A Peterson Graph Problem
Last Updated :
20 Feb, 2023
The following graph G is called a Petersen graph and its vertices have been numbered from 0 to 9. Some letters have also been assigned to vertices of G, as can be seen from the following picture:
Let’s consider a walk W in graph G, which consists of L vertices W1, W2, …, WL. A string S of L letters ‘A’ – ‘E’ is realized by walking W if the sequence of letters written along W is equal to S. Vertices can be visited multiple times while walking along W.
For example, S = ‘ABBECCD’ is realized by W = (0, 1, 6, 9, 7, 2, 3). Determine whether there is a walk W that realizes a given string S in graph G and if so then find the lexicographically least such walk. The only line of input contains one string S. If there is no walk W which realizes S, then output -1 otherwise, you should output the least lexicographical walk W which realizes S.
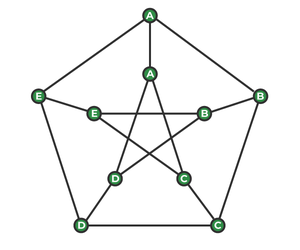
Example of a Petersen Graph
Examples:
Input : s = 'ABB'
Output: 016
Explanation: As we can see in the graph
the path from ABB is 016.
Input : s = 'AABE'
Output :-1
Explanation: As there is no path that
exists, hence output is -1.
Algorithm for a Peterson Graph Problem:
petersonGraphWalk(S, v):
begin
res := starting vertex
for each character c in S except the first one, do
if there is an edge between v and c in outer graph, then
v := c
else if there is an edge between v and c+5 in inner graph, then
v := c + 5
else
return false
end if
put v into res
done
return true
end
Below is the implementation of the above algorithm:
C++
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
char S[100005];
bool adj[10][10];
char result[100005];
bool findthepath(char* S, int v)
{
result[0] = v + '0';
for (int i = 1; S[i]; i++) {
if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A'] || adj[S[i] -
'A'][v]) {
v = S[i] - 'A';
}
else if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A' + 5] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A' + 5][v]) {
v = S[i] - 'A' + 5;
}
else
return false;
result[i] = v + '0';
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = adj[3][4] =
adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] =
adj[3][8] = adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] =
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = true;
char S[] = "ABB";
if (findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A') ||
findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A' + 5)) {
cout << result;
} else {
cout << "-1";
}
return 0;
}
|
Java
class GFG
{
static char []S = new char[100005];
static boolean [][]adj = new boolean[10][10];
static char[] result = new char[100005];
static boolean findthepath(char[] S, int v)
{
result[0] = (char) (v + '0');
for (int i = 1; i<(int)S.length; i++)
{
if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A'] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A'][v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A';
}
else if (adj[v][S[i] - 'A' + 5] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A' + 5][v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A' + 5;
}
else
return false;
result[i] = (char) (v + '0');
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = adj[3][4] =
adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] =
adj[3][8] = adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] =
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = true;
char S[] = "ABB".toCharArray();
if (findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A') ||
findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A' + 5))
{
System.out.print(result);
}
else
{
System.out.print("-1");
}
}
}
|
Python3
adj = [[False for i in range(10)] for j in range(10)]
result = [0]
def findthepath(S, v):
result[0] = v
for i in range(1, len(S)):
if (adj[v][ord(S[i]) - ord('A')] or
adj[ord(S[i]) - ord('A')][v]):
v = ord(S[i]) - ord('A')
else if (adj[v][ord(S[i]) - ord('A') + 5] or
adj[ord(S[i]) - ord('A') + 5][v]):
v = ord(S[i]) - ord('A') + 5
else:
return False
result.append(v)
return True
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = \
adj[3][4] = adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = \
adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] = adj[3][8] = \
adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] = \
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = True
S= "ABB"
S=list(S)
if (findthepath(S, ord(S[0]) - ord('A')) or
findthepath(S, ord(S[0]) - ord('A') + 5)):
print(*result, sep = "")
else:
print("-1")
|
C#
using System;
public class GFG
{
static bool [,]adj = new bool[10, 10];
static char[] result = new char[100005];
static bool findthepath(String S, int v)
{
result[0] = (char) (v + '0');
for (int i = 1; i < S.Length; i++)
{
if (adj[v,S[i] - 'A'] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A',v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A';
}
else if (adj[v,S[i] - 'A' + 5] ||
adj[S[i] - 'A' + 5,v])
{
v = S[i] - 'A' + 5;
}
else
return false;
result[i] = (char) (v + '0');
}
return true;
}
public static void Main(String[] args)
{
adj[0,1] = adj[1,2] = adj[2,3] = adj[3,4] =
adj[4,0] = adj[0,5] = adj[1,6] = adj[2,7] =
adj[3,8] = adj[4,9] = adj[5,7] = adj[7,9] =
adj[9,6] = adj[6,8] = adj[8,5] = true;
String S = "ABB";
if (findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A') || findthepath(S, S[0] - 'A' + 5))
{
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
else
{
Console.Write("-1");
}
}
}
|
Javascript
<script>
let adj = new Array(10).fill(0).map(() => new Array(10).fill(false))
let result = new Array(100005)
function findthepath(S, v) {
result[0] = v
for (let i = 1; i < S.length; i++) {
if (adj[v][S[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0)] ||
adj[S[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0)][v]) {
v = S[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0);
}
else if (adj[v][S[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0) + 5] ||
adj[S[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0) + 5][v]) {
v = S[i].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0) + 5;
}
else
return false;
result[i] = String.fromCharCode(v + '0'.charCodeAt(0));
}
return true;
}
adj[0][1] = adj[1][2] = adj[2][3] = adj[3][4] =
adj[4][0] = adj[0][5] = adj[1][6] = adj[2][7] =
adj[3][8] = adj[4][9] = adj[5][7] = adj[7][9] =
adj[9][6] = adj[6][8] = adj[8][5] = true;
let S = "ABB";
S = S.split("")
if (findthepath(S, S[0].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0)) || findthepath(S, S[0].charCodeAt(0) - 'A'.charCodeAt(0) + 5)) {
document.write(result.join(""));
}
else {
document.write("-1");
}
</script>
|
Time complexity: O(N)
The time complexity of the above program is O(N), where N is the length of the given string S. We are applying Breadth First Search here, which runs in linear time.
Space complexity: O(N)
The space complexity of the above program is O(N), where N is the length of the given string S. We are using two auxiliary arrays – result[] and S[] to store the path and the given string, respectively. Both of them require linear space.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...