What is the React Context API?
Last Updated :
06 Feb, 2024
In the React ecosystem, as your application grows, passing data down through component hierarchies can become cumbersome. This is where the Context API steps in, providing a centralized way to manage state across components.
What is the Context API?
At its core, the Context API is a mechanism that allows you to share specific information (like state or functions) with multiple components, eliminating the need for prop drilling.
The React Context API is a powerful tool for efficient state management, offering a cleaner alternative to prop drilling and enhancing overall code organization.
How Context API Works:
1. Creating a Context
The process begins by creating a context using the createContext() method. This serves as a blueprint for the shared data.
Javascript
/ Creating a context
const MyContext = React.createContext();
|
2. Providing the Context
The context provider, wrapped around components requiring access to shared data, is established using the Provider
Javascript
function MyApp() {
return (
<MyContext.Provider value={}>
{}
</MyContext.Provider>
);
}
|
3. Consuming the Context
Javascript
function AnotherComponent() {
const contextValue = React.useContext(MyContext);
}
|
Components nested within the provider can consume the shared data using the useContext hook or the Consumer component.
Steps to Create a Simple To-Do List with React Context API:
Let’s create a straightforward project – a to-do list application using React and the Context API. This project will showcase how the Context API can simplify state management in a real-world scenario.
Step 1: Start by creating a new React app using Create React App.
npx create-react-app todo-list-context
Step 2: Navigate to the root directry of project using the following the command.
cd todo-list-context
Project Structure:
Project Structure of todo list
package.json
"dependencies": {
"@testing-library/jest-dom": "^5.17.0",
"@testing-library/react": "^13.4.0",
"@testing-library/user-event": "^13.5.0",
"react": "^18.2.0",
"react-dom": "^18.2.0",
"react-scripts": "5.0.1",
"redux": "^5.0.1",
"web-vitals": "^2.1.4"
}
- In your src/index.js, wrap your App component with the TodoProvider.
- Now src/components/TodoForm.js , let’s create components to interact with the to-do list.
- Now its turn for src/components/TodoList.js
- Now, in your src/App.js, use the TodoForm and TodoList components.
Javascript
import React, { createContext, useState }
from 'react';
const TodoContext = createContext();
const TodoProvider = ({ children }) => {
const [todos, setTodos] = useState([]);
const addTodo = (text) => {
setTodos([...todos, { text, id: Date.now() }]);
};
const removeTodo = (id) => {
setTodos(todos.filter((todo) => todo.id !== id));
};
return (
<TodoContext.Provider value={{
todos,
addTodo, removeTodo
}}>
{children}
</TodoContext.Provider>
);
};
export { TodoProvider, TodoContext };
|
Javascript
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
import { TodoProvider } from './TodoContext';
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<TodoProvider>
<App />
</TodoProvider>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
|
Javascript
import React, { useState, useContext } from 'react';
import { TodoContext } from './TodoContext';
const TodoForm = () => {
const { addTodo } = useContext(TodoContext);
const [text, setText] = useState('');
const handleSubmit = (e) => {
e.preventDefault();
addTodo(text);
setText('');
};
return (
<form onSubmit={handleSubmit}>
<input
type="text"
value={text}
onChange={(e) => setText(e.target.value)}
placeholder="Add a new todo"
/>
<button type="submit">Add Todo</button>
</form>
);
};
export default TodoForm;
|
Javascript
import React, { useContext } from 'react';
import { TodoContext } from './TodoContext';
const TodoList = () => {
const { todos, removeTodo } = useContext(TodoContext);
return (
<ul>
{todos.map((todo) => (
<li key={todo.id}>
{todo.text}
<button onClick={() =>
removeTodo(todo.id)}>Remove</button>
</li>
))}
</ul>
);
};
export default TodoList;
|
Javascript
import React from 'react';
import TodoForm from './TodoForm';
import TodoList from './TodoList';
const App = () => {
return (
<div>
<h1>My Todo List</h1>
<TodoForm />
<TodoList />
</div>
);
};
export default App;
|
Start your application using the following command.
npm start
Output:
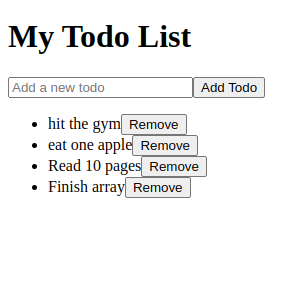
todo list app
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...