Rational Numbers: A rational number is a type of real number expressed as p/q, where q ≠ 0. Any fraction with a non-zero denominator qualifies as a rational number. Examples include 1/2, 1/5, 3/4, and so forth. Additionally, the number 0 is considered a rational number as it can be represented in various forms such as 0/1, 0/2, 0/3, etc.
In this article, learn about rational numbers, their properties, examples, and others in detail.
What are Rational Numbers?
Rational Number is a real number written in the form of p/q where p and q are integers and q is not equal to zero.
- Rational numbers can be expressed as fractions, decimals, and even zeros.
- All the numbers with a non-zero denominator that can be written in p/q form are rational numbers.
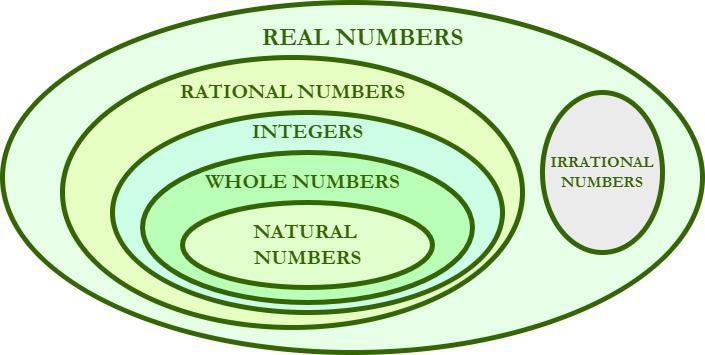
Rational Numbers Definition
A rational number is any number that can be written as a simple fraction. This includes all integers, as any integer z can be written as z/1.
Various types of numbers can be represented as rational numbers some of which are discussed below:
Fraction Form of Rational Number
A rational number is a ratio of two integers. Hence, in the fraction number, it can be written in the form of p/q where q is not equal to zero. Hence, any fraction with a non-zero denominator is a rational number.
Example
-2 / 5 is a rational number where -2 is an integer being divided by a non-zero integer 5
Decimal Form of Rational Number
A rational number can be also written in the decimal form if the decimal value is definite or has repeating digits after the decimal point.
Example
0.3 is a rational number. As the value 0.3 can be further expressed in the form of ratio or fraction as p/q
0.3 = 3/10
Also, 1.333333… can be represented as 4/3 hence, 1.33333… is a rational number.
The standard form of a rational number is, p/q
where,
- p and q are both integers with no common integers,
- q can never be zero.
For example, 2/6 is a rational number but it is not in its standard form as 2/6 has a common factor of 2 and it can further be simplified as 1/3. Thus, its standard form is 1/3.
Is 0 a Rational Number?
Yes, 0 is a rational number as it has a non-zero denominator. It can be written in the p / q form as,
0 = 0/1 = p / q
Learn, Zero is Rational or Not
How to Identify Rational Numbers?
Rational Numbers have various properties from which we can identify them some of which are given below:
- Natural numbers, Whole Numbers, Fractions, and Integers all are rational numbers.
- All terminating decimals are Rational Numbers.
- All recurring decimals are Rational Numbers.
- All the numbers which can be expressed as p/q where p and q are integers are Rational Numbers.
Note: Non-Recurring and Non Terminating decimals are Irrational Numbers.
Example: Check whether 2.69696969… is a rational number or not?
Solution:
Given Number 2.69696969… has repeating value 69 after decimal hence it is a rational number.
What are Positive and Negative Rational Numbers?
- If the rational number is positive, both p and q are positive integers.
- If the rational number takes the form -(p/q), then either p or q takes the negative value. It means that -(p/q) = (-p)/q = p/(-q)
Arithmetic Operations on Rational Numbers
We can perform various arithmetic operations on rational numbers which are,
- Addition
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Division
Addition
Let’s take two rational numbers p/q and s/t, adding these two using rules of addition we get
p/q + s/t = (pt+qs)/qt
Example: Add 3/5 + 2/7
Solution:
3/5 + 2/7 = (3×7 + 2×5) / 5×7
= (21 + 10) / 35
= 31 / 35
Subtraction
Let’s take two rational numbers p/q and s/t, subtracting these two using rules of subtraction we get
p/q – s/t = (pt – qs)/qt
Example: Subtract 3/5 – 2/7
Solution:
3/5 – 2/7 = (3×7 – 2×5) / 5×7
= (21 – 10) / 35
= 11 / 35
Multiplication
Let’s take two rational numbers p/q and s/t, multiplying these two using rules of multiplication we get
p/q × s/t = (p × s) / (q × t)
Example: Multiply 3/5 × 2/7
Solution:
3/5 × 2/7 = (3 × 2) / (5 × 7)
= 6 / 35
Division
Let’s take two rational numbers p/q and s/t, we know that divide is the inverse of multiply then dividing these two using rules of division we get
(p/q) / (s/t) = p/q × t/s = (p × t) / (q × s)
Example: Divide (3/5) / (2/7)
Solution:
(3/5) / (2/7) = 3/5 × 7/2
= (3 × 7) / (5 × 2)
= 21 / 10
Multiplicative Inverse of Rational Numbers
A Multiplicative Inverse of Rational Numbers is a number that when multiplied by the number results in 1. The general form of a rational number is p/q then its multiplicative inverse is q/p.
For example: For a rational number 2/3, then its multiplicative inverse is 3/2, such that,
2/3 × 3/2 = 1
Properties of Rational Numbers
Various properties of rational numbers are,
- The results are always a rational number if we multiply, add, or subtract any two rational numbers.
- Multiplying or dividing the numerator and denominator of any rational number with the same number does not change the number such that, p/q = ap/aq.
- Multiplication, Division, Addition, and Subtraction of any two rational numbers result in a rational number.
- The additive inverse of the rational number is zero as p/q + 0 = p/q
- The multiplicative inverse of the rational number is 1 as p/q × 1 = p/q
Rational Numbers and Irrational Numbers
Rational Numbers and Irrational Numbers both are subsets of real numbers the basic difference between them is that Rational Numbers can be represented as p/q whereas Irrational Numbers can not be represented as p/q.
All natural numbers, whole numbers, decimals, and others are subsets of rational numbers while irrational numbers are those numbers that are non-repeating and non-terminating numbers.
Examples of Rational Numbers
- 1, 2, 3,…
- 1/2, 2/3, 4/5,…
- 2.3 = 23/10, etc.
Examples of Irrational Numbers
- √2 = 1.414213…
- √3 = 1.7320508…
- Pi (π) = 3.142857…
- Euler’s Number (e) = 2.7182818284590452…….
How to Find Rational Numbers between Two Rational Numbers?
We can find Rational Numbers between Two Rational Numbers by two methods which are,
Method 1
For the given rational numbers find their equivalent rational numbers and then the number between them is found easily.
Example: Find the rational number between 1/2 and 4/3.
Solution:
1/2 = 3/6
4/3 = 8/6
Then rational numbers between 3/6 and 8/6 are 4/6, 5/6, 6/6, 7/6.
Method 2
In the second method, we find the mean of the given two numbers (m) and then find the mean of the first number with m and the mean of the second number with m, and repeated this process to get more numbers.
Example: Find the rational number between 1/2 and 4/3.
Solution:
Mean of 1/2, 4/3 = (1/2 + 4/3) / 2 = 11/12
Mean of 1/2, 11/12 = (1/2 + 11/12) / 2 = 17/24
Mean of 11/12, 4/3 = (11/12 + 4/3) / 2 = 27/24
Then rational numbers between 3/6 and 8/6 are 17/24, 11/12, 27/24.
People Also View:
Solved Examples on Rational Numbers
Example 1: What are the rational numbers between 3 and 5?
Solution:
Rational Numbers between 3 and 5 are 31/10, 32/10, 33/10, 34/10, 35/10, 36/10,…………..,49/10
Lets express 3 and 5 as rational numbers as
3 = 3×10/10 = 30/10
5= 5×10/10 = 50/10
Hence, the rational numbers between 3 and 5 are 30/10 and 50/10 are 31/10, 32/10, 33/10, 34/10, 35/10, 36/10, 37/10, 38/10, 39/10, 40/10, …………..49/10.
Example 2: What are the five rational numbers between 0 and 1?
Solution:
Five rational numbers between 0 and 1 are 0.1, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4 and 0.5.
Example 3: Simplify, 1/2 + 2/3 – 4/5
Solution:
1/2 + 2/3 – 4/5
= 7/6 – 4/5
= (35 – 24) / 30 = 9/30
= 3/10
Example 4: Simplify, 1/2 × 2/3 ÷ 4/5
Solution:
1/2 × 2/3 ÷ 4/5
= 1/2 × 2/3 × 5/4
= 5/12
FAQs on Rational Numbers
What are Rational Numbers?
Rational Numbers are subsets of real numbers, they can be written in the form of p/q where p and q are integers with no common factors, and q is not equal to 0. Examples of rational numbers are 1/5, 2/7, etc.
Is 2.6 a rational number?
Yes, 2.6 is a Rational Number. As rational numbers can be expressed as decimals values as well as fractions. The number can also be written as 26/10 which is the ratio of two integers.
The number 2.6 can be represented as shown below,
2.6 = 26/10 = 13/5
The number 13/5 is the ratio of two integers that are 13 integers divided by 5 integers and expressed in fraction form (as p/q where q is not equal to 0).
Is 3.14 a rational number?
Yes, the number 3.14 is a rational number. Since rational numbers can also be expressed as decimals with repeating digits after the decimal point.
The given number 3.14 can be expressed as
3.14/100 = 22/7
The number 22/7 is the ratio of two integers that are 22 integers divided by integer 7.
Is 0 a rational number?
Yes, 0 is a rational number because it has a non-zero denominator. Since the number 0 can also be written as 0/1.
Is Pi(π) a rational number?
Pi (π) can not be expressed in the form of p/q and hence it is not a rational number. Pi is a non-terminating and non-recurring decimal and its value equals 3.142857…
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...