Convection is one of the ways out of three ways, in which heat can transfer between systems or substances. Other than Convection, Conduction, and Radiation are the other two modes of heat transfer. It has probably been seen that if a cup of hot tea is left on a table for a long period, it cools down.
This is due to heat loss to the environment. As a result, heat transfer is described as the transmission of heat or thermal energy from one physical system to another. Therefore, when two bodies have a temperature differential, heat is transported from the hot body to the cooler body.
What is Convection?
The action of heat transmission through movement of major number of molecules inside fluids such as gases and liquids are known as convection.
The initial heat transmission between the item and the fluid occurs by conduction, but the bulk of the heat transfer occurs because of fluid motion. Solids do not experience convection because their basic particles do not move. The process of heat diffusion in solids is known as thermal conduction. Under normal conditions, gases and liquids are poor heat conductors, however, they may quickly transport heat by convection.
The image added below shows the transfer of heat through convection.

Heat Transfer by Convection: How Does It Work?
Convection is the process of heat transfer between a solid and a liquid or fluid that is in contact with the solid. When transmitting heat from one liquid to another through a barrier, convection is essential. Convectional heat transfer occurs either through thermal diffusion (fluid molecule motion) or advection, in which heat is transferred through the bulk motion of heat currents in the fluid.
The heat transfer through all three mediums Conduction, Convection, and Radiation is shown in the image below.
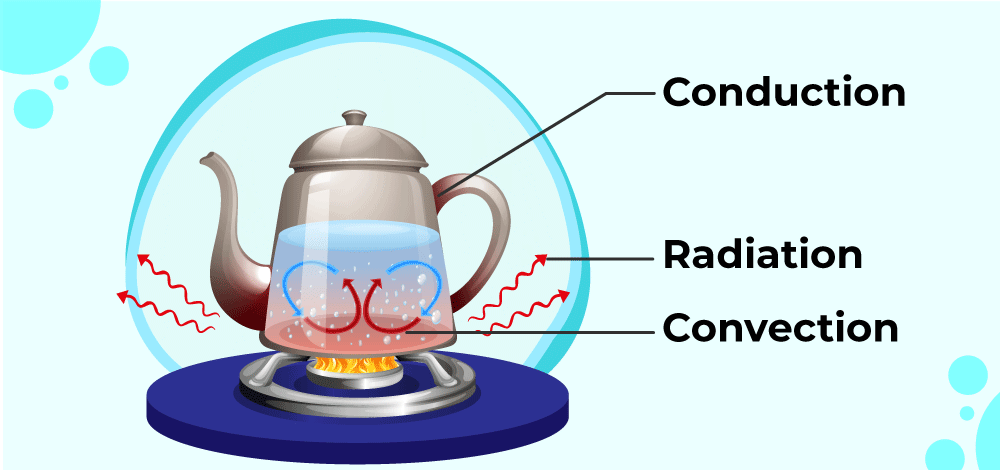
Thermal expansion occurs when any fluid is heated from below. The fluid’s density decreases in lower layers as it becomes hotter. The hotter, less dense part of the fluid rises because of buoyancy and is replaced by denser, colder fluid. When this part heats up, it also rises and is replaced by the upper colder layer, and the process is repeated. In this way, convection is used to transmit heat.
Check: Thermal Expansion Formula
Convection Examples
Melting Ice, raising hot air above the fire, modern air conditioning, car radiators, microwave convection oven, water heater, etc are examples of convection in our daily life. Other than these there are some more examples, which are as follows:
- Warm water goes toward the poles as it approaches the equator, whereas cooler water goes toward the equator.
- Warm-blooded animals use convection to circulate their blood, which helps to regulate their body temperature.
- The phenomenon of the sea and the land wind is one of the most prevalent examples of natural convection.
Sea Breeze
During the day, there is a wind from the sea. Both the water and the land are heated by the sun. Because water has a higher heating capacity than land, it receives more of the sun’s energy yet warms up considerably more slowly. As a result, the temperature above the land rises, heating the air in the surrounding environment.
Warm air expands because it is less dense, resulting in a low-pressure region over the land along the shore. Meanwhile, the water is under considerably higher pressure. Due to the pressure differences in the air, the air flows from sea to land. As a result, an unexpected gust of wind is felt known as the sea breeze.
The concept of the sea breeze is shown in the image added below.

Land Breeze
When the situation changes at night, these phenomena arise. The land and sea begin to chill as the sun sets. Due to variations in heat capacity, the land loses heat faster when compared to water. Comparably, the water temperature becomes higher, resulting in low air pressure there. This creates a cool wind off the coast, known as the land breeze.
The concept of the land breeze is shown in the image added below.

Type of Convection
Convection may be divided into two types, which are as follows:
- Natural Convection
- Forced Convection
Natural Convection
When the temperature difference occurs, it causes a density difference which produces the buoyant force and convection occurs. This process is termed natural convection. Some examples of natural convection are Oceanic winds, melting of Ice, blood circulation in warm-blooded animals, raising of hot air above the fire, etc.
Forced Convection
Forced convection occurs when an external source such as a pump or fan is utilized to produce convection. Utilizing water geysers or heaters for quick water heating, using fans on warm summer days, the engine of automobiles, and man-made suction devices are examples of forced convection.
Check: Difference between Sea Breeze and Land Breeze
Newton’s Law of Cooling
Under typical circumstances, convection heat transfer is proportional to the temperature differential between the components. This phenomenon has been stated by Newton’s law of cooling, which states:
The rate of heat transmission from anybody to its surroundings by convection is related to temperature difference between them. The difference in temperature should be minimal, and the radiating surface’s nature should stay unchanged.
Newton’s law of cooling is connected to forced convection, which is written as:
P = dq ⁄dt = hA(Ts – Tf)
where,
dq ⁄dt is the heat transfer rate,
h is the heat-transfer coefficient of convection,
A is the surface area of body, which is exposed,
Ts is the body temperature and
Tf is the fluid temperature.
Note: The value of h (heat-transfer coefficient) depends on Viscosity, Density, Specific heat capacity, and Thermal conductivity.
Read More,
Sample Questions on Convection
Question 1: What role does convection play in our daily lives?
Answer:
In the following situations, convection is used:
- When water is heated to a certain temperature, the water molecules expand and circulate in the vicinity. As a result of the heat being transported to different sections of the pot, the cold water begins to sink while the heated water rises.
- The air within the hot air balloon is continuously heated, making it warmer. The balloon, like the warm air, rises.
- In the afternoon, the land near the sea is warmer than in the evening. By the concept of convection, heated air rises and is replaced by colder air. Similarly, the air near the water is warmer than the air near the coast at night. This happens because heated air rises and is replaced by cold air.
Question 2: Why do not solid materials experience convection?
Answer:
Convection is the process of heat transfer through movement of particles. Since, the solid particles do not move, convection is not possible in solid materials.
Question 3: What are the processes through which convection occurs?
Answer:
When transferring heat from one liquid to another through a barrier, convection is essential. Convectional heat transfer occurs either through thermal diffusion (fluid molecule motion) or advection, in which heat is transferred through the bulk motion of heat currents in the fluid.
Question 4: What does “free” or “natural” convection mean?
Answer:
The mechanism of heat transmission is considered to be free or natural convection if the fluid motion is caused by a change in density caused by temperature gradients.
Question 5: Natural or induced convection, which has a higher heat transfer coefficient? What is the reason behind this?
Answer:
Since the convection heat transfer coefficient is primarily determined by characteristics such as fluid density, velocity, and viscosity, it is generally larger in forced convection than in natural convection.
Related article:
Convection – FAQs
What is Conduction, Convection, and Radiation?
- Conduction: Conduction is the transfer of heat through a material by direct contact whenever there is a difference in temperature. For example, a pot of boiling water on a hot stove burner will heat the metal of the pot through conduction.
- Convection: Convection is the transfer of heat through the movement of a fluid or gas, such as air or water. For example, the heating of water in a pot is an example of convection.
- Radiation: Radiation is the transfer of heat in the form of electromagnetic waves, such as infrared waves. For example, we can observe the rise in temperature around a boiling pot of water because of radiation.
What is a Convection Current?
The movement of fluid caused by temperature or a difference in density within the fluid is known as convection current.
What are the Types of Convection?
There are two types of convection, that is as follows:
- Natural Convection
- Forced Convection
Who postulated the Thermal Convection Current Theory?
Arthus Holmes postulated the theory of thermal convection current that explains the problems regarding the formation of features on the Earth’s surface, like mountains.
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...