Class 9 NCERT Solutions- Chapter 12 Heron’s Formula – Exercise 12.2
Last Updated :
04 Mar, 2021
Question 1. A park, in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has ∠ C = 90º, AB = 9 m, BC = 12 m, CD = 5 m and AD = 8 m. How much area does it occupy?
Solution:
Given, a quadrilateral ABCD where ∠C = 90º.
Construction: Join diagonal BD.

As we can see that, △DCB is right-angled at C
Hence, BC is the base and CD is height of △DCB, so
ar(△DCB) = 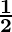 × Base × Height
× Base × Height
= 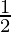 × 12 × 5
× 12 × 5
= 30 m2……………………………………(1)
As △DCB is right angle triangle we can calculate third side by Pythagoras theorem
BD2 = CB2 + CD2
BD2 = 122 + 52
BD = √(144+25)
BD = √169
BD =13 m
Now, Area of △DAB can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
AB = a = 9 m
AD = b = 8 m
BD = c = 13 m
Semi Perimeter (s) = 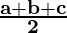
s = 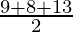
s = 15 m
ar(△DAB) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √15(15-9)(15-8)(15-13)
= √15×(6)×(7)×(2)
= 6√35 m2……………………………………..(2)
From (1) and (2), we can conclude that,
ar(ABCD) = ar(△DCB)+ar(△DAB)
= (30 + 6√35)
= (30 + 35.5)
≈ 65.5 m2 (approx.)
Question 2. Find the area of a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, DA = 5 cm and AC = 5 cm.
Solution:

Here, we can notice that in △ABC
AC2 = AB2 + BC2
52 = 32 + 42
25 = 25
LHS = RHS
As this triangle is satisfying the Pythagoras theorem, Therefore, △ABC is a right angle triangle, 90° at B.
Hence, BC is the base and AB is height of △ABC. so
So, ar(△ABC) = 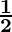 × Base × Height
× Base × Height
= 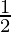 × 4 × 3
× 4 × 3
= 6 cm2……………………………….(1)
Now, Area of △DAC can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
AD = a = 5 cm
DC = b = 4 cm
AC = c = 5 cm
Semi Perimeter (s) = 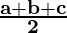
s = 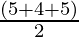
s = 7 cm
ar(△DAC) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √7(7-5)(7-4)(7-5)
= √7×(2)×(3)×(2)
= 2√21 cm2……………………………………..(2)
From (1) and (2), we can conclude that,
ar(ABCD) = ar(△ABC)+ar(△DAC)
= (6 + 2√21)
= (6 + 9.2(approx.))
≈ 15.2 cm2 (approx.)
Question 3. Radha made a picture of an aeroplane with coloured paper as shown in (Fig). Find the total area of the paper used.

Solution:
Total area of the paper used = (Area I + Area II + Area III + Area IV + Area V)
Area I: Triangle

Now, Area of triangle can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
a = 5 cm
b = 5 cm
c = 1 cm
Semi Perimeter (s) = 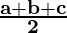
s = 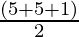
s = 5.5 cm
ar(△) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √5.5(5.5-5)(5.5-5)(5.5-1)
= √5.5×(0.5)×(0.5)×(4.5)
= 0.5×0.5×3√11
= 0.75√11
≈ 2.5 cm2 ……………………………………..(1)
Area II: Rectangle

Area of Rectangle = length×Breadth
= 1 × 6.5 = 6.5 cm2……………………………….(2)
Area III: Trapezium = Area of parallelogram EFAO + △ AFD

OD = 2cm
AD = OD-OA = 2-1 = 1 cm
Hence, △ AFD is equilateral.
PD = 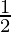 AD =
AD = 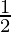 cm
cm
△ PFD is right angled at P, Pythagoras theorem is applicable
12=h2 +(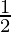 )2
)2
h = √(1-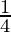 )
)
h = √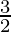 cm
cm
Area III:
= (Base × Height) + (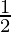 × Base × Height)
× Base × Height)
= (1 × 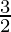 ) + (
) + (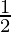 × 1 ×
× 1 × 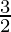 )
)
= 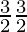
= 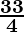 = 1.29 cm2…………………………………(3)
= 1.29 cm2…………………………………(3)
Area IV and V: 2 times Triangle

ar(△) = 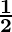 × Base × Height
× Base × Height
= 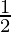 × 6 × 1.5
× 6 × 1.5
= 4.5 cm2
Area IV + Area V = 2×ar(△)
= 2×4.5
= 9 cm2 …………………………………(4)
Hence, Total area of the paper used = (Area I + Area II + Area III + Area IV + Area V)
= (1) + (2) + (3) + (4)
= 2.5 + 6.5 + 1.29 +9
= 19.29 cm2
Question 4. A triangle and a parallelogram have the same base and the same area. If the sides of the triangle are 26 cm, 28 cm and 30 cm, and the parallelogram stands on the base 28 cm, find the height of the parallelogram.
Solution:

Now, Area of △AEB can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
AE = a = 28 cm
EB = b = 30 cm
AB = c = 26 cm
Semi Perimeter (s) = 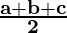
s = (28+30+26)/2
s = 42 cm
ar(△AEB) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √42(42-28)(42-30)(42-26)
= √42×(14)×(12)×(16)
= 336 cm2
As it is given, ar(△AEB) = ar(parallelogram ABCD)
336 = Base × Height
336 = 28 × h
h = 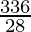
h = 12 cm
Hence, the height of the parallelogram = 12 cm
Question 5. A rhombus shaped field has green grass for 18 cows to graze. If each side of the rhombus is 30 m and its longer diagonal is 48 m, how much area of grass field will each cow be getting?
Solution:
ABCD is a rhombus having diagonal AC = 48 cm
side AB=BC=CD=AD=30 cm
Diagonal of Rhombus divides the area into two equal parts.

Now, ar(△ABC) can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
AB = a = 30 m
BC = b = 30 m
AC = c = 48 m
Semi Perimeter (s) = 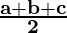
s = 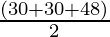
s = 54 m
ar(△ABC) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √54(54-30)(54-30)(54-48)
= √54×(24)×(24)×(6)
= 432 m2
Hence, Area of rhombus = 2 × (ar(△))
= 2 × 432 = 864 m2
Area for 18 cows = 864 m2
Area for each cow = 864 / 18 = 48 m2
Question 6. An umbrella is made by stitching 10 triangular pieces of cloth of two different colours (see Fig. 12.16), each piece measuring 20 cm, 50 cm and 50 cm. How much cloth of each colour is required for the umbrella?
Solution:
Let’s consider for each triangle.

Now, for each ar(△)can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
a = 50 cm
b = 50 cm
c = 20 cm
Semi Perimeter (s) = 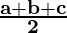
s = 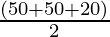
s = 60 cm
ar(△) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √60(60-50)(60-50)(60-20)
= √60×(10)×(10)×(40)
= 200√6 cm2
Hence, the Total Area = 5×200√6
= 1000√6 cm2
Question 7. A kite in the shape of a square with a diagonal 32 cm and an isosceles triangle of base 8 cm and sides 6 cm each is to be made of three different shades as shown in Fig. How much paper of each shade has been used in it?
Solution:

As the area of kite is in the square, it area will be
Area of kite = 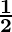 ×(diagonal)2
×(diagonal)2
= 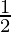 ×32×32
×32×32
= 512 cm2
Diagonal divides area into equal areas.
Area of kite = Area I + Area II
512 = 2 × Area I
Area I =Area II = 256 cm2……………………………..(1)
Area III: Area of triangle
Now, for each ar(△)can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
a = 6 cm
b = 6 cm
c = 8 cm
Semi Perimeter (s) = 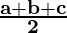
s = 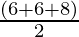
s = 10 cm
ar(△) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √10(10-6)(10-6)(10-8)
= √10×(4)×(4)×(2)
= 8√5 cm2………………………………(2)
Question 8. A floral design on a floor is made up of 16 tiles which are triangular, the sides of the triangle being 9 cm, 28 cm and 35 cm (see Fig). Find the cost of polishing the tiles at the rate of 50p per cm2.
Solution:

Area for each triangle will be:
Now, for each ar(△)can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
a = 9 cm
b = 28 cm
c = 35 cm
Semi Perimeter (s) = 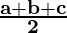
s = 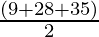
s = 36 cm
ar(△) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √36(36-9)(36-28)(36-35)
= √36×(27)×(8)×(1)
= 36√6 cm2
As there are 16 tiles, so total area = 16 × 36√6
= 1410.906 cm2
As 1 cm2 = 50 p = ₹ 0.5
1410.906 cm2 = ₹ 0.5 ×1410.906
= ₹ 705.45
Question 9. A field is in the shape of a trapezium whose parallel sides are 25 m and 10 m. The non-parallel sides are 14 m and 13 m. Find the area of the field.

Solution:

AB = 25 m
EB = AB-AE = 25-10 = 15 m
Now, for ar(△ECB) can be calculated by Heron’s Formula, where
a = 13 m
b = 14 m
c = 15 m
Semi Perimeter (s) = 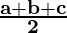
s = 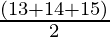
s = 21 m
ar(△ECB) = √s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)
= √21(21-3)(21-14)(21-15)
= √21×(18)×(7)×(6)
= 84 m2 ………………………….(1)
ar(△ECB) = 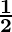 × Base × Height
× Base × Height
84 m2 = 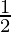 × 15 × h
× 15 × h
h =  m
m
h = 11.2 m
Total Area = Area of parallelogram AECD + ar(△ECB)
= (Base × Height) + 84m2
= 10 × 11.2 + 84
Total Area = 196 m2
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...