Differentiation allows us to analyze how a function changes over its domain. We define the process of finding the derivatives as differentiation. The derivative of any function f(x) is represented as d/dx.f(x).
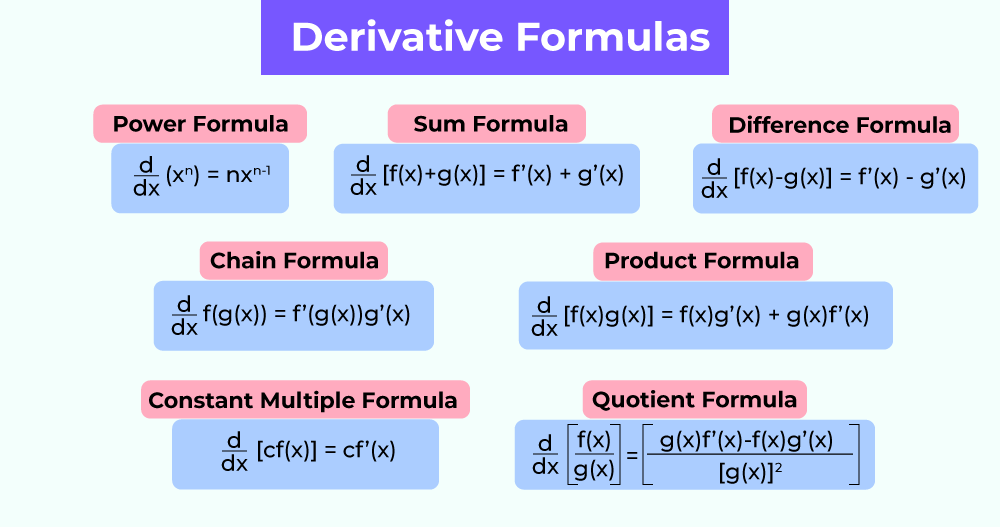
In this article, we will learn about various differentiation formulas for Trigonometric Functions, Inverse Trigonometric Functions, Logarithmic Functions, etc. and their examples in detail.
What is Differentiation?
Differentiation is defined as the rate of change of one quantity with respect to the other quantity. .
For any function y = f(x), if the input value changes from x to x + h then y = f(x + h) then the differentiation of the f(x) with respect to x is defined as,
dy/dx = limh→0 {f(x+h) – f(x)}/{(x+h) – x}
Mathematically,
dy/dx = f'(x) = limh→0 {f(x+h) – f(x)}/h
Differentiation formulas are used to find the differentiation of the various functions. The first principle formula states that, for any function f(x) its derivative with respect to x is,
f'(x) = limh→0 {f(x+h) – f(x)}/h
Basic Differentiation Formulas
The differentiation formulas for some elementary functions are:
| Function (y =) |
Differentiation Formula (dy/dx =) |
| c (constant) |
0 |
| xn (power) |
nxn-1 |
| ln x (logarithmic) |
1/x |
| ex(exponent) |
ex |
| ax (exponent) |
ax log a |
Differentiation of Trigonometric Functions
Derivatives of the trigonometric functions are:
| Function (y =) |
Derivative (dy/dx =) |
| sin x |
cos x |
| cos x |
-sin x |
| tan x |
sec² x |
| sec x |
sec x · tan x |
| cosec x |
-cosec x · cot x |
| cot x |
-cosec² x |
Differentiation of Inverse Trigonometric Functions
The differentiation formulas for the Inverse trigonometric functions are :
| Function (y =) |
Differentiation Formula (dy/dx =) |
| sin⁻¹ x |
1/√(1 – x²) |
| cos⁻¹ x |
-1/√(1 – x²) |
| tan⁻¹ x |
1/(1 + x²) |
| sec⁻¹ x |
1/(|x|·√(x² – 1)) |
| cosec⁻¹ x |
-1/(|x|·√(x² – 1)) |
| cot⁻¹ x |
-1/(1 + x²) |
Differentiation of Hyperbolic Functions
Let’s discuss the Differentials of Hyperbolic functions.
| Function (y =) |
Differentiation Formula (dy/dx =) |
| sinh x |
cosh x |
| cosh x |
sinh x |
| tanh x |
sech² x |
| sech x |
-sech x · tanh x |
| cosech x |
-cosech x · coth x |
| coth x |
-cosech² x |
Differentiation Rules
Various rules of finding the derivative of functions have been given below :
| Rules |
Function Form (y =) |
Differentiation Formula (dy/dx =) |
| Sum Rule |
u(x) ± v(x) |
du/dx ± dv/dx |
| Product Rule |
u(x) × v(x) |
u dv/dx + v du/dx |
| Quotient Rule |
u(x) ÷ v(x) |
(v du/dx – u dv/dx) / v² |
| Chain Rule |
f(g(x)) |
f'[g(x)] g'(x) |
| Constant Rule |
k f(x), k ≠ 0 |
k d/dx f(x) |
Differentiation of Special Functions
If we have two parametric functions x = f(t), y = g(t), where t is the parameter, then the differentiation of parametric functions is as follows,
As dy/dt = g'(t) and dx/dt = f'(t) then dy/dx is given by:
dy/dx = (dy/dt)/(dx/dt) = g'(t)/f'(t)
Implicit Differentiation
Some functions are of the type where separating dependent variable (y) and independent variable (x) is not possible these functions are of the form f(x,y) = 0 the differentiation of these functions is not found using the normal formulas then the differentiation of these functions is found using the concept as shown in the example added below,
Example: Find the differentiation of x2 + y2 + 4xy = 0
Solution:
x2 + y2 + 4xy = 0
Differentiating with respect to x,
2x + 2ydy/dx + 4(xdy/dx + y) = 0
⇒ 2x + 4y + 2dy/dx(y + 2x) = 0
⇒ x + 2y + dy/dx(y + 2x) = 0
⇒ dy/dx(y + 2x) = -(x + 2y)
⇒ dy/dx = -(x + 2y)/(y + 2x)
Higher Order Differentiation
Higher order differentiation is nothing but the differentiation of a function more than one time suppose we have a function y = f(x) then its differential in higher order is calculated as,
First Derivative = dy/dx = f'(x)
Second Derivative = d2y/dx2 = f”(x)
Third Derivative = d3y/dx3 = f”'(x)
….
….
nth Derivative = dny/dxn = f(n)(x)
This can be understood using the example added below,
Example: Find the second-order derivative of f(x) = 4x4 + 3x3 + 2x2 + x + 1
Solution:
f(x) = 4x4 + 3x3 + 2x2 + x + 1
Differentiating with respect to x,
f‘(x) = 4(4x3) + 3(3x2) + 2(2x) + 1 + 0
⇒ f'(x) = 16x3 + 9x2 + 4x + 1
For second-order derivative differentiating with respect to x,
f”(x) = 16(3x2) + 9(2x) + 4 + 0
⇒ f”(x) = 48x2 + 18x + 4
This is the required second-order derivative.
Related :
Examples of Differentiation
Let’s solve some example problems on the rules of derivative.
Example 1: Find the differentiation of y = 4x3 + 7x2 + 11x + 12
Solution:
Given
Differentiating with respect to x,
dy/dx = 4(3x2) + 7(2x) + 11(1) + 0
⇒ dy/dx = 12x2 + 14x + 11
This is the required differentiation
Example 2: Find the differentiation of y = cos(log x)
Solution:
Given
Differentiating with respect to x,
dy/dx = d/dx{cos (log x)}
⇒ dy/dx = sin (log x).{d/dx(log x)}
⇒ dy/dx = sin (log x).(1/x)
This is the required differentiation
Example 3: Find the differentiation of y = tan (3x2 + 4x)
Solution:
Given
Differentiating with respect to x,
dy/dx = 1/{1 + (3x2 + 4x)2}2 d/dx(3x2 + 4x)
⇒ dy/dx = 1/{1 + (3x2 + 4x)2}2 (6x + 4)
⇒ dy/dx = (6x + 4)/{1 + (3x2 + 4x)2}2
This is the required differentiation
Practice Problems on Differentiation
Problem 1: Find the derivative of the function f(x) = 3x2 + 5x – 2.
Problem 2: Determine the derivative of g(x) = \frac{1}{x}.
Problem 3: Find the derivative of h(x) = \sqrt{x^3 + 2x – 1}.
Problem 4: Determine the derivative of y(x) = e^{2x}.
Problem 5: Find the derivative of f(x) = \ln(x^2 + 3x).
What is Differentiation?
We define Differentiation as the rate of change of one quantity with respect to the other quantity. We represent the differentiation of y = f(x) as, dy/dx.
What is Product rule of Differentiation?
The differentiation of Product rule is,
For the function f(x) = u.v the differentiation of f(x) is,
f'(x) = ud/dx(v) + vd/dx(u)
What is Differentiation of cot x?
The differentiation of y = cot x is,
dy/dx = -cosec2x
What is the Differentiation of sec x?
The differentiation of y = sec x is,
dy/dx = sec x. tan x
What is Differentiation of log x?
The differentiation of y = log x is,
dy/dx = 1/x
What is Differentiation of tan x?
The differentiation of y = tan x is,
dy/dx = sec2 x
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...