Python | Stack using Doubly Linked List
Last Updated :
05 Jan, 2023
A stack is a collection of objects that are inserted and removed using Last in First out Principle(LIFO). User can insert elements into the stack, and can only access or remove the recently inserted object on top of the stack. The main advantage of using LinkedList over array for implementing stack is the dynamic allocation of data whereas in the array, the size of the stack is restricted and there is a chance of stack overflow error when the size of the stack is exceeded the maximum size.
Stack Operations:
1. push() : Insert the element into Stack and assign the top pointer to the element.
2. pop() : Return top element from the Stack and move the top pointer to the second element of the Stack.
3. top() : Return the top element.
4. size() : Return the Size of the Stack.
5. isEmpty() : Return True if Stack is Empty else return False.
6. printstack() : Print all elements of the stack.
Below is the implementation of the above-mentioned stack operations using Doubly LinkedList in Python:
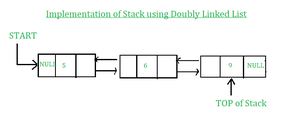
Implementation of Stack using Doubly Linked List
Python3
class Node:
def __init__(self, data):
self.data = data
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.head = None
def push(self, data):
if self.head is None:
self.head = Node(data)
else:
new_node = Node(data)
self.head.prev = new_node
new_node.next = self.head
new_node.prev = None
self.head = new_node
def pop(self):
if self.head is None:
return None
elif self.head.next is None:
temp = self.head.data
self.head = None
return temp
else:
temp = self.head.data
self.head = self.head.next
self.head.prev = None
return temp
def top(self):
return self.head.data
def size(self):
temp = self.head
count = 0
while temp is not None:
count = count + 1
temp = temp.next
return count
def isEmpty(self):
if self.head is None:
return True
else:
return False
def printstack(self):
print("stack elements are:")
temp = self.head
while temp is not None:
print(temp.data, end ="->")
temp = temp.next
if __name__=='__main__':
stack = Stack()
print("Stack operations using Doubly LinkedList")
stack.push(4)
stack.push(5)
stack.push(6)
stack.push(7)
stack.printstack()
print("\nTop element is ", stack.top())
print("Size of the stack is ", stack.size())
stack.pop()
stack.pop()
stack.printstack()
print("\nstack is empty:", stack.isEmpty())
|
Output:
Stack operations using Doubly LinkedList
stack elements are:
7->6->5->4->
Top element is 7
Size of the stack is 4
stack elements are:
5->4->
stack is empty: False
Time Complexity for operations:
- Push(): O(1)
- pop(): O(1)
- top(): O(1)
- size(): O(N)
- isEmpty(): O(1)
- printStack(): O(N)
Auxiliary Space for operations:
- Push(): O(1)
- pop(): O(1)
- top(): O(1)
- size(): O(1)
- isEmpty(): O(1)
- printStack(): O(1)
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...