0-1 BFS (Shortest Path in a Binary Weight Graph)
Last Updated :
17 Apr, 2024
Given a graph where every edge has weight as either 0 or 1. A source vertex is also given in the graph. Find the shortest path from the source vertex to every other vertex.
For Example:
Input : Source Vertex = 0 and below graph Having vertices like(u,v,w):
Edges: [[0,1,0], [0, 7, 1], [1,2,1], [1, 7, 1], [2, 3, 0], [2, 5, 0], [2, 8, 1], [3, 4, 1],[3, 5, 1],[4, 5, 1],[5, 6, 1],[6, 7, 1],[7, 8, 1]]
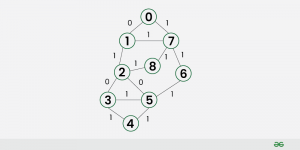
Output : Shortest distances from given source
0 0 1 1 2 1 2 1 2
Explanation :
Shortest distance from 0 to 0 is 0
Shortest distance from 0 to 1 is 0
Shortest distance from 0 to 2 is 1
..................
A simple way to find nearby nodes is called 0-1 BFS. Instead of marking visited nodes with a boolean array, it checks a condition at each step. It uses a double-ended queue to store nodes. If an edge has a weight of 0, the node is inserted at the front of the queue. But if the edge has a weight of 1, the node goes at the back.
This method is similar to Dijkstra’s algorithm. It updates the shortest distance to a node based on its neighboring nodes. A node is added to the queue only if its distance could be improved by the previous node’s distance. This helps find the optimal path to reach nodes.
This way works well in many cases. When taking a point from the line (like Dijkstra’s way), it means that point has the smallest weight left. If there is a next point with weight 0, it is the same distance as the point just taken. But if the next point has weight 1, it is now the farthest away of all points still in the line. This is because all other points either connect straight to the current point or connect to points already taken.
C++
// C++ program to implement single source
// shortest path for a Binary Graph
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
/* no.of vertices */
#define V 9
// a structure to represent edges
struct node
{
// two variable one denote the node
// and other the weight
int to, weight;
};
// vector to store edges
vector <node> edges[V];
// Prints shortest distance from given source to
// every other vertex
void zeroOneBFS(int src)
{
// Initialize distances from given source
int dist[V];
for (int i=0; i<V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
// double ende queue to do BFS.
deque <int> Q;
dist[src] = 0;
Q.push_back(src);
while (!Q.empty())
{
int v = Q.front();
Q.pop_front();
for (int i=0; i<edges[v].size(); i++)
{
// checking for the optimal distance
if (dist[edges[v][i].to] > dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight)
{
dist[edges[v][i].to] = dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight;
// Put 0 weight edges to front and 1 weight
// edges to back so that vertices are processed
// in increasing order of weights.
if (edges[v][i].weight == 0)
Q.push_front(edges[v][i].to);
else
Q.push_back(edges[v][i].to);
}
}
}
// printing the shortest distances
for (int i=0; i<V; i++)
cout << dist[i] << " ";
}
void addEdge(int u, int v, int wt)
{
edges[u].push_back({v, wt});
edges[v].push_back({u, wt});
}
// Driver function
int main()
{
addEdge(0, 1, 0);
addEdge(0, 7, 1);
addEdge(1, 7, 1);
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 0);
addEdge(2, 5, 0);
addEdge(2, 8, 1);
addEdge(3, 4, 1);
addEdge(3, 5, 1);
addEdge(4, 5, 1);
addEdge(5, 6, 1);
addEdge(6, 7, 1);
addEdge(7, 8, 1);
int src = 0;//source node
zeroOneBFS(src);
return 0;
}
// Java Program to implement 0-1 BFS
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Deque;
public class ZeroOneBFS {
private static class Node {
int to; // the ending vertex
int weight; // the weight of the edge
public Node(int to, int wt) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = wt;
}
}
private static final int numVertex = 9;
private ArrayList<Node>[] edges = new ArrayList[numVertex];
public ZeroOneBFS() {
for (int i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
edges[i] = new ArrayList<Node>();
}
}
public void addEdge(int u, int v, int wt) {
edges[u].add(edges[u].size(), new Node(v, wt));
edges[v].add(edges[v].size(), new Node(u, wt));
}
public void zeroOneBFS(int src) {
// initialize distances from given source
int[] dist = new int[numVertex];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
dist[i] = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
// double ended queue to do BFS
Deque<Integer> queue = new ArrayDeque<Integer>();
dist[src] = 0;
queue.addLast(src);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int v = queue.removeFirst();
for (int i = 0; i < edges[v].size(); i++) {
// checking for optimal distance
if (dist[edges[v].get(i).to] >
dist[v] + edges[v].get(i).weight) {
// update the distance
dist[edges[v].get(i).to] =
dist[v] + edges[v].get(i).weight;
// put 0 weight edges to front and 1
// weight edges to back so that vertices
// are processed in increasing order of weight
if (edges[v].get(i).weight == 0) {
queue.addFirst(edges[v].get(i).to);
} else {
queue.addLast(edges[v].get(i).to);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < dist.length; i++) {
System.out.print(dist[i] + " ");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ZeroOneBFS graph = new ZeroOneBFS();
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 0);
graph.addEdge(0, 7, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 7, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 3, 0);
graph.addEdge(2, 5, 0);
graph.addEdge(2, 8, 1);
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 1);
graph.addEdge(3, 5, 1);
graph.addEdge(4, 5, 1);
graph.addEdge(5, 6, 1);
graph.addEdge(6, 7, 1);
graph.addEdge(7, 8, 1);
int src = 0;//source node
graph.zeroOneBFS(src);
return;
}
}
# Python3 program to implement single source
# shortest path for a Binary Graph
from sys import maxsize as INT_MAX
from collections import deque
# no.of vertices
V = 9
# a structure to represent edges
class node:
def __init__(self, to, weight):
# two variable one denote the node
# and other the weight
self.to = to
self.weight = weight
# vector to store edges
edges = [0] * V
for i in range(V):
edges[i] = []
# Prints shortest distance from
# given source to every other vertex
def zeroOneBFS(src: int):
# Initialize distances from given source
dist = [0] * V
for i in range(V):
dist[i] = INT_MAX
# double ende queue to do BFS.
Q = deque()
dist[src] = 0
Q.append(src)
while Q:
v = Q[0]
Q.popleft()
for i in range(len(edges[v])):
# checking for the optimal distance
if (dist[edges[v][i].to] >
dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight):
dist[edges[v][i].to] = dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight
# Put 0 weight edges to front and 1 weight
# edges to back so that vertices are processed
# in increasing order of weights.
if edges[v][i].weight == 0:
Q.appendleft(edges[v][i].to)
else:
Q.append(edges[v][i].to)
# printing the shortest distances
for i in range(V):
print(dist[i], end = " ")
print()
def addEdge(u: int, v: int, wt: int):
edges[u].append(node(v, wt))
edges[u].append(node(v, wt))
# Driver Code
if __name__ == "__main__":
addEdge(0, 1, 0)
addEdge(0, 7, 1)
addEdge(1, 7, 1)
addEdge(1, 2, 1)
addEdge(2, 3, 0)
addEdge(2, 5, 0)
addEdge(2, 8, 1)
addEdge(3, 4, 1)
addEdge(3, 5, 1)
addEdge(4, 5, 1)
addEdge(5, 6, 1)
addEdge(6, 7, 1)
addEdge(7, 8, 1)
# source node
src = 0
zeroOneBFS(src)
# This code is contributed by
# sanjeev2552
// C# Program to implement 0-1 BFS
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
class ZeroOneBFS {
private class Node {
public int to; // the ending vertex
public int weight; // the weight of the edge
public Node(int to, int wt) {
this.to = to;
this.weight = wt;
}
}
private const int numVertex = 9;
private List<Node>[] edges = new List<Node>[numVertex];
public ZeroOneBFS() {
for (int i = 0; i < edges.Length; i++) {
edges[i] = new List<Node>();
}
}
public void addEdge(int u, int v, int wt) {
edges[u].Add(new Node(v, wt));
edges[v].Add(new Node(u, wt));
}
public void zeroOneBFS(int src) {
// initialize distances from given source
int[] dist = new int[numVertex];
for (int i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
dist[i] = int.MaxValue;
}
// double ended queue to do BFS
Queue<int> queue = new Queue<int>();
dist[src] = 0;
queue.Enqueue(src);
while (queue.Count > 0) {
int v = queue.Dequeue();
for (int i = 0; i < edges[v].Count; i++) {
// checking for optimal distance
if (dist[edges[v][i].to] >
dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight) {
// update the distance
dist[edges[v][i].to] =
dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight;
// put 0 weight edges to front and 1
// weight edges to back so that vertices
// are processed in increasing order of weight
if (edges[v][i].weight == 0) {
queue.Enqueue(edges[v][i].to);
} else {
queue.Enqueue(edges[v][i].to);
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < dist.Length; i++) {
Console.Write(dist[i] + " ");
}
}
static void Main(string[] args) {
ZeroOneBFS graph = new ZeroOneBFS();
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 0);
graph.addEdge(0, 7, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 7, 1);
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 1);
graph.addEdge(2, 3, 0);
graph.addEdge(2, 5, 0);
graph.addEdge(2, 8, 1);
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 1);
graph.addEdge(3, 5, 1);
graph.addEdge(4, 5, 1);
graph.addEdge(5, 6, 1);
graph.addEdge(6, 7, 1);
graph.addEdge(7, 8, 1);
int src = 0;//source node
graph.zeroOneBFS(src);
return;
}
}
// This code is contributed by Prajwal Kandekar
<script>
// Javascript Program to implement 0-1 BFS
class Node
{
constructor(to,wt)
{
this.to = to;
this.weight = wt;
}
}
let numVertex = 9;
let edges = new Array(numVertex);
function _ZeroOneBFS()
{
for (let i = 0; i < edges.length; i++) {
edges[i] = [];
}
}
function addEdge(u,v,wt)
{
edges[u].push(edges[u].length, new Node(v, wt));
edges[v].push(edges[v].length, new Node(u, wt));
}
function zeroOneBFS(src)
{
// initialize distances from given source
let dist = new Array(numVertex);
for (let i = 0; i < numVertex; i++) {
dist[i] = Number.MAX_VALUE;
}
// double ended queue to do BFS
let queue = [];
dist[src] = 0;
queue.push(src);
while (queue.length!=0) {
let v = queue.shift();
for (let i = 0; i < edges[v].length; i++) {
// checking for optimal distance
if (dist[edges[v][i].to] >
dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight) {
// update the distance
dist[edges[v][i].to] =
dist[v] + edges[v][i].weight;
// put 0 weight edges to front and 1
// weight edges to back so that vertices
// are processed in increasing order of weight
if (edges[v][i].weight == 0) {
queue.unshift(edges[v][i].to);
} else {
queue.push(edges[v][i].to);
}
}
}
}
for (let i = 0; i < dist.length; i++) {
document.write(dist[i] + " ");
}
}
_ZeroOneBFS();
addEdge(0, 1, 0);
addEdge(0, 7, 1);
addEdge(1, 7, 1);
addEdge(1, 2, 1);
addEdge(2, 3, 0);
addEdge(2, 5, 0);
addEdge(2, 8, 1);
addEdge(3, 4, 1);
addEdge(3, 5, 1);
addEdge(4, 5, 1);
addEdge(5, 6, 1);
addEdge(6, 7, 1);
addEdge(7, 8, 1);
let src = 0;//source node
zeroOneBFS(src);
// This code is contributed by avanitrachhadiya2155
</script>
This problem can also be solved by Dijkstra but the time complexity will be O(E + V Log V) whereas by BFS it will be O(V+E).
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...