Representation of Relation in Graphs and Matrices
Last Updated :
20 Sep, 2023
Previously, we have already discussed Relations and their basic types.
Combining Relation:
Suppose R is a relation from set A to B and S is a relation from set B to C, the combination of both the relations is the relation which consists of ordered pairs (a,c) where a ? A and c ? C and there exist an element b ? B for which (a,b) ? R and (b,c) ? S. This is represented as RoS.
Inverse Relation:
A relation R is defined as (a,b) ? R from set A to set B, then the inverse relation is defined as (b,a) ? R from set B to set A. Inverse Relation is represented as R-1
R-1 = {(b,a) | (a,b) ? R}.
Complementary Relation:
Let R be a relation from set A to B, then the complementary Relation is defined as- {(a,b) } where (a,b) is not ? R.
Representation of Relations:
Relations can be represented as- Matrices and Directed graphs.
Relation as Matrices:
A relation R is defined as from set A to set B, then the matrix representation of relation is MR= [mij] where
mij = { 1, if (a,b) ? R
0, if (a,b) does not ? R }
Properties:
- A relation R is reflexive if the matrix diagonal elements are 1.
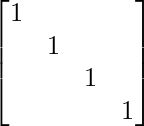
- A relation R is irreflexive if the matrix diagonal elements are 0.
- A relation R is symmetric if the transpose of relation matrix is equal to its original relation matrix. i.e. MR = (MR)T.

- A relation R is antisymmetric if either mij = 0 or mji =0 when i?j.
- A relation follows join property i.e. the join of matrix M1 and M2 is M1 V M2 which is represented as R1 U R2 in terms of relation.
- A relation follows meet property i.r. the meet of matrix M1 and M2 is M1 ^ M2 which is represented as R1 ? R2 in terms of relation.
Relations as Directed graphs:
A directed graph consists of nodes or vertices connected by directed edges or arcs. Let R is relation from set A to set B defined as (a,b) ? R, then in directed graph-it is represented as edge(an arrow from a to b) between (a,b).
Properties:
- A relation R is reflexive if there is loop at every node of directed graph.
- A relation R is irreflexive if there is no loop at any node of directed graphs.
- A relation R is symmetric if for every edge between distinct nodes, an edge is always present in opposite direction.
- A relation R is asymmetric if there are never two edges in opposite direction between distinct nodes.
- A relation R is transitive if there is an edge from a to b and b to c, then there is always an edge from a to c.
Example:
The directed graph of relation R = {(a,a),(a,b),(b,b),(b,c),(c,c),(c,b),(c,a)} is represented as :

Since, there is loop at every node, it is reflexive but it is neither symmetric nor antisymmetric as there is an edge from a to b but no opposite edge from b to a and also directed edge from b to c in both directions. R is not transitive as there is an edge from a to b and b to c but no edge from a to c.
Related Articles:
Relations and their types
Share your thoughts in the comments
Please Login to comment...