Message switching techniques
Last Updated :
26 Apr, 2024
Switching is the technique by which nodes control or switch data to transmit it between specific points on a network. In message switching the entire message is transmitted without any break from one node to another. There is no direct link present between the sender and the receiver in message switching.
What is Message Switching?
Message switching is a switching mechanism in which a message is sent as a single unit and routed to intermediary nodes where it is stored and forwarded. The message-switching approach does not provide a dedicated path between the sender and receiver. In message switching, end-users communicate by sending and receiving messages that include the entire data to be shared. Messages are the smallest individual unit. Also, the sender and receiver are not directly connected. Several intermediate nodes transfer data and ensure that the message reaches its destination. Message-switched data networks are hence called hop-by-hop systems.
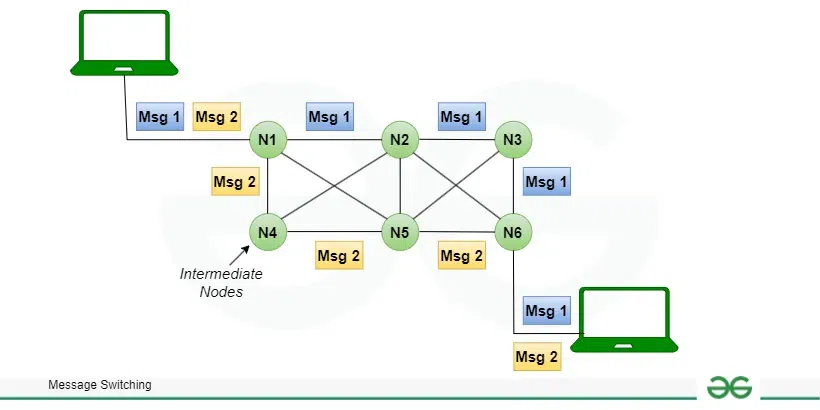
Message Switching
- Store and forward – The intermediate nodes have the responsibility of transferring the entire message to the next node. Hence, each node must have storage capacity. A message will only be delivered if the next hop and the link connecting it are both available, otherwise, it’ll be stored indefinitely. A store-and-forward switch forwards a message only if sufficient resources are available and the next hop is accepting data. This is called the store-and-forward property.
- Message delivery – This implies wrapping the entire information in a single message and transferring it from the source to the destination node. Each message must have a header that contains the message routing information, including the source and destination.
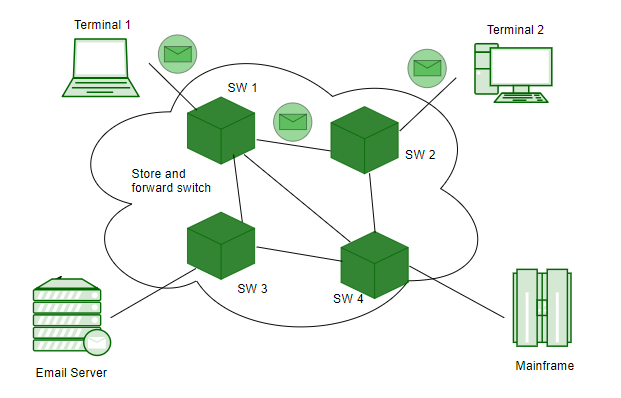
Message switching network consists of transmission links (channels), store-and-forward switch nodes, and end stations as shown in the following picture:
Advantages of Message Switching
- As message switching is able to store the message for which communication channel is not available, it helps in reducing the traffic congestion in the network.
- In message switching, the data channels are shared by the network devices.
- It makes traffic management efficient by assigning priorities to the messages.
- Because the messages are delivered via a store and forward method, it is possible to include priority in them.
- It allows for infinite message lengths.
- Unlike circuit switching, it does not necessitate the actual connection of source and destination devices.
Disadvantages of Message Switching
- Message switching cannot be used for real-time applications as storing messages causes delay.
- In message switching, the message has to be stored for which every intermediate device in the network requires a large storing capacity.
- Because the system is so intricate, people are frequently unaware of whether or not messages are correctly conveyed. This could cause problems in social relationships.
- The type of message switching does not create a dedicated path between the devices. It is not dependable communication because there is no direct relationship between sender and receiver.
Applications of Message Switching
The store-and-forward method was implemented in telegraph message switching centres. Today, although many major networks and systems are packet-switched or circuit-switched networks, their delivery processes can be based on message switching. For example, in most electronic mail systems the delivery process is based on message switching, while the network is in fact either circuit-switched or packet-switched.
Difference Between Message Switching and Packet Switching
|
Message Switching
|
Packet Switching
|
|
In message switching the complete message is passed across a network.
|
In packet switching the entire message is broken into smaller units known as Packets.
|
|
In this, computer language used is ASCII, baudot, morse.
|
In packet switching, binary type is used.
|
|
Message exist only in one location in the network.
|
Packets of the message exist in many places in the network.
|
|
Access time is reduced due to increase in performance as packets are stored in disk.
|
Packets are stored in main memory.
|
|
In message switching there is no limit on block size.
|
Packet switching places a tight upper limit on block size.
|
|
Physical links are allocated dynamically.
|
Virtual links are made simultaneously.
|
Frequently Asked Question on Message Switching – FAQs
Where is message switching used?
Military networks, ad hoc sensor networks, and satellite communications uses message switching technology.
What moves messages between networks?
Routers work at the network layer of the OSI model, efficiently transmitting data between local area networks.
What is the role of addressing in message switching?
Addressing is critical in message switching since it determines the path a message goes throughout the network.
How does message switching ensure message delivery?
Message switching often uses error detection and correction techniques to assure message delivery.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...