Bayes’s Theorem for Conditional Probability
Last Updated :
28 Jun, 2021
We strongly recommend to refer below post as a pre-requisite for this.
Conditional Probability
Bayes’s formula
Below is Bayes’s formula.
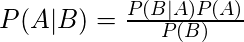
The formula provides the relationship between P(A|B) and P(B|A). It is mainly derived from conditional probability formula discussed in the
previous post.
Consider the below formulas for conditional probabilities P(A|B) and P(B|A)
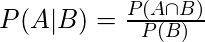
—-(1)
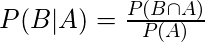
—-(2)
Since P(B ? A) = P(A ? B), we can replace P(A ? B) in the first formula with P(B|A)P(A)
After replacing, we get the given formula.
Product Rule
Product rule states that
(1) 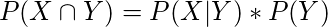
So the joint probability that both X and Y will occur is equal to the product of two terms:
From the product rule :
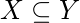
implies
P(X|Y) = P(X)/P(Y)
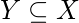
implies
P(X|Y) = 1
Chain rule
When the above product rule is generalized we lead to chain rule. Let there are
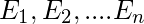
n events . Then, the joint probability is given by
(2) 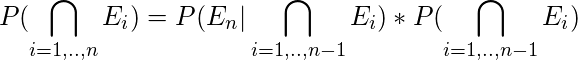
Bayes’ Theorem
From the product rule,
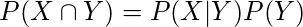
and
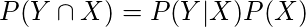
. As
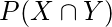
and
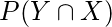
are same .
(3) 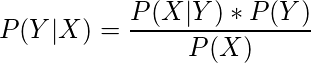
where
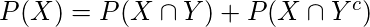
.
Example : Box P has 2 red balls and 3 blue balls and box Q has 3 red balls and 1 blue ball. A ball is selected as follows:
(i) Select a box
(ii) Choose a ball from the selected box such that each ball in
the box is equally likely to be chosen. The probabilities of
selecting boxes P and Q are (1/3) and (2/3), respectively.
Given that a ball selected in the above process is a red ball, the probability that it came from the box P is (GATE CS 2005)
(A) 4/19
(B) 5/19
(C) 2/9
(D) 19/30
Solution:
R --> Event that red ball is selected
B --> Event that blue ball is selected
P --> Event that box P is selected
Q --> Event that box Q is selected
We need to calculate P(P|R)?
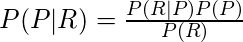 P(R|P) = A red ball selected from box P
= 2/5
P(P) = 1/3
P(R) = P(P)*P(R|P) + P(Q)*P(R|Q)
= (1/3)*(2/5) + (2/3)*(3/4)
= 2/15 + 1/2
= 19/30
Putting above values in the Bayes's Formula
P(P|R) = (2/5)*(1/3) / (19/30)
= 4/19
P(R|P) = A red ball selected from box P
= 2/5
P(P) = 1/3
P(R) = P(P)*P(R|P) + P(Q)*P(R|Q)
= (1/3)*(2/5) + (2/3)*(3/4)
= 2/15 + 1/2
= 19/30
Putting above values in the Bayes's Formula
P(P|R) = (2/5)*(1/3) / (19/30)
= 4/19
Exercise A company buys 70% of its computers from company X and 30% from company Y. Company X produces 1 faulty computer per 5 computers and company Y produces 1 faulty computer per 20 computers. A computer is found faulty what is the probability that it was bought from company X?
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...