads:");
System.out.printf("[");
// Looking out using for each loop
for (Thread thread : tarray) {
System.out.println(thread);
}
// Display commands
System.out.printf("]\n");
System.out.println(Thread.getAllStackTraces());
ClassLoader classLoader = thread1.getContextClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader.toString());
System.out.println(thread1.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread2.setUncaughtExceptionHandler(thread1.getDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread1.setContextClassLoader(thread2.getContextClassLoader());
thread1.setDefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(thread2.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
thread1 = new Thread(obj);
StackTraceElement[] trace = thread1.getStackTrace();
System.out.println("Printing stack trace elements for thread1:");
for (StackTraceElement e : trace) {
System.out.println(e);
}
ThreadGroup grp = thread1.getThreadGroup();
System.out.println("ThreadGroup to which thread1 belongs " + grp.toString());
System.out.println(thread1.getUncaughtExceptionHandler());
System.out.println("Does thread1 holds Lock? " + thread1.holdsLock(obj2));
Thread.dumpStack();
}
}
Output:
3
main
Thread1 name: Thread-0
Thread1 ID: 10
Priority of thread1 = 5
RUNNABLE
Is thread2 interrupted? false
Is thread2 alive? true
Is thread1 a daemon thread? true
Is thread1 interrupted? false
thread1 waiting for thread2 to join
thread2 going to sleep for 5000 ms
thread2 going to sleep for 5000 ms
Thread2 interrupted
New name set for thread 1child thread xyz
Thread[child thread xyz, 5, main]
List of active threads:
[Thread[main, 5, main]
Thread[Thread-1, 5, main]
null
]
{Thread[Signal Dispatcher, 9, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@33909752,
Thread[Thread-1, 5, main]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@55f96302,
Thread[main, 5, main]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@3d4eac69,
Thread[Attach Listener, 5, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@42a57993,
Thread[Finalizer, 8, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@75b84c92,
Thread[Reference Handler, 10, system]=[Ljava.lang.StackTraceElement;@6bc7c054}
sun.misc.Launcher$AppClassLoader@73d16e93
null
Printing stack trace elements for thread1:
ThreadGroup to which thread1 belongs java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main, maxpri=10]
java.lang.ThreadGroup[name=main, maxpri=10]
Does thread1 holds Lock? false
java.lang.Exception: Stack trace
at java.lang.Thread.dumpStack(Unknown Source)
at generic.Test.main(Test.java:111)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...